-
Case Report
Pelvic Intravenous Leiomyomatosis – Case Report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(8):412-415
08-01-2016
Summary
Case ReportPelvic Intravenous Leiomyomatosis – Case Report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(8):412-415
08-01-2016Views127See moreAbstract
Introduction
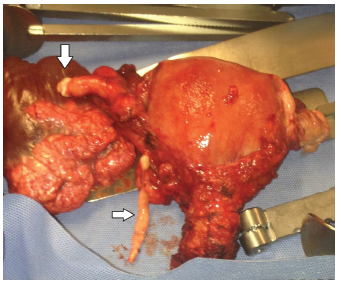
Intravenous leiomyomatosis is a benign and rare condition that can result in cardiac events with fatal outcomes when left untreated. Intravenous leiomyomatosis is probably underestimated because the diagnosis is easily missed. We present a case of an intravenous leiomyomatosis without extra-pelvic involvement, with a brief review of this pathology.
Case Report
46-year-old woman submitted to hysterectomy and bilateral adnexectomy because of a pelvic mass detected in ultrasound. During the surgery, intravenous leiomyomatosis diagnosis was suspected. Pathological analysis confirmed this suspicion. Further imaging exams were performed without detecting any anomalies related to this condition. The patient remained with no evidence of disease after one year of follow-up.
Conclusion
Intravenous leiomyomatosis is a rare condition that can lead to serious complications. Early diagnosis followed by an appropriate treatment is very important to patient outcome, and underdiagnoses can be counteracted if the gynecologist is aware of this entity.
-
Relato de Caso
Benign metastasizing uterine leiomyoma: case reports
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(8):411-414
10-09-2009
Summary
Relato de CasoBenign metastasizing uterine leiomyoma: case reports
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(8):411-414
10-09-2009DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000800007
Views76Benign metastazing leiomyomatosis (BML) is a rare disease in which the lung is the most affected extra-uterine organ. The BML histology is compatible with benignity and similar to that found in the myometrial leiomyoma. A history of surgically treated uterine myomatosis is reported by most of the patients with metastatic disease. We report the cases of two patients with uterine metastazing leiomyomatosis. In the first case, a 55-year-old patient presented lung nodes over 20 years after being submitted to hysterectomy due to uterine leiomyoma. The histological and immunohistochemical studies from the lung node revealed that it was an implant of benign leiomyoma. The second patient, a 65-years-old woman, presented lung and retroperitoneal nodes 20 years after being submitted to a hysterectomy due to uterine leiomyoma.
Key-words Case reportsHysterectomyLeiomyomaLeiomyomatosisLung neoplasmsRetroperitoneal neoplasmsUterine neoplasmsSee more


