-
Original Article10-23-2024
Nipple-sparing mastectomy in young versus elderly patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo90
Abstract
Original ArticleNipple-sparing mastectomy in young versus elderly patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo90
Views178See moreAbstract
Objective:
In this study, we compared indications and outcomes of 115 young (< 40 years) versus 40 elderly (> 60 years) patients undergoing nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM) as risk-reducing surgery or for breast cancer (BC) treatment.
Methods:
Between January 2004 and December 2018, young and elderly patients undergoing NSM with complete data from at least 6 months of follow-up were included.
Results:
BC treatment was the main indication for NSM, observed in 85(73.9%) young versus 33(82.5%) elderly patients, followed by risk-reducing surgery in 30(26.1%) young versus 7(17.5%) elderly patients. Complication rates did not differ between the age groups. At a median follow-up of 43 months, the overall recurrence rate was higher in the younger cohort (p = 0.04). However, when stratified into local, locoregional, contralateral, and distant metastasis, no statistical difference was observed. During the follow-up, only 2(1.7%) young patients died.
Conclusion:
Our findings elucidate a higher recurrence rate of breast cancer in younger patients undergoing NSM, which may correlate with the fact that age is an independent prognostic factor. High overall survival and low complication rates were evidenced in the two groups showing the safety of NSM for young and elderly patients.
-
Original Article09-06-2024
Immediate prepectoral versus submuscular breast reconstruction in nipple-sparing mastectomy: a retrospective cohort analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo76
Abstract
Original ArticleImmediate prepectoral versus submuscular breast reconstruction in nipple-sparing mastectomy: a retrospective cohort analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo76
Views284Abstract
Objective
To evaluate early complications in prepectoral breast reconstruction.
Methods
A retrospective cohort study including 180 consecutive cases of nipple-sparing mastectomy, comparing immediate breast reconstruction with subpectoral to prepectoral mammary implants in 2012-2022. Clinical and demographic characteristics and complications in the first three months following surgery were compared between the two techniques.
Results
The prepectoral technique was used in 22 cases (12.2%) and the subpectoral in 158 (87.8%). Median age was higher in the prepectoral group (47 versus 43.8 years; p=0.038), as was body mass index (25.1 versus 23.8; p=0.002) and implant volume (447.5 versus 409 cc; p=0.001). The prepectoral technique was more associated with an inframammary fold (IMF) incision (19 cases, 86.4% versus 85, 53.8%) than with periareolar incisions (3 cases, 13.6% versus 73, 46.2%); (p=0.004). All cases in the prepectoral group underwent direct-to-implant reconstruction compared to 54 cases (34.2%) in the subpectoral group. Thirty-eight complications were recorded: 36 (22.8%) in the subpectoral group and 2 (9.1%) in the prepectoral group (p=0.24). Necrosis of the nipple-areola complex/skin flap occurred in 27 patients (17.1%) in the subpectoral group (prepectoral group: no cases; p=0.04). The groups were comparable regarding dehiscence, seroma, infection, and hematoma. Reconstruction failed in one case per group (p=0.230). In the multivariate analysis, IMF incision was associated with the prepectoral group (aOR: 34.72; 95%CI: 2.84-424.63).
Conclusion
The incidence of early complications was comparable between the two techniques and compatible with previous reports. The clinical and demographic characteristics differed between the techniques. Randomized clinical trials are required.
Key-words Breast implantationBreast implantsBreast neoplasmsMammaplastyMastectomyNipplesPectoralis musclesSurgical procedures, operativeSee more -
Original Article00-00-2024
Outcomes after elevation of serratus anterior fascia flap versus serratus muscle flap in direct-to-implant breast reconstruction following mastectomy: a prospective study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo13
Abstract
Original ArticleOutcomes after elevation of serratus anterior fascia flap versus serratus muscle flap in direct-to-implant breast reconstruction following mastectomy: a prospective study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo13
Views416Abstract
Objective:
The purpose of this study was to compare postoperative pain between SF flap and serratus anterior muscle (SM) in direct-to-implant breast reconstruction.
Methods:
This is a prospective cohort study that included 53 women diagnosed with breast cancer who underwent mastectomy and one-stage implant-based breast reconstruction from January 2020 to March 2021. Twenty-nine patients (54.7%) had SF elevation, and 24 patients (45.3%) underwent SM elevation. We evaluated patient-reported early postoperative pain on the first day after surgery. Also, it was reported that all surgical complications in the first month and patient reported outcomes (PROs) were measured with the BRECON 23 questionnaire.
Results:
The serratus fascia group used implants with larger volumes, 407.6 ± 98.9 cc (p < 0.01). There was no significant difference between the fascial and muscular groups regarding the postoperative pain score reported by the patients (2 versus 3; p = 0.30). Also, there was no difference between the groups regarding early surgical complications and PROs after breast reconstruction.
Conclusion:
The use of SF seems to cause less morbidity, which makes the technique an alternative to be considered in breast reconstruction. Although there was no statistical difference in postoperative pain scores between the fascia and serratus muscle groups.
Key-words Breast implantsBreast neoplasmsbreast reconstructionFasciaMastectomyPainPostoperative periodSee more -
Original Article01-23-2022
Oncological Outcomes of Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy in an Unselected Population Evaluated in a Single Center
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(11):1052-1058
Abstract
Original ArticleOncological Outcomes of Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy in an Unselected Population Evaluated in a Single Center
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(11):1052-1058
Views146Abstract
Objective
Nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM) has been traditionally used in selected cases with tumor-to-nipple distance > 2 cm and negative frozen section of the base of the nipple. Recommending NSM in unselected populations remains controversial. The present study evaluated the oncological outcomes of patients submitted to NSM in an unselected population seen at a single center.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study included unselected patients with invasive carcinoma or ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) who underwent NSM in 2010 to 2020. The endpoints were locoregional recurrence, disease-free survival (DFS), and overall survival (OS), irrespective of tumor size or tumor-to-nipple distance.
Results
Seventy-six patients (mean age 46.1 years) (58 invasive carcinomas/18 DCIS) were included. The most invasive carcinomas were hormone-positive (60%) (HER2 overexpression: 24%; triple-negative: 16%), while 39% of DCIS were high-grade. Invasive carcinomas were T2 in 66% of cases, with axillary metastases in 38%. Surgical margins were all negative. All patients with invasive carcinoma received systemic treatment and 38% underwent radiotherapy. After a mean of 34.8 months, 3 patients with invasive carcinoma (5.1%) and 1 with DCIS (5.5%) had local recurrence. Two patients had distant metastasis and died during follow-up. The 5-year OS and DFS rates for invasive carcinoma were 98% and 83%, respectively.
Conclusion
In unselected cases, the 5-year oncological outcomes following NSM were found to be acceptable and comparable to previous reports. Further studies are required.
Key-words Breast neoplasmsMastectomynipple-sparing mastectomysegmental mastectomysubcutaneous mastectomySee more -
Review Article07-17-2020
Progress in Local Treatment of Breast Cancer: A Narrative Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(6):356-364
Abstract
Review ArticleProgress in Local Treatment of Breast Cancer: A Narrative Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(6):356-364
Views164Abstract
The present paper reports on the local treatment of breast cancer from a historical perspective. A search for articles written in English was made in the Medline and EMBASE databases, and 40 papers were selected. Over the past 10 years, various randomized, controlled clinical trials on the local treatment of breast cancer indicated that patients with the samemolecular subtypemay receive different individualized surgical treatments aimed atoptimizing systemic adjuvant therapy. With a view to retaining the gainsmade in diseasefree and overall survival, surgical techniques have advanced from radical surgery to conservative mastectomies, thus reducing sequelae, while adjuvant and neoadjuvant therapies have contributed toward controlling the disease, both distant metastases and local recurrence. Current studies evaluate whether future breast cancer therapy may even succeed in eliminating surgery to the breast and axilla altogether.
Key-words Breast cancer/therapybreast-conserving therapyMastectomyneoadjuvant and adjuvant therapysentinel node biopsySee more -
Original Article03-01-2017
Upper Limb Functionality and Quality of Life in Women with Five-Year Survival after Breast Cancer Surgery
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(3):115-122
Abstract
Original ArticleUpper Limb Functionality and Quality of Life in Women with Five-Year Survival after Breast Cancer Surgery
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(3):115-122
Views200See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the correlation between upper limb functionality and quality of life in women with five-year survival following breast cancer surgical treatment. The secondary objective was to evaluate the function of the ipsilateral upper limb and the quality of life in relation to the type of surgery and the presence of pain.
Methods
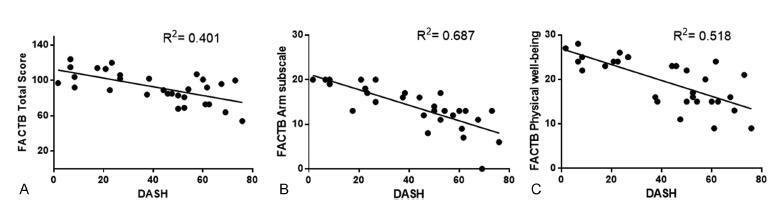
The Disabilities of Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH), and the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy - Breast plus Arm Morbidity (FACTB + 4) questionnaires were used to evaluate upper limb function and quality of life respectively. Data distribution was verified by the Shapiro-Wilk test. Pearson's correlation coefficient was used for the parametric variables, and Spearman's rank correlation coefficient was used for the distribution of non-parametric variables. The statistical significance was set at 5% (p < 0.05).
Results
The study included 30 patients, with a mean age of 51.23 (±8.72) years. The most common complications were: pain (50%), adherence (33.3%), and nerve lesion (20.0%). There was a moderate negative correlation between the instruments DASH and FACTB + 4 (total score), r = -0.634, and a strong negative correlation between the DASH and the FACTB + 4 armsubscale, r = -0.829. The scores of both questionnaires showed significant difference on the manifestation of pain. However, there was no significant difference found when comparing the scores considering the type of surgery performed.
Conclusions
Five years after surgery, the patients showed regular functionality levels on the ipsilateral upper limb and decreased quality of life, especially in the group manifesting pain.
-
Original Article07-05-2013
Volume of breast tissue excised during breast-conserving surgery in patients undergoing preoperative systemic therapy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(5):221-225
Abstract
Original ArticleVolume of breast tissue excised during breast-conserving surgery in patients undergoing preoperative systemic therapy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(5):221-225
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000500006
Views154See morePURPOSE: We aimed to determine whether clinical examination could adequately ascertain the volume of tissue to be resected during breast-conserving surgery after neoadjuvant therapy. METHODS: We reviewed the clinical reports of 279 patients with histologically diagnosed invasive breast carcinomas treated with neoadjuvant therapy followed by surgery or with primary surgery alone. We estimated volumes of excised tissues, the volume of the tumor mass and the optimal volume required for excision based on 1 cm of clear margins. The actual excess of resected volume was estimated by calculating the resection ratio measured as the volume of the resected specimen divided by the optimal specimen volume. The study endpoints were to analyze the extent of tissue resection and to ascertain the effect of excess resected tissue on surgical margins in both groups of patients. RESULTS: The median tumor diameter was 2.0 and 1.5 cm in the surgery and neoadjuvant therapy groups, respectively. The median volume of resected mammary tissue was 64.3 cm³ in the primary surgery group and 90.7 cm³ in the neoadjuvant therapy group. The median resection ratios in the primary surgery and neoadjuvant therapy groups were 2.0 and 3.3, respectively (p<0.0001). Surgical margin data were similar in both groups. Comparison of the volume of resected mammary tissues with the tumor diameters showed a positive correlation in the primary surgery group and no correlation in the neoadjuvant therapy group. CONCLUSION: Surgeons tend to excise large volumes of tissue during breast-conserving surgery after neoadjuvant therapy, thereby resulting in a loss of the correlation between tumor diameter and volume of the excised specimen.
-
Original Article03-30-2010
Immediate breast reconstruction effects on quality of life of women with mastectomy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(12):602-608
Abstract
Original ArticleImmediate breast reconstruction effects on quality of life of women with mastectomy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(12):602-608
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010001200007
Views100See morePURPOSE: to prospectively evaluate the effects of immediate breast reconstruction on the quality of life of women who underwent mastectomy. METHODS: 76 women that underwent mastectomy at Centro de Atenção Integral à Saúde da Mulher da Universidade Estadual de Campinas, in Campinas, São Paulo, Brazil, from August 2007 to December 2008, were included. Two groups were formed: 41 women who underwent mastectomy combined with immediate breast reconstruction (M+RI) and 35 that were subjected to mastectomy alone (M). The quality of life evaluation was assessed with the World Health Organization's questionnaire - Quality of Life (WHOQOL-100). The questionnaire was administered on three occasions: at the time of admission, one month after surgery, and again six months after surgery. The WHOQOL-100 scores were calculated according to analysis' guidelines by the World Health Organization. For comparison of the scores between groups, it was used the Student's t-test, Fisher exact test, chi-square test, and Mann-Whitney test. For the analysis of repeated measures over time, ANOVA and ANOVA for repeated measures were used. RESULTS: at all time points evaluated, beginning with the preoperative assessment, the average quality of life scores of the M+IR Group were higher than those of the M Group, primarily in the "physical", "psychological", "level of independence" and "social relationships" domains of the questionnaire. Of the six areas covered by the questionnaire, three ("physical", "social relations", "environment") showed no significant differences between groups. The M+IR Group had a better score (15.5 to 14.9 for the M+IR and 14.3 to 14.2 for M; p=0.04) in the psychological domain. There was a significant reduction in the level of independence in the first month after surgery in both groups, with a significant recovery after six months. CONCLUSIONS: the present results suggest that immediate breast reconstruction is significantly beneficial regarding the psychological aspects of quality of life, without affecting the patient's physical functionality.


