Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo9
03-18-2025
To evaluate the continuation rate, satisfaction, and reasons for discontinuation of depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA) in adolescents treated in a mental health service.
Prospective cohort study conducted in a reference unit for the care of adolescents with mental disorders (MDs) and intellectual disabilities (IDs). All patients received a gynecological consultation and an educational group on contraceptive methods. Sociodemographic data on age, education and gynecological data (menarche, coitarche, regularity of menstrual cycles and presence of symptoms) were collected. Follow-up was quarterly for 12 months, during which symptoms, desire to continue, and satisfaction with the use of the quarterly injectable were assessed.
Eight hundred and sixty-two sexually active adolescents were supported, 532 adolescents chose to use the quarterly injectable, and 69 of these agreed to participate in the study. The mean age of users was 15.5 years (SD=0.91). After 12 months of follow-up, 34 (49.3%) of the 69 adolescents continued to use the method and 36 (52.3%) were satisfied. Among the 33 (47.8%) who discontinued use, the most common reasons were irregular bleeding and weight gain.
Adolescents with intellectual disabilities and/or other mental disorders showed a significant rate of continuation and satisfaction with the use of the depot medroxyprogesterone acetate at 12 months, and the most common reasons for discontinuation were irregular uterine bleeding and weight gain.
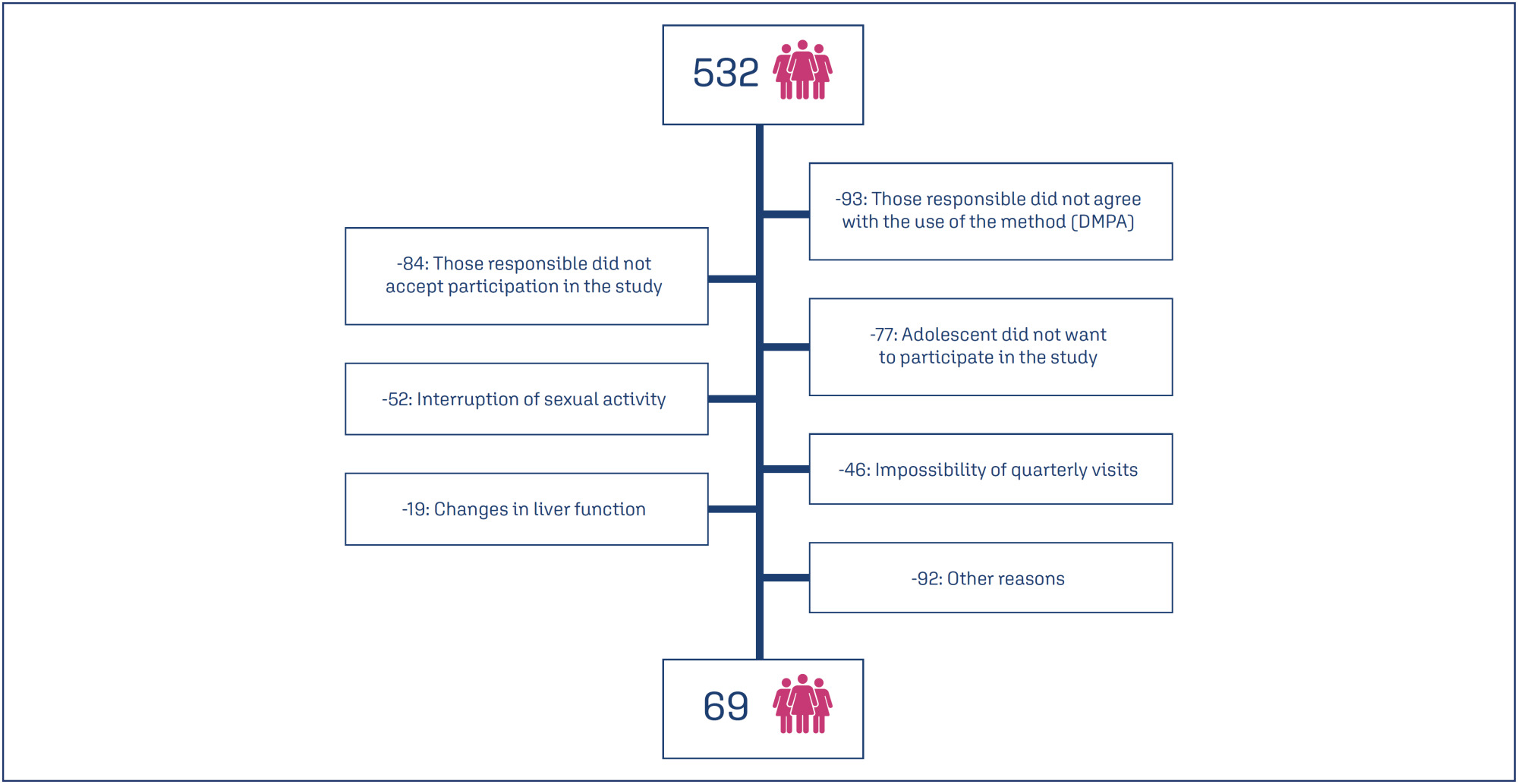
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(10):486-491
10-01-2015
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005347
To determine adherence to dual contraception using depot-medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA) and condom among HIV-infected women.
A cross-sectional study carried out from December 2013 to September 2014 at a local reference center, with application of questionnaire elaborated after Delphi panel and content validation to 114 HIV(+) women aged 15 to 49 years, using DMPA plus condom for contraception.
Mean age was 33.2±7.2 years, mean time since HIV detection was 8.1±5.2 years, mean time of antiretroviral use was 6.8±5 years and mean CD4 cells/mm count was 737.6±341.1. Sexual HIV acquisition was reported by 98.2% (112/114), antiretroviral use by 85.9% (98/114), and 77.7% (84/114) had a CD4>500/mm count. Having a single sex partner was reported by 78.9% (90/114), with HIV serodiscordance in 41.2% (47/114) of couples, 21.9% did not know the serological status of their partner and in 37.7% of cases (43/114) the partner was unaware of the HIV(+) status of the woman. The last pregnancy was unplanned in 71.9% of cases (82/114) and 14.9% of the women had become pregnant the year before, with pregnancy being unplanned in 70.5% (12/17) of cases. Current use of DMPA was reported by 64.9% (74/114), with genital bleeding in 48.2% (55/114) and weight gain in 67.5% (77/114). Use of a male condom was reported by 62.2% of the subjects (71/114). Three reported that they always used a female condom and ten that they eventually used it. Unprotected vaginal sex was reported by 37.7% (43/114) and unprotected anal intercourse was reported by 32.4% (37/114). Partner resistance to use a condom occurred in 30.7% of cases (35/114). Dual contraception using DMPA with condom was reported by 42.9% (49/114). A partner who resisted wearing a condom was associated with poor adhesion (PR=0.3; 95%CI 0.2-0.7; p<0.001). A partner who was unaware that a woman was infected with HIV favored adherence (PR=1.8; 95%CI 1.2-2.7; p=0.013).
The percentage of dual contraception using DMPA plus condom was 42.9%, maintaining unplanned pregnancies and unprotected sex. Resistance of partners to use a condom increased three times the chance of a woman not adhering to dual contraception, and the partner not knowing women's HIV infection almost doubled the chance to adhere to safe contraception. Goals: to offer new hormonal contraceptives and to involve the partners in contraception and serologic detection tests.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(3):181-186
06-26-2001
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000300008
Purpose: to evaluate the incidence of side effects and acceptance (continuity rate) of depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA) as an injectable three-monthly contraceptive given to adolescents in our milien. Method: forty adolescents (70% lactating) started to use DMPA and were followed-up for a mean of 14.2 months. Spontaneous complaints, menstrual changes, physical examination and laboratory data were collected and studied using Wilcoxon or McNemar tests. Results: the most frequent complaints were abdominal pain (16.6%) and headache (15.2%). Predominant menstrual patterns were spotting and oligomenorrhea. Significant variation of the systolic blood pressure was not observed during the follow-up. There was a slight fall in the levels of diastolic blood pressure, at the limit of significance. Significant deviations from baseline regarding fasting glucose were not noted, but the mean hemoglobin concentration tended to increase. Weight gain (mean 3.9 kg at 12 months) and menstrual irregularity (occurred in more than 70% of all visits) were the main reasons for discontinuation of the method. Twenty-seven patients were accompanied during 12 months and the continuity rate at that time was 81.5%. Conclusion: depot medroxyprogesterone acetate is a satisfactory contraceptive method for adolescents.