Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(11):811-819
To investigate the characteristics of women who had preterm birth (PTB) and related outcomes according to ethnicity.
A secondary analysis of a multicenter cross-sectional study conducted in Brazil. Women who had PTB were classified by self-report as white and non-white. Clinical, pregnancy, and maternal data were collected through postpartum interviews and reviews of medical charts. The sociodemographic, obstetric and clinical characteristics of the women, as well as the mode of delivery and the neonatal outcomes among different ethnic groups were compared through a bivariate analysis.
Of the 4,150 women who had PTB, 2,317 (55.8%) were non-white, who were more likely: to be younger than 19 years of age (prevalence ratio [PR]: 1.05; 95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 1.01-1.09); to be without a partner; to live on low income; to have lower levels of schooling; to have ≥ 2 children; to perform strenuous work; to be fromthe Northeastern region of Brazil rather than the from Southern region; to have a history of ≥ 3 deliveries; to have an interpregnancy interval<12 months; to have pregnancy complications such as abortion, PTB, preterm premature rupture of membranes (pPROM), and low birth weight; to initiate antenatal care (ANC) visits in the second or third trimesters; to have have an inadequate number of ANC visits; to be under continuous overexertion; to smoke in the first and second or third trimesters; and to have anemia and gestational hypertension. The maternal and neonatal outcomes did not differ between the groups, except for the higher rate of low birth weight (73.7% versus 69.0%) in infants born to non-white women, and the higher rate of seizures (4.05% versus 6.29%) in infants born to white women.
Unfavorable conditions weremore common in non-whites than inwhites. Proper policies are required to decrease inequalities, especially in the context of prematurity, when women and their neonates have specific needs.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(4):171-179
To evaluate the use of tocolysis in cases of preterm birth due to spontaneous preterm labor in a Brazilian sample.
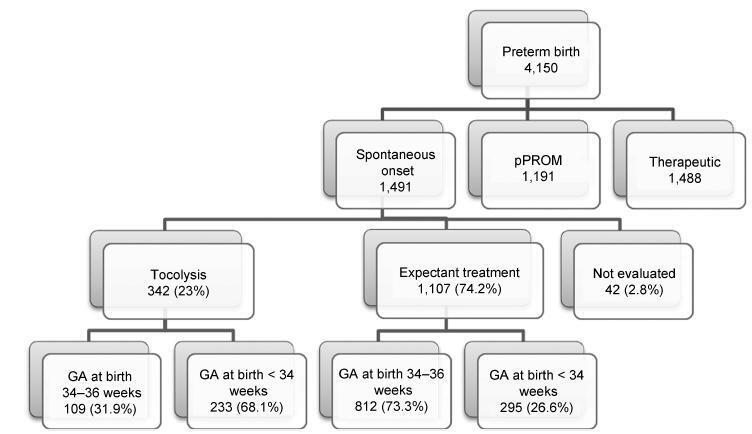
A sample of 1,491 women with preterm birth due to spontaneous preterm labor were assessed, considering treatment with tocolysis or expectant management, according to gestational age at birth (< 34 weeks and 34 to 36 þ 6 weeks) and drugs prescribed. The study took place in 20 Brazilian hospitals from April 2011 to July 2012. Bivariate analyses were conducted to evaluate associations with sociodemographic and obstetric characteristics and odds ratios with their respective 95% confidence intervals were estimated for maternal and neonatal outcomes.
A total of 1,491 cases of preterm birth were considered. Tocolysis was performed in 342 cases (23%), 233 of which (68.1%) were delivered before 34 weeks. Within the expectant management group, 73% was late preterm and with more advanced labor at the time of admission. The most used drugs were calcium channel blockers (62.3%), followed by betamimetics (33%). Among the subjects in the tocolysis group, there were more neonatal and maternal complications (majority non-severe) and an occurrence of corticosteroid use that was 29 higher than in the expectant management group.
Tocolysis is favored in cases of earlier labor and also among thosewith less than 34 weeks of gestation, using preferably calcium channel blockers, with success in achieving increased corticosteroid use. Tocolysis, in general, was related to higher maternal and neonatal complication rates, which may be due to the baseline difference between cases at admission. However, these results should raise awareness to tocolysis use.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(4):209-224
To review the existing recommendations on the prenatal care of women with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), based on currently available scientific evidence.
An integrative review was performed by two independent researchers, based on the literature available in the MEDLINE (via PubMed), EMBASE and The Cochrane Library databases, using the medical subject headings (MeSH) terms “systemic lupus erythematosus” AND “high-risk pregnancy” OR “prenatal care.” Studies published in English between 2007 and 2017 were included; experimental studies and case reports were excluded. In cases of disagreement regarding the inclusion of studies, a third senior researcher was consulted. Forty titles were initially identified; four duplicates were excluded. After reading the abstracts, 7 were further excluded and 29 were selected for a full-text evaluation.
Systemic lupus erythematosus flares, preeclampsia, gestation loss, preterm birth, fetal growth restriction and neonatal lupus syndromes (mainly congenital heartblock) were the major complications described. The multidisciplinary team should adopt a specific monitoring, with particular therapeutic protocols. There are safe and effective drug options that should be prescribed for a good control of SLE activity.
Pregnant women with SLE present an increased risk for maternal complications, pregnancy loss and other adverse outcomes. The disease activity may worsen and, thereby, increase the risk of other maternal-fetal complications. Thus, maintaining an adequate control of disease activity and treating flares quickly should be a central goal during prenatal care.