Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(8):481-487
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000800003
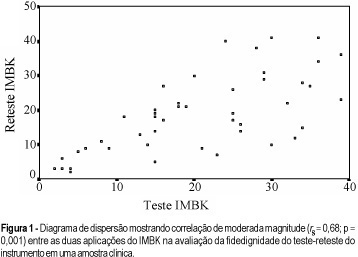
Purpose: based on the knowledge that the reliability of an instrument is essential for a correct interpretation of the results of research, the purpose of the present study is to evaluate the reliability of one of the menopausal indexes more often used in clinical practice and research, the Blatt and Kupperman Menopausal Index (BKMI). Methods: the population consisted of 60 climacteric patients attended at the Gynecology Outpatient Clinic of the Lauro Wanderley University Hospital of the Federal University of Paraíba in João Pessoa city. The reliability coefficient was analyzed by the test-retest method, whose application was done on two different occasions with an interval of four weeks, without administration of medicines. Results: the variation of the score observed with the application of BKMI at the first measurement was 2 to 41, with a median of 18 and mean of 18.8 (± 10.76), while at the second measurement, the menopausal index was 20.2 (± 10.51), median 19, and values ranging from 2 to 39. Despite these results, a Speaman (r s) coefficient of 0.68 (p = 0.001), which is a coefficient of only moderate intensity, was observed. Conclusions: the test-retest reliability in the application of the BKMI shows that, although this instrument presented a statistically moderate reliability, the intensity observed does not represent a reliable measurement. Considering that a correlational study is only a type of screening of the quality of a measurement method, we concluded that other studies must be performed with the purpose of evaluating the reliability and the validity of the BKMI. It is possible that the attribuition of different values to the items of BKMI and the inclusion of symptoms directly related to the estrogenic defficiency, like symptoms of vaginal atrophy, would make the instrument more reliable.