Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(1):41-45
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000100006
Purpose: the morphologic and morphometric aspects of the breasts of rats in permanent estrus submitted to danazol were studied. Methods: the animals were divided into three groups: group A (n = 12) received water and was used as control, group B (n = 13) was exposed to 20 mg danazol kg-1 day-1, and group C (n = 10) was exposed to 80 mg danazole kg-1 day-1 for 35 consecutive days. The microscopic study evaluated the ductal and acinar distribution. Histometry of the relationship duct/stroma was based on the principles of stereology with a Zeiss k-10X ocular, with Integrationsplatte I reticulum of Weibel of 25 hits, with 100X magnification. For each studied section, 10 aleatoric fields were counted, with a total of 250 points. The variance analysis test (Kruskal-Wallis) was applied to compare the three groups in relation to the mean number of alveoli and ducts (alpha = 0.05). Results: when submitted to morphological study, all groups presented lobules with alveoli lined with cubic cells with nuclei in their central or basal portion. Small amounts of eosinophilic material were observed in some cases in the lumen, with no differences between the groups. At morphometry, with a magnification of 100X, a mean number of 28.6 ducts/10 fields was found in group A, 28.4 in group B and 29.2 in group C (Kruskal-Wallis test: Hcrit = 0.1). The mean number of alveoli in 10 fields was 5.9, 9.3 and 6.5 in groups A, B and C, respectively (Kruskal-Wallis test: Hcrit = 2.9), with no significant differences between the groups. Conclusion: danazol did not cause any changes in the morphology and morphometry of the permanent estrus mammary epithelium.
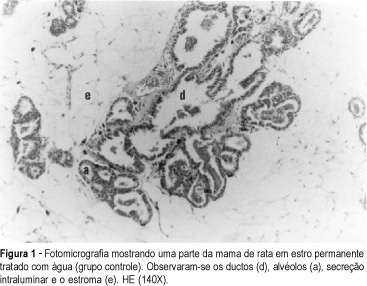
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(8):499-504
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000800004
Purpose: to evaluate factors that might influence the results of nonphamacological treatment (verbal guidance) in women with clinical mastalgia. Methods: an uncontrolled study of the experimental type was conducted on a sample of 128 women with a clear history of clinical mastalgia treated with verbal guidance. A visual analogue scale for pain was used before and after treatment to evaluate pain intensity and mastalgia was classified into grade I (mild), grade II (moderate) and grade III (severe) according to pain intensity. The Cardiff Breast Score (CBS), modified, was also used to evaluate the clinical response to treatment. Data were analyzed statistically using the chi² test (Epi-Info 6.04). Results: we noted that factors such as parity, menarche, age at first term delivery and breast-feeding had no significant effect (p=0.19, p=0.31, p=0.80 and p=0.54, respectively) on the results of nonpharmacological treatment (verbal guidance). On the other hand, when age was taken into consideration, 26 patients (78.8%) aged 40 years or older were found to benefi more from verbal guidance, with a significant difference (p=0.01) when compared to younger women. Conclusion: reproductive factors such as parity, menarche, age at first term delivery and breast-feeding did not affect the results of nonpharmacological treatment (verbal guidance), whereas the age factor had a specific and significant effect on the results.