Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(8):595-599
To describe the hematological changes, the platelet indices in particular, in pregnant women with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) compared to healthy pregnant women.
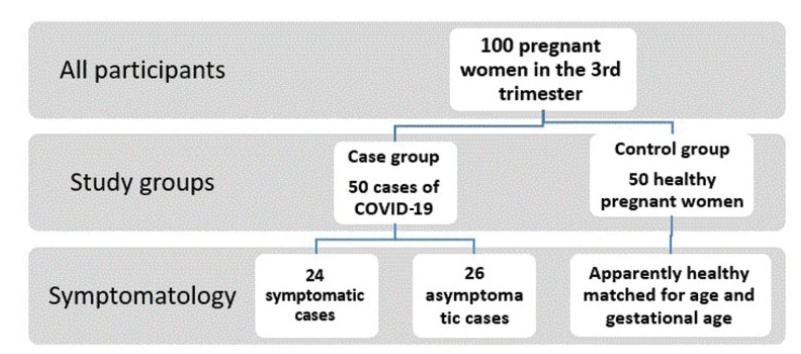
A retrospective case-control study conducted at the Al Yarmouk Teaching Hospital, in Baghdad, Iraq, involving 100 pregnant women, 50 with positive viral DNA for COVID-19 (case group), and 50 with negative results (control group); both groups were subjected to a thorough hematological evaluation.
Among the main hematological variables analyzed, the platelet indices, namely the mean platelet volume (MPV) and the platelet distribution width (PDW), showed statistically significant differences (MPV: 10.87±66.92 fL for the case group versus 9.84±1.2 fL for the control group; PDW: 14.82±3.18 fL for the case group versus 13.3±2.16 fL for the controls). The criterionvalue of the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve forPDWat a cutoffpoint of>11.8 fL showed a weak diagnostic marker, while the MPV at a cutoff value of>10.17 fL showed a good diagnostic marker.
The MPV and PDW are significantly affected by the this viral infection, even in asymptomatic confirmed cases, and we recommend that both parameters be included in the diagnostic panel of this infection.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(3):201-206
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000300005
OBJECTIVE: to evaluate platelet parameters in normal and pre-eclamptic pregnant women. METHODS: a controlled cross-sectional study was carried out. The medical records of the women who had delivered in the Hospital Universitário Júlio Müller-Cuiabá/MT, from January 1, 2001 to July 31, 2002, were reviewed. The pregnant women were pre-selected based on their platelet parameters analyses performed after the 28th week of gestation. Two groups of study were analyzed: PE group (36 pre-eclamptic women) and NP group (58 normal pregnant women). The platelet parameters analyzed by the automated method were: platelet counts, mean platelet volume (MPV), platelet distribution width (PDW) and platelet - large cells ratio (P-LCR). For statistical analysis the Student t-test and the chi-square test were used to compare the groups, and to evaluate the degree of dependence among the variables, the coefficient of determination was used (r²). For all these tests, the significance level considered was p < 0.05. RESULTS: the platelet counts did not show difference between the two groups. However, all other platelet indices (MPV, PDW and P-LCR) were significantly higher in the PE group. The severity of the disease was documented in 91.7% of the pre-eclamptic women, despite the fact that none of the patients included had shown thrombocytopenia as a criterion of severity. Negative correlation was detected between the platelet counts and the other platelet parameters analyzed and there was positive correlation between MPV and PDW, MPV and P-LCR, and PDW and P-LCR. Positive correlation was also observed between MPV, PDW and P-LCR, and the maximum systolic and diastolic blood pressures. CONCLUSIONS: pre-eclampsia was associated with these platelet parameters, suggesting alterations of the platelet functions. The clinical applicability of these parameters, as early markers of severity of pre-eclampsia, needs more studies.