Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(9):503-510
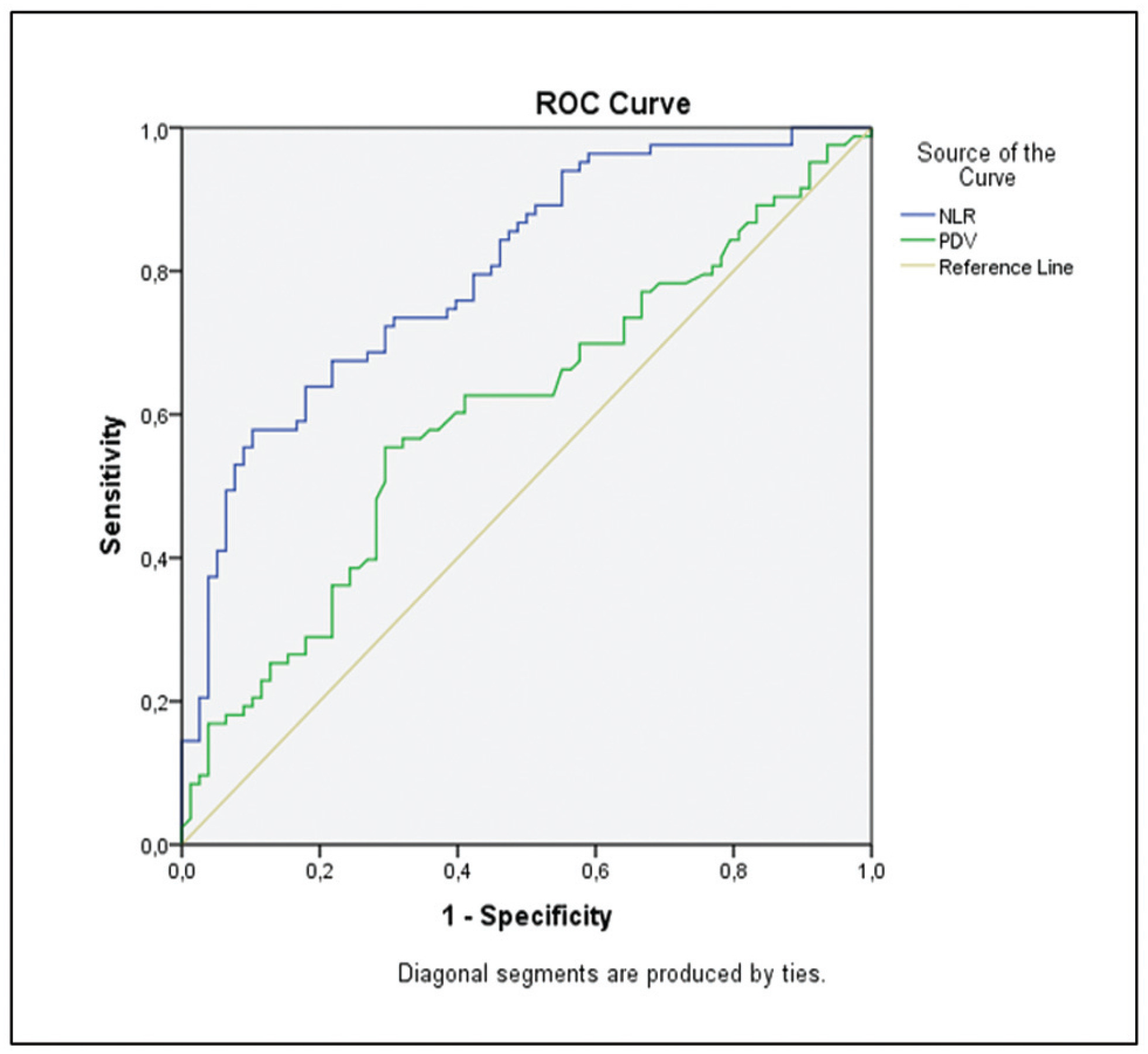
The availability of reliable and inexpensive markers that can be used to determine the risk of rupture during methotrexate (MTX) treatment in ectopic pregnancies (EPs) is considerable. The aim of the present study is to investigate the role of systemic inflammatory markers such as leukocytes (or white blood cells, WBCs), the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), and platelet distribution width (PDW), which are among the parameters of the complete blood count (CBC), in the prediction of rupture of EPs under MTX treatment.
A total of 161 patients with tubal EP who underwent a single-dose methotrexate (MTX) protocol were retrospectively analyzed, and the control group (n = 83) included patients cured by MTX, while the ruptured group (n = 78) included patients who were operated on for tubal rupture during the MTX treatment. The features of EP, beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG) levels, sonographic findings, and CBC-derived markers such as WBC, NLR, and PDW, were investigated by comparing both groups.
The NLR was found to be higher in the ruptured group, of 2.92 ± 0.86%, and significantly lower in the control group, of 2.09 ± 0.6%. Similarly, the PDW was higher (51 ± 9%) in the ruptured group, and it was significantly lower a (47 ± 13%) in the control group (p < 0.05). Other CBC parameters were similar in both groups (p > 0.05).
Systemic inflammation markers derived from CBC can be easily applied to predict the risk of tubal rupture in Eps, since the CBC is an inexpensive and easy-to-apply test, which is first requested from each patient during hospitalization.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(11):1014-1020
Cervical pregnancy is challenging for the medical community, as it is potentially fatal. The treatment can be medical or surgical; however, there are no protocols that establish the best option for each case. The objective of the present study was to describe the cases of cervical pregnancy admitted to a tertiary university hospital over a period of 18 years.
A retrospective study based on a review of the medical records of all cervical pregnancies admitted to the Women's Hospital at Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Southeastern Brazil, from 2000 to 2018.
We identified 13 cases of cervical pregnancy out of a total of 673 ectopic pregnancies; only 1 case was initially treated with surgery because of hemodynamic instability. Of the 12 cases treated conservatively, 7 were treated with single-dose intramuscular methotrexate, 1, with intravenous and intramuscular methotrexate, 1, with intravenous methotrexate, 1, with 2 doses of intramuscular methotrexate, and 2, with intra-amniotic methotrexate. Of these cases, one had a therapeutic failure that required a hysterectomy. Two women received blood transfusions. Four women required cervical tamponade with a Foley catheter balloon for hemostasis. There was no fatal outcome.
Cervical pregnancy is a rare and challenging condition from diagnosis to treatment. Conservative treatment was the primary method of therapy used, with satisfactory results. In cases of increased bleeding, cervical curettage was the initial treatment, and it was associated with the use of a cervical balloon for hemostasis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(12):800-804
In recent years, there has been an increase in the incidence of ectopic pregnancies; therefore, it is important for tertiary centers to report their approaches and outcomes to expand and improve treatment modalities. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the general characteristics, treatment and outcomes of cases diagnosed with ectopic pregnancy.
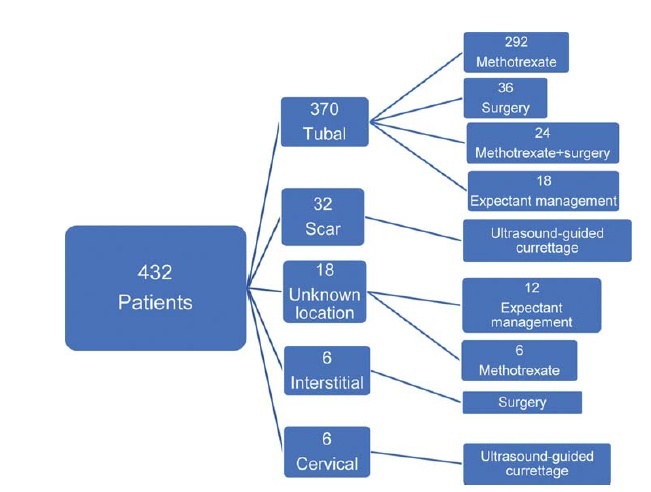
In total, 432 patients treated for ectopic pregnancy between February 2016 and June 2019 were retrospectively evaluated.
Overall, 370 patients had tubal pregnancy, 32 had cesarean scar pregnancy, 18 had pregnancy of unknown location, 6 had cervical pregnancy, and 6 had interstitial pregnancy. The most important risk factors were advanced age (> 35 years; prevalence: 31.2%) and smoking (prevalence: 27.1%). Thirty patients who did not have any symptoms of rupture and whose human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG) levels were ≤ 200 mIU/ml were followed-up with expectant management, while 316 patients whose β-hCG levels were between 1,500 mIU/ml and 5,000 mIU/ml did not have an intrauterine gestational sac on the transvaginal or abdominal ultrasound, did not demonstrate findings of rupture, and were treated with a systemic multi-dose methotrexate treatment protocol. In total, 24 patients who did not respond to the medical treatment, 20 patients whose β-hCG levels were > 5,000 mIU/ml, 16 patients who had shown symptoms of rupture at the initial presentation, and 6 patients diagnosed with interstitial pregnancy underwent surgery. Patients with cervical and scar pregnancies underwent ultrasound-guided curettage, and no additional treatment was needed.
The fertility status of the patients, the clinical and laboratory findings, and the levels of β-hCG are the factors that must be considered in planning the appropriate treatment.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(3):165-168
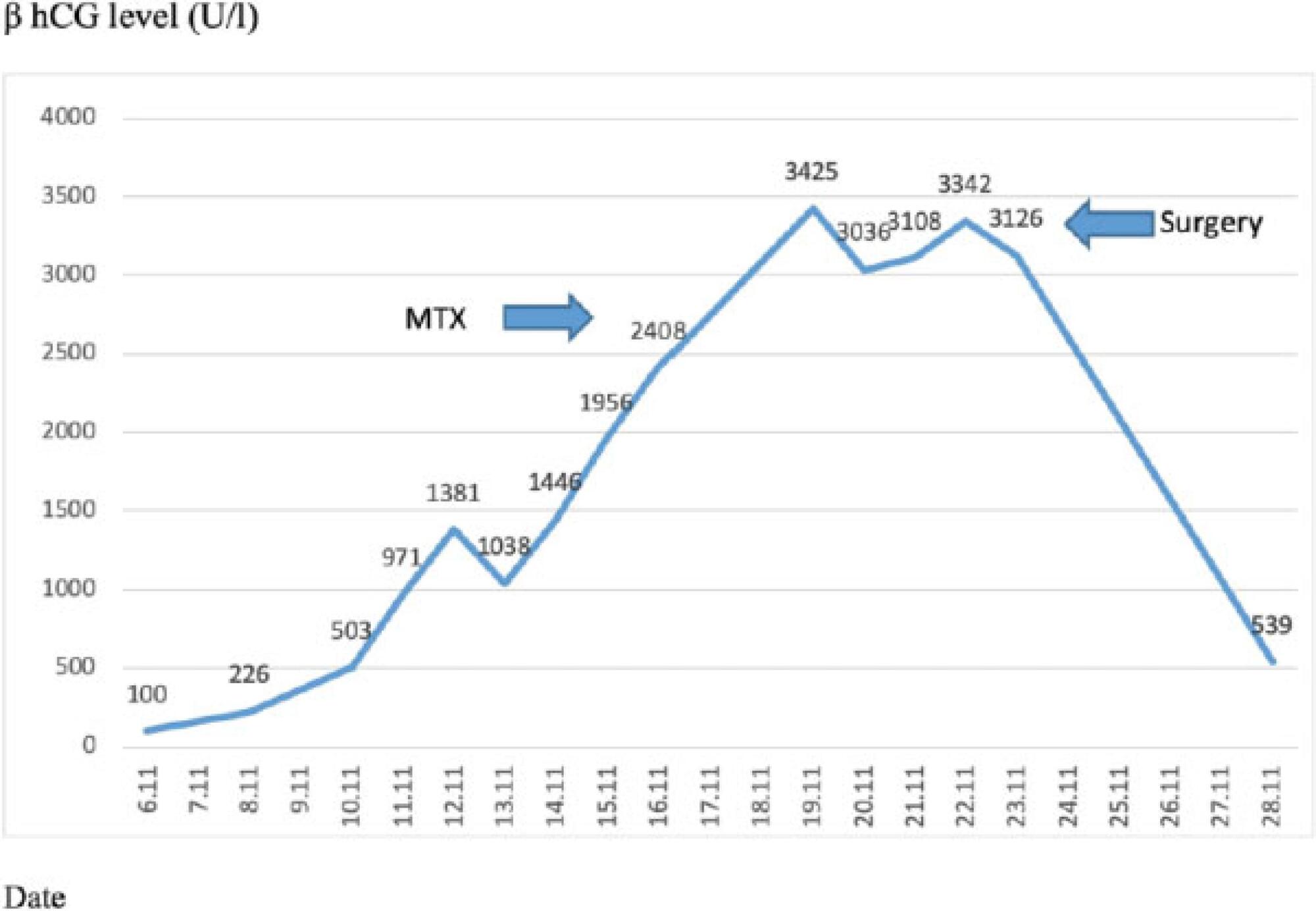
Bilateral tubal ectopic pregnancy is a very rare form of ectopic pregnancy. The incidence is higher in women undergoing assisted reproductive techniques or ovulation induction. We report the case of bilateral tubal ectopic pregnancy. The patient was 30 years old and had a 3-year history of infertility; she was referred to the in-vitro fertilization (IVF) program because of tubal factor infertility. A pregnancy resulted from the transfer of two embryos during an artificial cycle. Despite the increase in β-hCG values during the follow-up, 22 days after the embryo transfer, the β-hCG levels were 2,408 U/L and the serum progesterone (P4) level was 10.53 ng/ml. After application with methotrexate, β-hCG levels did not decrease effectively. Moreover, the sonographic screening revealed a suspicious bilateral tubal focus for ectopic pregnancy. A mini-laparotomy was performed and a bilateral tubal pregnancy was found. In the case of unilateral tubal pregnancy after the transfer of two embryos, the situation of the other tube should be systematically checked and β-hCG levels should be monitored.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(11):680-685
Our aim is to demonstrate the importance of methotrexate (MTX) therapy for the treatment of ectopic pregnancy (EP).
This retrospective study consisted of 99 patients (72 tubal EPs, 20 pregnancies of unknown location (PUL), 4 cesarean section (CS) scar EPs and 3 cervical EPs) treated with MTX.
Methotrexate therapy was successful in 68.5% of EPs. There were statistically significant differences between the MTX success and failure groups based on ultrasonographic findings, patient complaints, gestational week and serum human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) values. The MTX success rates in PUL and tubal pregnancies were 95% and 61.1%, respectively. The MTX success rates in single-dose, two-dose and multi-dose protocol groups were 86.9%, 28.6% and 40%, respectively. All cervical and CS scar ectopic pregnancies were treated successfully with MTX therapy.
Methotrexate might be the first-line treatment option for EPs under certain conditions. Physicians must be more cautious in cases with higher hCG values, the presence of abdominal-pelvic pain, the presence of fetal cardiac activity, larger gestational sac (GS) diameters, and more advanced gestational weeks according to the last menstrual period.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(5):233-237
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000500008
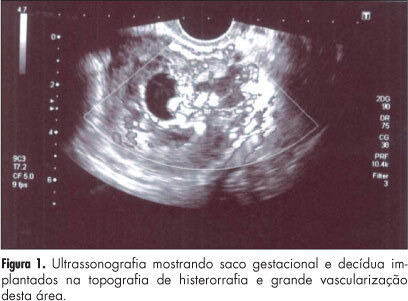
Implantation of a pregnancy within a cesarean delivery scar is considered to be the rarest form of ectopic pregnancy, with a high morbidity and mortality. Pregnancy in a cesarean delivery scar may cause catastrophic complications which may result in hysterectomy and compromise the reproductive future of a woman. We report an ectopic pregnancy in cesarean scar case in a 28-year old pregnant woman that was treated with success with the association between three treatment modalities (methotrexate, uterine artery embolization and curettage) and preserve her fertility.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(3):118-121
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000300005
PURPOSE: To report the use of colpotomy for the treatment of ectopic pregnancies. METHODS: This was a retrospective cross-sectional study conducted on all women hospitalized with a clinical-laboratory suspicion of ectopic pregnancy who did not fulfill the criteria for drug treatment with methothrexate, during the period from February 2007 to August 2008. Demographic variables, gynecologic history and characteristics associated with treatment were obtained by reviewing the medical records. RESULTS: Eighteen women were included in the study. Mean age was 27±5.2 years. All patients presented ruptured ectopic pregnancy and all were submitted to partial salpingectomy. Surgical time ranged from 30 to 120 minutes (mean: 64.5 minutes) calculated from the moment when the patient entered the operating room to the moment when she left it. No patient presented postoperative infection. Mean time of hospitalization was 40±14.3 hours. The medications used during the postoperative period were similar in all cases, being based on nonsteroid anti-inflammatory drugs, dipyrone, paracetamol and meperidine, as needed. The diet was reintroduced 8 hours after the end of surgery. CONCLUSIONS: The use of colpotomy in the treatment of ectopic pregnancy showed good results, with the absence of important complications and a short hospitalization time. The basic surgical instruments needed for this procedure are relatively common to all hospitals, and the surgical technique is reproducible.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(3):149-159
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000300008
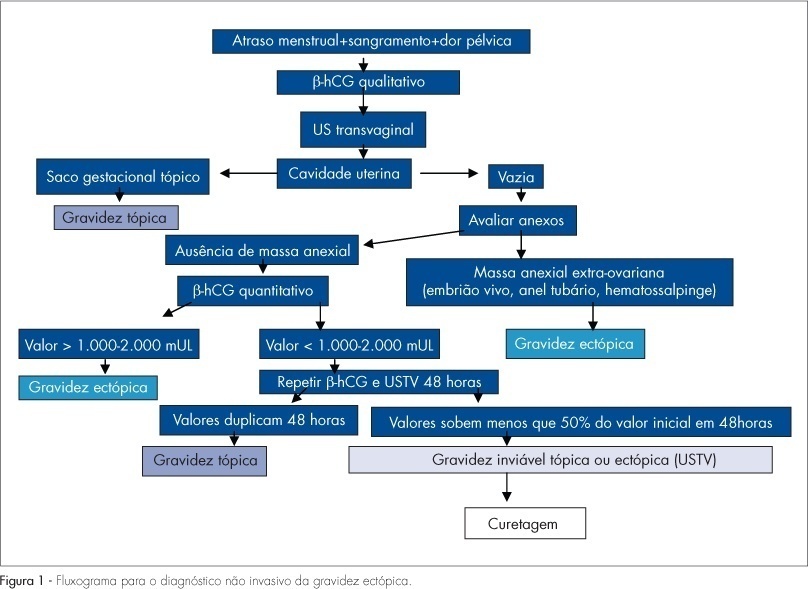
It is advisable to do the non-invasive diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy precociously, before there is the tube rupture, combining for that the transvaginal ultrasonography with the dosage of the b-fraction of the chorionic gonadotrophin. A range of treatment options may be used. Either a surgical intervention or a clinical treatment may be taken into consideration. Laparotomy is indicated in cases of hemodynamic instability. Laparoscopy is the preferential route for the treatment of tube pregnancy. Salpingectomy should be performed in patients having the desired number of children, while salpingostomy should be indicated in patients willing to have more children, when the b-hCG titers are under 5,000 mUI/mL and the surgical conditions are favorable. The use of methotrexate (MTX) is a consecrated clinical procedure and should be indicated as the first option of treatment. The main criteria for MTX indication are hemodynamic stability, b-hCG <5,000 mUI/mL, anexial mass <3,5 cm, and no alive embryo. It is preferable a single intramuscular dose of 50 mg/m², because it is easier, more practical and with less side effects. Protocol with multiple doses should be restricted for the cases with atypical localization (interstitial, cervical, caesarean section scar and ovarian) with values of b-hCG >5,000 mUI/mL and no alive embryo. Indication for local treatment with an injection of MTX (1 mg/kg) guided by transvaginal ultrasonography should occur in cases of alive embryos, but with an atypical localization. An expectant conduct should be indicated in cases of decrease in the b-hCG titers within 48 hous before the treatment, and when the initial titers are under 1,500 mUI/mL. There are controversies between salpingectomy and salpingostomy, concerning the reproductive future. Till we reach an agreement in the literature, the advice to patients who are looking forward to a future gestation, is to choose either surgical or clinical conservative conducts.