Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(6):442-451
07-27-2021
To determine the adequacy of compliance with antenatal care (ANC) by pregnant women in Peru and to identify the associated factors.
An analytical cross-sectional study of data from the 2019 Peruvian Demographic and Family Health Survey (Encuesta Demográfica y de Salud Familiar, ENDES, in Spanish) was conducted. The dependent variable was adequate compliance with ANC (provided by skilled health care professionals; first ANC visit during the first trimester of pregnancy; six or more ANC visits during pregnancy; ANC visits with appropriate content) by women aged 15 to 49 years in their last delivery within the five years prior to the survey. Crude and adjusted prevalence ratios and their 95% confidence intervals were calculated using a log-binomial regression model.
A total of 18,386 women were analyzed, 35.0% of whom adequately complied with ANC. The lowest proportion of compliance was found with the content of ANC (42.6%). Sociodemographic factors and those related to pregnancy, such as being in the age groups of 20 to 34 years and 35 to 49 years, havingsecondaryor higher education, belonging to a wealth quintile of the population other than the poorest, being from the Amazon region, not being of native ethnicity, having a second or third pregnancy, and having a desired pregnancy, increased the probability of presenting adequate compliance with ANC.
Only 3 out of 10women in Peru showed adequate compliancewith ANC. Compliance with the content of ANC must be improved, and strategies must be developed to increase the proportion of adequate compliance with ANC.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(10):614-620
12-21-2020
To evaluate the global productivity regarding original articles on maternal near-miss (MNM).
We conducted a bibliometric analysis of original articles published from 2008 to November 2019 in the journals indexed in the Scopus database. The averages of the number of articles by author, of the number of authors by article, of the number of citations by article, and the total number of documents with one or more authors were obtained. An analysis of the co-citation of authors and a co-occurrence analysis of the terms included in the titles and abstracts were performed and were presented as network visualization maps.
A total of 326 original articles were analyzed. There was an increase in the number of articles (p < 0.001; average annual growth rate = 12.54%;). A total of 1,399 authors, an average number of articles per author of 4.29, with an index of authors per document of 0.23, and an index of co-authors per document of 8.16 were identified. A total of 85 countries contributed with original articles on MNM. Among the top ten countries regarding the contribution of articles, five were low and middle-income countries (LMICs). Brazil had the highest volume of production (31.1%;), followed by the US (11.5%;). Terms related to countries and the measurement of the rates and cases of MNM and the associated factors were found in recent years in the analysis of the co-occurrence of terms.
There was an increase in the production of original articles on MNM, with a significant participation of authors and institutions from LMICs, which reveals a growing interest in the use of MNM indicators to improve the quality of maternal health care.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(10):659-668
12-21-2020
To identify the most effective procedures recommended for the prevention of preeclampsia.
A systematic review was performed in the following databases: Pubmed/MEDLINE, CINAHL, Web of Science, Cochrane and LILACS via the Virtual Health Library (VHL). A manual search was also performed to find additional references. The risk of bias, the quality of the evidence, and the classification of the strength of the recommendations were evaluated using the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations (GRADE) approach.
In the initial search in the databases, the total number of articles retrieved was 351, and 2 were retrieved through the manual search; after duplicate articles were removed, 333 citations remained. After a thorough review of the titles and abstracts, 315 references were excluded. Accordingly, 18 articles were maintained for selection of the complete text (phase 2). This process led to the exclusion of 6 studies. In total, 12 articles were selected for data extraction and qualitative synthesis.
The articles selected for the study were analyzed, and we inserted the synthesis of the evidence in the online software GRADEpro Guideline Development Tool (GDT) (McMaster University and Evidence Prime Inc. All right reserved. McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontário, Canada); thus, it was possible to develop a table of evidence, with the quality of the evidence and the classification of the strength of the recommendations.
In total, seven studies recommended the individual use of aspirin, or aspirin combined with calcium, heparin or dipyridamole. The use of calcium alone or in combination with phytonutrients was also highlighted. All of the studies were with women at a high risk of developing preeclampsia.
According to the studies evaluated, the administration of aspirin is still the best procedure to be used in the clinical practice to prevent preeclampsia.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(1):12-18
03-27-2020
To assess the prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus and the main associated risk factors in the population served by the Brazilian Unified Health System in the city of Caxias do Sul, state of Rio Grande do Sul.
A descriptive, cross-sectional and retrospective study was conducted. Maternal variables were collected from the medical records of all pregnant women treated at the basic health units in 2016. Hyperglycemia during pregnancy (pregestational diabetes, overt diabetes and gestational diabetes mellitus) was identified by analyzing the results of a 75-g oral glucose tolerance test, as recommended by the Brazilian Ministry of Health. Based on the data, the women were allocated into two groups: the gestational diabetes group and the no gestational diabetes group.
The estimated prevalence of gestational diabetes among 2,313 pregnant women was of 5.4% (95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 4.56-6.45). Pregnant women with 3 or more pregnancies had twice the odds of having gestational diabetes compared with primiparous women (odds ratio [OR]=2.19; 95%CI: 1.42-3.37; p<0.001). Pregnant women aged 35 years or older had three times the odds of having gestational diabetes when compared with younger women (OR=3.01; 95%CI: 1.97-4.61; p<0.001). Overweight pregnant women were 84% more likely to develop gestational diabetes than those with a body mass index lower than 25 kg/m2 (OR =1.84; 95%CI: 1.25-2.71; p=0.002). A multivariable regression analysis showed that being overweight and being 35 years old or older were independent variables.
In this population, the prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus was of 5.4%. Age and being overweight were predictive factors for gestational diabetes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(8):376-383
08-01-2017
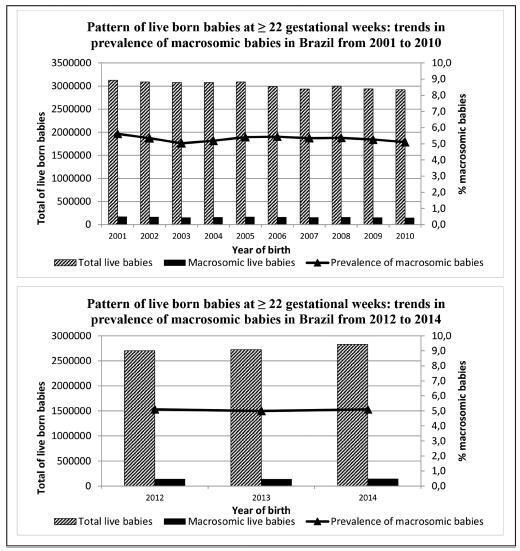
To describe the trends in the prevalence of macrosomia (birth weight ± 4,000 g) according to gestational age in Brazil in the periods of 2001-2010 and 2012-2014.
Ecological study with data from the Brazilian Live Birth Information System (SINASC, in the Portuguese acronym) regarding singleton live newborns born from 22 gestational weeks. The trends in Brazil as a whole and in each of its five regions were analyzed according to preterm (22-36 gestational weeks) and term (37-42 gestational weeks) strata. Annual Percent Changes (APCs) based on the Prais-Winsten method and their respective 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were used to verify statistically significant changes in 2001-2010.
In Brazil, the prevalence of macrosomic births was of 5.3% (2001-2010) and 5.1% (2012-2014). The rates were systematically higher in the North and Northeast Regions both in the preterm and in term strata. In the preterm stratum, the North Region presented the highest variation in the prevalence of macrosomia (+137.5%) when comparing 2001 (0.8%) to 2010 (1.9%). In the term stratum, downward trends were observed in Brazil as a whole and in every region. The trends for 2012-2014 were more heterogeneous, with the prevalence systematically higher than that observed for 2001-2010. The APC in the preterm stratum (2001-2010) showed a statistically significant trend change in the North (APC: 15.4%; 95%CI: 0.6-32.3) and South (APC: 13.5%; 95%CI: 4.8-22.9) regions. In the term stratum, the change occurred only in the North region (APC:-1.5%; 95%CI: -2.5--0.5).
The prevalence of macrosomic births in Brazil was higher than 5.0%. Macrosomia has potentially negative health implications for both children and adults, and deserves close attention in the public health agenda in Brazil, as well as further support for investigation and intervention.