-
Review Article09-01-2018
Multiple Pregnancy: Epidemiology and Association with Maternal and Perinatal Morbidity
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):554-562
Abstract
Review ArticleMultiple Pregnancy: Epidemiology and Association with Maternal and Perinatal Morbidity
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):554-562
Views353See moreAbstract
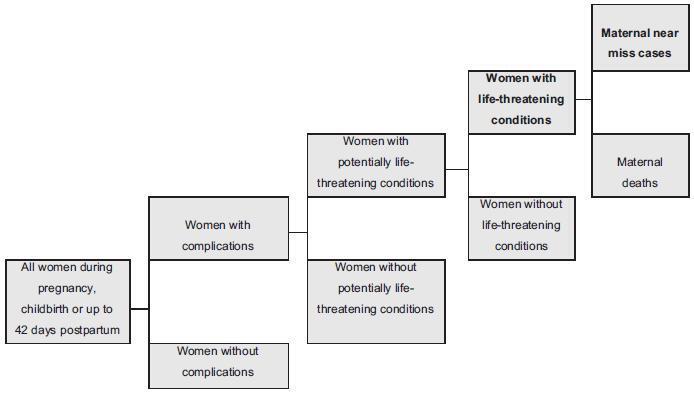
Twin pregnancy accounts for 2 to 4% of total births, with a prevalence ranging from 0.9 to 2.4% in Brazil. It is associated with worse maternal and perinatal outcomes. Many conditions, such as severe maternal morbidity (SMM) (potentially life-threatening conditions and maternal near-miss) and neonatal near-miss (NNM) still have not been properly investigated in the literature. The difficulty in determining the conditions associated with twin pregnancy probably lies in its relatively low occurrence and the need for larger population studies. The use of the whole population and of databases from large multicenter studies, therefore, may provide unprecedented results. Since it is a rare condition, it ismore easily evaluated using vital statistics from birth e-registries. Therefore, we have performed a literature review to identify the characteristics of twin pregnancy in Brazil and worldwide. Twin pregnancy has consistently been associated with SMM, maternal near-miss (MNM) and perinatal morbidity, with still worse results for the second twin, possibly due to some characteristics of the delivery, including safety and availability of appropriate obstetric care to women at a high risk of perinatal complications.
-
Original Article10-06-2000
Natural Triplet Pregnancies: Maternal Complications and Perinatal Results
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(7):413-419
Abstract
Original ArticleNatural Triplet Pregnancies: Maternal Complications and Perinatal Results
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(7):413-419
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000700003
Views136See morePurpose: to analyze maternal complications and perinatal results of triplet pregnancies. Method: retrospective study of maternal and perinatal data on all triplets weighing >500 g delivered in a period of 8 years at Maternidade Escola de Vila Nova Cachoeirinha. Results: between 1990-1998, 18 women gave birth to triplets, representing 1 in every 2,060 deliveries. The main complications were preterm delivery (94.4%) and preeclampsia (44.4%) and 83.3% of these patients needed hospitalization before delivery, for 1-50 days, most in order to inhibit preterm labor. Cesarean section was performed in 88.9%, the mean gestational age at birth was 34.2 weeks (+ 1.8), mean weight 1,827 g (+ 421), 20.4% weighed <1,500 g and 75.9% weighed 1,500-2,499 g. Birth weight discrepancy (> 25%) occurred in 38.9% of these pregnancies and 35.2% of the 54 fetuses were small for gestational age. Eighty-six percent of live-born infants had neonatal morbidity and 3.7% had evident congenital anomalies. Perinatal mortality was 16.7%, 7.4% due to intrauterine demise and 9.3% due to neonatal death. The mean duration of hospitalization in the neonatal ward was 18.5 days; late neonatal sepsis was the main cause of death. Conclusion: triplet pregnancies had high a incidence of obstetric complications, demanded prolonged maternal hospitalization and ended almost always in surgical delivery. Intrauterine and neonatal death rates were high, neonatal morbidity was detected in almost all live-born infants and their hospitalization was long, exposing these prematures to infection, their main cause of death. Triplet pregnancies carry high maternal and fetal risks and should be managed at tertiary facilities.


