-
Original Article08-15-2022
Does Obesity Aggravate Climacteric Symptoms in Postmenopausal Women?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(6):586-592
Abstract
Original ArticleDoes Obesity Aggravate Climacteric Symptoms in Postmenopausal Women?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(6):586-592
Views223See moreAbstract
Objective
To determine if there is a correlation between body mass index (BMI) and climacteric symptoms in postmenopausal women.
Methods
The study sample was composed of 109 postmenopausal women with a mean age of 57 ± 8 years, mean body mass index (BMI) of 30 ± 6 kg/m2, and 8 ± 8 years after menopause. For the assessment of the climacteric symptoms, the Blatt-Kupperman Index (BKI), the Menopause Rating Scale (MRS), and the Cervantes Scale (CS) were used. Data analysis was performed through the Chi-squared test, analysis of variance (ANOVA) with the Bonferroni post hoc test, and multiple linear regression. The level of significance adopted was of p < 0.05. The statistical analyses were performed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, United States) software, version 26.0.
Results
The multiple linear regression showed a positive association (p<0.01) between BMI values and menopause symptoms when adjusted for age and time after menopause in the 3 questionnaires used (BKI: B = 0.432; CS: B = 304; and MRS: B = 302). Regarding symptom scores, the obese women had higher mean scores (p<0.05) when compared to eutrophic women (BKI = 28 ± 10 and 20 ± 10; and MRS = 20 ± 10 and 13±7, respectively). In the Chi-squared analysis, 28% of obese women had severe symptoms and 46% had moderate symptoms, while only 1% and 46% of eutrophic women had these same symptoms.
Conclusion
There is an association between BMI and climacteric symptoms, and overweight or obese women have more intense and moderate symptoms than eutrophic women.
-
Original Article02-28-2022
Performance of the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool Associated with Muscle Mass Measurements and Handgrip to Screen for the Risk of Osteoporosis in Young Postmenopausal Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):32-39
Abstract
Original ArticlePerformance of the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool Associated with Muscle Mass Measurements and Handgrip to Screen for the Risk of Osteoporosis in Young Postmenopausal Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):32-39
Views187See moreAbstract
Objective
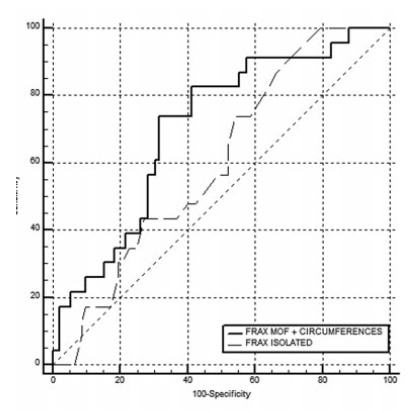
To evaluate the improvement in screening accuracy of the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX) for the risk of developing osteoporosis among young postmenopausal women by associating with it clinical muscle mass measures.
Methods
A sample of postmenopausal women was submitted to calcaneal quantitative ultrasound (QUS), application of the FRAX questionnaire, and screening for the risk of developing sarcopenia at a health fair held in the city of São Bernardo do Campo in 2019. The sample also underwent anthropometric measurements, muscle mass, walking speed and handgrip tests. A major osteoporotic fracture (MOF) risk ≥ 8.5% on the FRAX, a classification of medium risk on the clinical guideline of the National Osteoporosis Guideline Group (NOGG), and a QUS T-score ≤ -1.8 sd were considered risks of having low bone mass, and QUS T-score ≤ -2.5sd, risk of having fractures.
Results
In total, 198 women were evaluated, with a median age of 64±7.7 years, median body mass index (BMI) of 27.3±5.3 kg/m2 and median QUS T-score of -1.3±1.3 sd. The accuracy of the FRAX with a MOF risk ≥ 8.5% to identify women with T-scores ≤ -1.8 sd was poor, with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.604 (95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 0.509-0.694) for women under 65 years of age, and of 0.642 (95%CI: 0.571-0.709) when age was not considered. Including data on muscle mass in the statistical analysis led to a significant improvement for the group of women under 65 years of age, with an AUC of 0,705 (95%CI: 0.612-0.786). The ability of the high-risk NOGG tool to identify T-scores ≤ -1.8 sd was limited.
Conclusion
Clinical muscle mass measurements increased the accuracy of the FRAX to screen for osteoporosis in women aged under 65 years.
-
Original Article01-19-2021
The Effectiveness of Melissa Officinalis L. versus Citalopram on Quality of Life of Menopausal Women with Sleep Disorder: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(2):126-130
Abstract
Original ArticleThe Effectiveness of Melissa Officinalis L. versus Citalopram on Quality of Life of Menopausal Women with Sleep Disorder: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(2):126-130
Views315See moreAbstract
Objective
The present study aimed to assess the effect of Melissa Officinalis L. (a combination of lemon balm with fennel fruit extract) compared with citalopram and placebo on the quality of life of postmenopausal women with sleep disturbance.
Methods
The present study is a randomized, double-blind, placebo clinical trial among 60 postmenopausal women with sleep disturbance who were referred to a university hospital from 2017 to 2019. The participants were randomized to receive M. Officinalis L. (500 mg daily), citalopram (30 mg) or placebo once daily for 8 weeks. The Menopause-Specific Quality of Life (MENQOL) questionnaire was self-completed by each participant at baseline and after 8 weeks of the intervention and was compared between groups.
Results
The mean for all MENQOL domain scores were significantly improved in the M. Officinalis L. group compared with citalopram and placebo (p < 0.001). The mean ± standard deviation (SD) after 8 weeks in the M. Officinalis L., citalopram and placebo groups was 2.2 ± 0.84 versus 0.56 ± 0.58 versus 0.36 ± 0.55 in the vasomotor (p < 0.001), 1.02 ± 0.6 versus 0.28 ± 0.2 versus 0.17 ± 0.1 in the psychomotor-social (p < 0.001), 0.76 ± 0.4 versus 0.25 ± 0.1 versus 0.11 ± 0.1 in the physical and 2.3 ± 1.0 versus 0.35 ± 0.5 versus 0.41 ± 0.5 in the sexual domain, respectively.
Conclusions
The results revealed that M. Officinalis L. may be recommended for improving the quality of life of menopausal women with sleep disturbance. Trial registration The present study was registered by the name “Comparison of the efficacy of citalopram and compound of Asperugo procumbens and foeniculum vulgare in treatment of menopausal disorders” with the code in the Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials (IRCT).
-
Original Article03-27-2020
Construct and Criterion Validity of the Postmenopause Sexuality Questionnaire – PMSQ
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(1):26-34
Abstract
Original ArticleConstruct and Criterion Validity of the Postmenopause Sexuality Questionnaire – PMSQ
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(1):26-34
Views59See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the construct and criterion validity of the Postmenopause Sexuality Questionnaire (PMSQ).
Methods
The present methodological questionnaire validation study included postmenopausal women. The construct validity was tested by factor analysis and the criterion validity was performed using the correlation between the PMSQ and the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI). The ROC curve was used to verify sensitivity, specificity and to determine the cutoff point of the PMSQ.
Results
A total of 181 women with amean age of 56.4 ± 5.7 years old were evaluated. The exploratory factor analysis showed that the PMSQ presented Kaiser test = 0.88 and χ2 = 3293.7 (p < 0.001), commonalities ≥ 0.5, and extraction of 9 factors with eigenvalue ≥ 1; explaining 66.3% of the total variance. The PMSQ presented factor loadings between 0.4 and 0.8. A strong correlation between the 2 questionnaires (r = 0.79; p = 0.000) was shown. The cutoff point of the PMSQ was ≤ 55.5, assuming 87.9% sensitivity and 78.9% specificity (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
Since the PMSQ showed a strong correlation with the FSFI questionnaire, it presented good psychometric properties to assess the sexuality in postmenopausal women. Based on these results, the PMSQ could be widely tested as a specific instrument to examine the sexual function in postmenopausal women. Future studies, designed to examine the PMSQ instrument in different populations, are needed.
-
Original Article08-15-2019
Validation of the Six-item Female Sexual Function Index in Middle-Aged Brazilian Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(7):432-439
Abstract
Original ArticleValidation of the Six-item Female Sexual Function Index in Middle-Aged Brazilian Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(7):432-439
Views208See moreAbstract
Objective
To validate the six-item female sexual function index (FSFI-6) in middleaged Brazilian women.
Methods
Cross-sectional observational study, involving 737 (premenopausal n = 117, perimenopausal n = 249, postmenopausal n = 371) Brazilian sexually active women, aged between 40 and 55 years, not using hormonal contraceptive methods. The Brazilian FSFI-6 was developed from the translation and cultural adaptation of the Portuguese FSFI-6 version. The participants completed a general questionnaire, the FSFI-6, and the menopause rating scale (MRS). The validation was performed by AMOS 16.0 software (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) for a confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). The chi-square of degrees of freedom (χ2/df), the comparative fit index (CFI), the Tucker- Lewis index (TLI) and the root-mean-square error of approximation (RMSEA) were used as indices of goodness of fit. Cronbach α coefficient was used for internal consistency.
Results
The process of cultural adaptation has not altered the Brazilian FSFI-6, as compared with the original content. The CFA for the FSFI-6 score showed an acceptable fit (χ2/df = 3.434, CFI = 0.990, TLI = 0.980, RMSEA = 0.058, 90% confidence interval (90%CI) = 0.033-0.083, p ≤ 0.001) and a good reliability was established in FSFI-6 and MRS (Cronbach α = 0.840 and = 0.854, respectively). In addition, 53.5% of the sample had low sexual function.
Conclusion
The FSFI-6 was translated and adapted to the Brazilian culture and is a consistent and reliable tool for female sexual dysfunction screening in Brazilianmiddleaged women.
-
Original Article12-01-2017
Mandibular Inferior Cortex Erosion on Dental Panoramic Radiograph as a Sign of Low BoneMineral Density in Postmenopausal Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(12):663-669
Abstract
Original ArticleMandibular Inferior Cortex Erosion on Dental Panoramic Radiograph as a Sign of Low BoneMineral Density in Postmenopausal Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(12):663-669
Views171See moreAbstract
Objective
To examine the role of the panoramic mandibular radiograph in the diagnosis of low bone mineral density (BMD) in postmenopausal women.
Methods
A cross-sectional study including volunteer women aged over 40 years in amenorrhea due to ovarian failure for at least 12 months, who were cared for at the climacteric outpatient clinic of a university hospital in the city of Cuiabá, in the state of Mato Grosso, Brazil. The panoramic radiographs were evaluated using a specific software. Two aspects were analyzed in the mandibular panoramic radiograph: a qualitative aspect regarding the shape of the mandibular cortical bone, and a quantitative aspect regarding thewidth of themandibular cortical bone. Themorphology of themandibular cortical bone in the digital panoramic radiograph was determined bilaterally by the observation of the bone structure between the mental foramen and the base of the jaw. The mandibular cortical bonewas categorized into three groups. Themental index (MI)was used to evaluate the thickness of themandibular cortical bone through a perpendicular line drawn fromthe base of the mandible at the height of the center of the mental foramen, with another line drawn tangent to the inferior border of the mandible, and a third line parallel to the line at the superior border of themandible. The MI data are expressed in millimeters, with a normal value of 3.0 mm. The densities of the lumbar spine and femur, expressed in g/cm2, were categorized as normal, osteopenia or osteoporosis.
Results
The agreement index between the MI and the BMD of the lumbar spine was good (Kappa = 0.718), but the same index between the MI and the BMD of the femoral neck was poor (Kappa = 0.443). An excellent agreement occurred when the mandibular cortical index (MCI) was compared with the BMD of the lumbar spine (Kappa = 0.912). The agreement between MCI and the BMD in the femur was moderated (Kappa = 0.579).
Conclusion
The radiomorphometric indices evaluated in the mandibular panoramic radiograph are capable of identifying postmenopausal women with low mineral density in the mandible, and the results can be used to refer these women to appropriate medical investigation and/or treatment.
-
Original Article11-01-2017
Brazilian Women’s Health after 65 Years of Age
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(11):608-613
Abstract
Original ArticleBrazilian Women’s Health after 65 Years of Age
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(11):608-613
Views193See moreAbstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate the health aspects of Brazilian women older than 65 years of age.
Design
This was a retrospective study that included 1,001 Brazilian women cared for in the gynecological geriatric outpatient office of our institution. We report a crosssectional analysis of female adults aged over 65 years, including data on demographics, clinical symptoms such as vasomotor symptoms, associated morbidities, physical examination and sexual intercourse. We used the chi-squared test to assess the data.
Results
The age of the patients on their first clinic visit ranged from65 to 98 years, with a mean age of 68.56 ± 4.47 years; their mean age at the time of natural menopause was 48.76 ± 5.07 years. The most frequent clinical symptoms reported during the analyzed period were hot flashes (n = 188), followed by arthropathy, asthenia, and dry vagina. The most frequent associated morbidities after 65 years of age were systemic arterial hypertension, gastrointestinal disturbance, diabetes mellitus, and depression, among others. The assessment of the bodymass index (BMI) found decreases inBMIwith increased age. At the time of the visit, 78 patients reported sexual intercourse. The majority of women reporting sexual intercourse (89.75%, n = 70) were between 65 and 69 years of age, 8.97% (n = 7) were between 70 and 74 years of age, and only 1.28% (n = 1) of those were aged older than 75 years.
Conclusions
Our findings suggested that vasomotor symptoms can persist after 65 years of age. There was a significant decrease in sexual intercourse with increased age. The cardiovascular disturbances in our study are health concerns in these women.


