Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):443-452
09-01-2017
To define transvaginal ultrasound reference ranges for uterine cervix measurements according to gestational age (GA) in low-risk pregnancies.
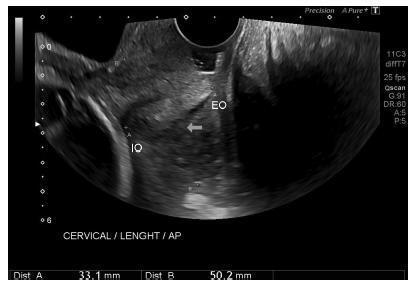
Cohort of low-risk pregnantwomen undergoing transvaginal ultrasound exams every 4 weeks, comprisingmeasurements of the cervical length and volume, the transverse and anteroposterior diameters of the cervix, and distance fromthe entrance of the uterine artery into the cervix until the internal os. The inter- and intraobserver variabilities were assessed with the linear correlation coefficient and the Student t-test. Within each period of GA, 2.5, 10, 50, 90 and 97.5 percentiles were estimated, and the variation by GA was assessed with analysis of variance for dependent samples. Mean values and Student t-test were used to compare the values stratified by control variables.
After confirming the high reproducibility of the method, 172 women followed in this cohort presented a reduction in cervical length, with an increase in volume and in the anteroposterior and transverse diameters during pregnancy. Smaller cervical lengths were associated with younger age, lower parity, and absence of previous cesarean section (C-section).
In the studied population, we observed cervical length shortening throughout pregnancy, suggesting a physiological reduction mainly in the vaginal portion of the cervix. In order to better predict pretermbirth, cervical insufficiency and premature rupture of membranes, reference curves and specific cut-off values need to be validated.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(9):639-646
01-19-2003
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000900004
PURPOSE: to evaluate the association between the variability of amniotic fluid index (AFI) values with gestational age and some sociodemographic and obstetric variables among low-risk pregnant women. METHOD: a comparative study was carried out including 2868 low-risk pregnant women who had routine obstetric ultrasound examination, including fetal biometry and the measurement of AFI, from 20 to 42 weeks of gestation. The data were analyzed using Student's t test, analysis of variance of mean AFI values along gestational ages, according to other control variables, and also by multiple linear regression analysis. RESULTS: there was no significant variation of mean AFI values during the time of pregnancy neither when separately evaluating its association with maternal age, color, education, smoking habit, parity, and the presence of previous cesarean section scars, nor when the evaluation was performed through multivariate analysis. In this situation only the increase in gestational age showed to be associated with the decrease of AFI. Generally speaking, the mean AFI values fluctuated between 140 and 180 mm between the 20th and the 36th week, then showing values below 140 mm in a progressive decrease after this limit of gestational age. CONCLUSIONS: AFI values do not show a significant variation during pregnancy regarding the studied sociodemographic and obstetric variables.