Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(8):456-464
10-09-2023
Evaluate the different perspectives that involve the choice of long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs), the issues related to this process and the consequences of deciding one method in the women's in the primary health care (PHC) center in Sousas, a district in Campinas, SP (Brazil).
This is an analytical cross-sectional study, it was performed at the PHC in Sousas. Data were collected through the analysis of medical records and interviews with women who live in Sousas and had the insertion of the copper intrauterine device (IUD) (D) from April 2021 to April 2022 or the etonogestrel implant (I) from May to December 2022. The study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Medical Science School at the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP).
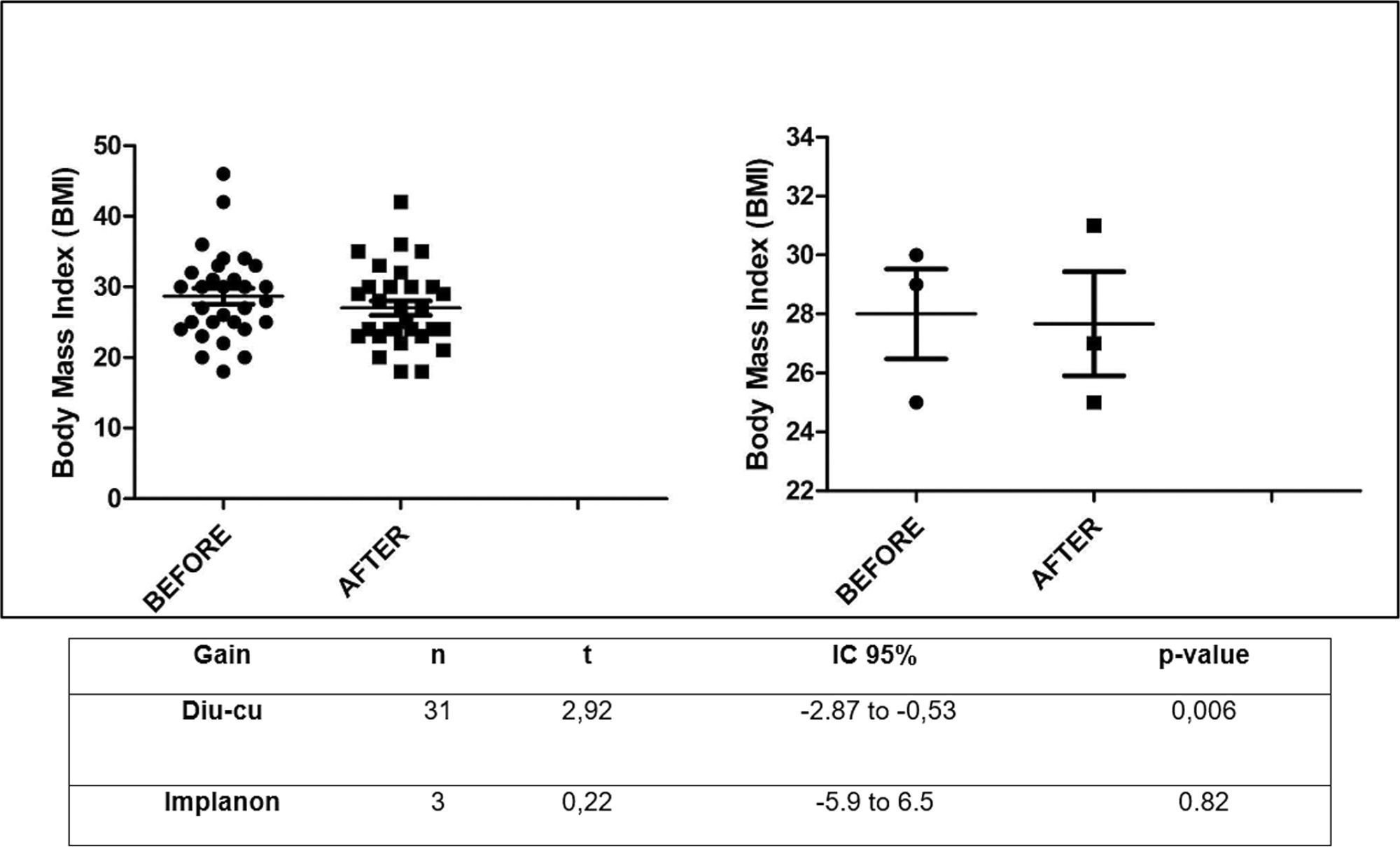
Reason for choosing this LARC: medical (D: 52%; I: 100%), easy adhesion (D: 71%; I: 67%), effectiveness (D: 55%; I: 100%). Indication by health professionals (D: 65%; I: 100%). And improvement of clinical characteristics: mood (D: 77%; I: 67%), body mass index (BMI; D: 52%; I: 33%), and libido (D: 84%; I: 67%).
It is suggested that women tend to decide between LARCs when guided by their doctor or PHC health professionals, and they select LARCs because of the ease of use and low failure rates. Therefore, this study highlights how LARCs can positively interfere in the aspects that pervade contraception, such as BMI, libido, and mood.