-
Original Article
Exercise in Pregnancy: The Impact of an Intervention Program in the Duration of Labor and Mode of Delivery
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(2):68-75
02-01-2019
Summary
Original ArticleExercise in Pregnancy: The Impact of an Intervention Program in the Duration of Labor and Mode of Delivery
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(2):68-75
02-01-2019Views171See moreAbstract
Objective
To access the benefits or harms of an exercise program, based on the current American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists guidelines, on the mode of delivery, duration and onset of labor.
Methods
A study performed at the Hospital Senhora da Oliveira between October 2015 and February 2017. This was a quasi-experimental study involving 255 women divided into two groups: an intervention group engaged in a controlled and supervised exercise program during pregnancy (n = 99), and a control group that did not participate in the exercise program (n = 156). Data were collected in two stages: during the 1st trimester biochemical screening (before the beginning of the program), through a written questionnaire, and after delivery, from the medical files of the patients. The significance level in the present study was 5% (p = 0.05).
Results
The control group had higher odds of induced labor (odds ratio [OR] 2.71; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.42-5.17; p = 0.003), when compared with women who underwent the intervention. No differences were found between the groups in instrumental vaginal deliveries, cesarean rate, time until the beginning of the active phase, duration of the active phase, and duration of the second stage of labor.
Conclusion
The implementation of a controlled and supervised exercise program in pregnancy was associated with significantly lower odds of induced deliveries.
-
Original Article
Induction of Labor using Misoprostol in a Tertiary Hospital in the Southeast of Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(10):523-528
10-01-2017
Summary
Original ArticleInduction of Labor using Misoprostol in a Tertiary Hospital in the Southeast of Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(10):523-528
10-01-2017Views203See moreAbstract
Purpose
To assess cases of labor induction with vaginal 25-μg tablets of misoprostol and maternal outcomes in a tertiary hospital in southeastern Brazil.
Methods
This was a retrospective cohort study of 412 pregnant women with indication for labor induction. Labor induction was performed with vaginal 25-μg tablets ofmisoprostol in pregnant women with Bishop scores < 6. Stepwise regression analysis was used to identify the factors present at the beginning of induction that could be used as predictors of successful labor induction.
Results
A total of 69% of the pregnant women who underwent labor induction progressed to vaginal delivery, and 31% of the women progressed to cesarean section. One or two misoprostol tablets were used in 244 patients (59.2%). Of the 412 patients, 197 (47.8%) required oxytocin later on in the labor process, after induction with misoprostol. The stepwise regression analysis showed that only Bishop scores of 4 and 5 and previous vaginal delivery were independent factors with statistical significance in the prediction of successful vaginal labor induction (β = 0.23, p < 0.001, for a Bishop score of 4 and 5, and β = 0.22, p < 0.001, for previous vaginal delivery).
Conclusion
Higher Bishop scores and previous vaginal delivery were the best predictors of successful labor induction with vaginal 25-μg tablets of misoprostol.
-
Original Article
Sonographic Cervical Shortening after Labor Induction is a Predictor of Vaginal Delivery
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(12):585-588
12-01-2016
Summary
Original ArticleSonographic Cervical Shortening after Labor Induction is a Predictor of Vaginal Delivery
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(12):585-588
12-01-2016Views91See moreABSTRACT
Objective:
Analyzing if the sonographic evaluation of the cervix (cervical shortening) is a prognostic marker for vaginal delivery.
Methods:
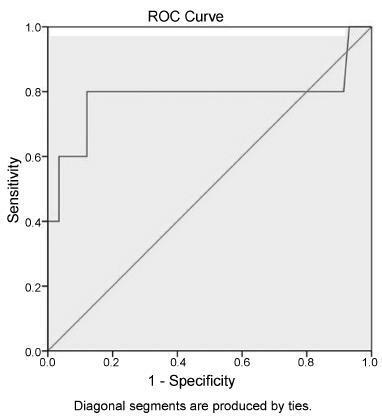
Women who underwent labor induction by using dinoprostone were enrolled. Before the induction and three hours after it, the cervical length was measured by ultrasonography to obtain the cervical shortening. The cervical shortening was introduced in logistic regression models among independent variables and for calculating receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves.
Results:
Each centimeter in the cervical shortening increases the odds of vaginal delivery in 24.4% within 6 hours; in 16.1% within 24 hours; and in 10.5% within 48 hours. The best predictions for vaginal delivery are achieved for births within 6 and 24 hours, while the cervical shortening poorly predicts vaginal delivery within 48 hours.
Conclusion:
The greater the cervical shortening 3 hours after labor induction, the higher the likelihood of vaginal delivery within 6, 24 and 48 hours.
-
Trabalhos Originais
Comparison between active management with oxytocin and expectant management for premature rupture of membranes at term
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(9):495-501
04-09-1998
Summary
Trabalhos OriginaisComparison between active management with oxytocin and expectant management for premature rupture of membranes at term
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(9):495-501
04-09-1998DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000900002
Views100See moreObjective: to compare the expectant versus active management with oxytocin in a Brazilian population of pregnant women with premature rupture of membranes (PROM) at term. Methods: a prospective, randomized and multicenter clinical trial was performed, evaluating variables concerning the time from PROM until the onset of labor and delivery, and maternal and neonatal hospitalization periods. Two hundred pregnant women with PROM at term were selected from four public hospitals in São Paulo state, from November 1995 to February 1997. They were randomly divided into two groups: active management, with oxytocin induction of labor until 6 h of PROM; and expectant management, waiting for the spontaneous onset of labor up to 24 h. The data were analyzed with the Epi-Info and SPSS-PC+ packages, using the statistical c², Student's t and log-rank tests. Results: the results indicate that the differences between the two managements concern to the longer time needed for the expectant management group until onset of labor and delivery, besides the higher number of women and neonates who remained in hospital for more than three days. Conclusions: the time between admission and onset of labor and delivery, and also the latent period were longer in the expectant management group.
-
Trabalhos Originais
Effect of nipple stimulation on Bishop scores in term pregnancies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(1):13-17
03-15-1999
Summary
Trabalhos OriginaisEffect of nipple stimulation on Bishop scores in term pregnancies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(1):13-17
03-15-1999DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000100003
Views49See morePurpose: to evaluate if the nipple stimulation performed by primigravidae, at 40 weeks, modifies Bishop index. Method: 64 primigravidae, without clinical or obstetrical complications were studied, in two groups. One group, called nipple stimulation group (N.S.G.) had 29 pregnant women. The other, named control group (C.G.) included 35 pregnant women. The N.S.G. performed the nipple stimulation test, bilaterally, from left to right, for two minutes followed by five minutes of rest, during thirty minutes. The test was done three times a day up to 41 weeks of pregnancy or beginning of labor. Statistical analysis of the results was performed using Student's t test, with 5 % significance. Results: once nipple stimulation was completed in the N.S.G., it was compared with the C.G. considering time of delivery. The results showed no significant differences between the groups regarding cervix modification, according to the Bishop index. Conclusions: there were no differences of the Bishop index in primigravidae, with more than 40 weeks of pregnancy, who performed nipple stimulation test, when compared with pregnant women of the control group.
-
Trabalhos Originais
Labor Induction with Misoprostol: Comparison of Two Dose Regimens
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(9):527-531
05-22-1999
Summary
Trabalhos OriginaisLabor Induction with Misoprostol: Comparison of Two Dose Regimens
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(9):527-531
05-22-1999DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000900005
Views95See morePurpose: to compare the efficacy and safety between two doses of intravaginal misoprostol for cervical ripening and induction of labor. Patients and Methods: sixty-one patients with medical indication for induction of labor and unfavorable cervix were included in this study. Twenty-eight of them received 25 µg and thirty-three 50 µg misoprostol, every four hours until delivery. Results: premature rupture of membranes, prolonged gestation and preeclampsia were the main indications for labor induction. The time interval, in minutes, from insertion of misoprostol until delivery was similar for the 25 µg (416.3 ± 148.1) and 50 µg (425.0 ± 135.9) groups. The percentage of vaginal delivery was 82.2% and 81.9% in the groups of 25µg and 50 µg, respectively. There was no significant difference between the two groups regarding fetal or maternal complications. Conclusions: the administration of intravaginal misoprostol was shown to be an efficient and safe method for cervical ripening and induction of labor. The dose of 25 µg was similarly effective and safe when compared to 50 µg.
-
Artigos Originais
Sublingual versus vaginal misoprostol for labor induction of term pregnancies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(1):24-31
07-05-2005
Summary
Artigos OriginaisSublingual versus vaginal misoprostol for labor induction of term pregnancies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(1):24-31
07-05-2005DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000100006
Views113See morePURPOSE: to compare the effectiveness and safety of sublingual misoprostol (25 µg) versus vaginal misoprostol (25 µg) (Prostokos®) for labor induction with gestational age > 37 weeks and unripe cervices. METHODS: a randomized controlled clinical trial was performed at the Maternidade Monteiro de Morais (CISAM-UPE), in Recife - PE, Brazil, from October 2003 to February 2004. One hundred and twenty-three women with gestational age > 37 weeks, Bishop score <8, not in labor and with medical indication for interruption of pregnancy were included in this study. The women received randomly 25 µg sublingual misoprostol or 25 µg vaginal misoprostol every 6 h, not exceeding eight doses. In order to evaluate the differences between the groups, means, standard deviations, Student's t-test, c² trend and Mann-Whitney test were used. The statistical significance was considered to be 5%. RESULTS: there were no significant differences between the number of women with vaginal delivery in the sublingual group as compared with the vaginal group (65.5 vs 75.8%, p<0.22), or in the interval of time between the induction onset and delivery (24 h and 42 min vs 20 h and 37 min respectively, p=0.11). The two groups, sublingual and vaginal, also did not differ as to the hyperstimulation syndrome (1.7 vs 3.2%, p=0.95), meconium incidence (5.2 vs 4.8%, p=0.74), Apgar score <7 at 5 min (3.4 vs 4.8%, p=0.98) and other adverse effects. CONCLUSION: twenty-five micrograms of sublingual misoprostol every six h presented the same effectiveness and safety as an equal vaginally administered dose of this substance. Sublingual misoprostol seems to be acceptable and is another option to be considered for labor induction.
-
Trabalhos Originais
Factors associated with vaginal delivery in high-risk pregnant women submitted to labor induction with misoprostol
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(1):21-29
04-23-2004
Summary
Trabalhos OriginaisFactors associated with vaginal delivery in high-risk pregnant women submitted to labor induction with misoprostol
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(1):21-29
04-23-2004DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000100004
Views88See morePURPOSE: to determine the main factors associated with vaginal delivery in high-risk pregnant women submitted to labor induction with vaginal misoprostol (50 µg). METHODS: this is a secondary analysis of an open nonrandomized clinical trial that included 61 high-risk pregnant women admitted at the "Maternidade-Escola Assis Chateaubriand", Fortaleza (Ceará). All women had singleton pregnancies with alive fetuses, gestational age >37 weeks and Bishop scores <7. Misoprostol was vaginally administered at doses of 50 µg every 6 h for a maximum of four doses. Univariate and multiple logistic regression analyses were performed to determine association between vaginal delivery (dependent variable) and independent variables (predictive), and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were constructed for parity and Bishop scores. RESULTS: parity (one or more previous deliveries), Bishop scores >4 and interval induction to delivery <6 h were significantly associated with vaginal delivery, while tachysystole reduced the probability of vaginal delivery. A multivariate stepwise logistic regression was then performed to evaluate each of these as independent predictors. Parity (OR = 5.41, 95% CI = 4.18-6.64) and Bishop score >4 (OR = 3.30, 95% CI = 2.15-4.45) were significant independent predictors for vaginal delivery. In the ROC curve for parity and Bishop score, sensitivity of 63.2% and positive predictive value of 100% were found. The area under the ROC curve was 86.8%, significantly higher than 50% (p=0.023). CONCLUSIONS: the most important predictive factors for vaginal delivery after induction with misoprostol were parity and Bishop score. These characteristics should be considered when choosing schemes and doses of misoprostol for cervical ripening and labor induction.


