Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(5):289-296
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) is associated with poor perinatal prognosis and a higher risk of stillbirth, neonatal death, and cerebral palsy. Its detection and the evaluation of its severity by new Doppler velocimetric parameters, such as aortic isthmus (AoI), are of great relevance for obstetrical practice. The AoI is a vascular segment that represents a point of communication between the right and left fetal circulations. It is considered to be a functional arterial shunt that reflects the relationship between the systemic and cerebral impedances, and has recently been proposed as a tool to detect the status of hemodynamic balance and prognosis of IUGR in fetuses. In the present review, we noticed that in healthy fetuses, the AoI net flow is always antegrade, but in fetuses with IUGR the deterioration of placental function leads to progressive reduction in its flow until it becomes mostly retrograde; this point is associated with a drastic reduction in oxygen delivery to the brain. The more impaired the AoI flow is, the greater is the risk of impairment in the Doppler velocimetry of other vessels; and the alterations of the AoI Doppler seem to precede other indicators of severe hypoxemia. Although there seems to be an association between the presence of retrograde flow in the AoI and the risk of long-term neurologic disability, its role in the prediction of perinatal morbi-mortality remains unclear. The AoI Doppler seems to be a promising tool in the management of fetuses with IUGR, but more studies are needed to investigate its employment in clinical practice.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(10):799-805
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004001000007
PURPOSE: to assess risk factors for low Apgar score. METHODS: this was a cross-sectional study preformed in a random sample of patients admitted to a level III maternity hospital in 2001. The outcome was low Apgar score defined as an Apgar score 1-6 (study group) versus Apgar score 7-10 (control group) in the first minute of life. The first step was the evaluation of the association of each possible risk factor with low Apgar score. The second step was multivariate analysis with the backward stepwise logistic regression model. RESULTS: there were 39 (14%) depressed newborns which were compared to 238 (86%) not depressed babies. The final analysis (multivariate) showed an association between low Apgar score and previous case of stillbirth (OR=52.6), preterm labor threat (OR=33.8), low birth weight, less than 2,500 g body weight (OR=11.2) and previous cesarean section (OR=7.4). Some factors acted as a protection, including birth weight, in grams (OR=0.9), female sex of the newborn (OR=0.1), medical complications (OR=0.4) and prematurity (gestational age < 37 weeks, OR=0.1). CONCLUSION: the study may help in the identification of fetuses at great risk of asphyxia, allowing proper reference within the health system and planning of effective assistance in neonatal intensive care units.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(8):523-527
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000800007
Purpose: to study perinatal outcome in asthmatic pregnant patients who required hospital admission to control acute exacerbations. Patients and Method: retrospective study of 12 pregnant asthmatic patients admitted at the Hospital das Clínicas, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, FMRP-USP, during the period between 1992 and 1996. The analyzed data included: maternal age, prenatal care, length of hospitalization, gestational age at delivery, type of delivery, neonatal weight and Apgar score. Results: among the 12 asthmatic pregnant patients 7 did not have prenatal care for acute exacerbation treatment before hospitalization. Three of 12 developed preeclampsia (one with premature rupture of membranes and infection of the amniotic cavity and one with premature separation of the placenta); 2 of 12 were diagnosed with premature placental aging (one with premature labor and twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome and one with oligohydramnios); 1 of 12 was diagnosed with oligohydramnios and fetal death and had pneumonia, and 1 of 12 was diagnosed with polyhydramnios. Among the infants, 3 were small for gestational age. Conclusions: perinatal complications were more frequent in asthmatic pregnant patients who required hospital care for the acute exacerbations. Chronic asthmatic patients in reproductive age should be advised before pregnancy about the prophylactic measures to reduce the incidence of acute crises and exacerbations during pregnancy should be treated promptly.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(7):485-489
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000700009
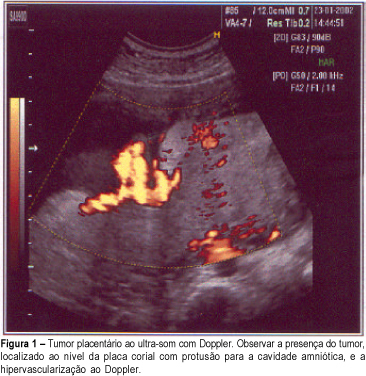
The most frequently nontrophoblastic tumor of the placenta found is chorioangioma, with an incidence of about 1%. When they are small, they do not significantly affect the fetus, but the large ones can cause intrauterine growth restriction, polyhydramnios, premature delivery, congestive heart failure and fetal death. The authors report a case of chorioangioma in a 28-year-old woman, second gestation, whose diagnosis was established at the 32nd week by ultrasound and confirmed by the anatomopathological examination. Ultrasonography evaluations showed chronic fetal distress and the delivery was performed at 36 weeks. The newborn results were satisfactory with Apgar 9-10 and fetal weight 2.460 g.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(5):301-306
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000500003
Purpose: to compare the outcome of pregnancies with and without threatened abortion presenting alive embryo/fetus between 6 and 13 weeks at sonographic evaluation. Method: this was a retrospective case-control study, carried out from February 1998 to December 1999. Criteria for inclusion were: topic and single pregnancy; embryo/fetus cardiac activity present in the ultrasound scan; gestational age between 6 weeks and 13 weeks and 6 days, absence of fetal anomalies, absence of attempt of abortion by drugs or manipulation, absence of maternal disease, known pregnancy result. A total of 1531 pregnancies were examined, of which 258 with threatened abortion (case group) and 1273 without threatened abortion (control group). The two groups were compared regarding outcome such as: abortion, stillbirth, prematurity and intrauterine growth restriction. Results: the percentage of abortion (11,7%) and prematurity (17,8%) were higher in the group with threatened abortion (p<0.001 and p=0.026, respectively). The frequency of stillbirth and intrauterine growth restriction did not differ significantly between the groups.Conclusion: threatened abortion with alive embryo/fetus in 6- to 13- week gestation presented a higher abortion risk and subsequent prematurity.