Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(10):482-491
10-01-2016
Identify factors associated with infant mortality by a hierarchical model based on socioeconomic, health care, obstetric and biological determinants in a northeastern Brazilian capital.
Observational, retrospective cohort study based on secondary data of births and deaths of infants of mothers living in the city of Teresina.
Based on the distal level of determination of infant mortality, the characteristics that remained statistically significant were maternal age, maternal education and maternal occupation (p< 0.001). In the intermediate level, all variables were statistically significant, particularly the type of pregnancy and delivery (p< 0.001). The gender of the baby was the proximal level feature that had no significant association with the outcome, while the other variables of this level had association (p< 0.001).
This study evidenced that, in addition to biological factors, socioeconomic status and maternal and child health care are important to determine infant mortality.
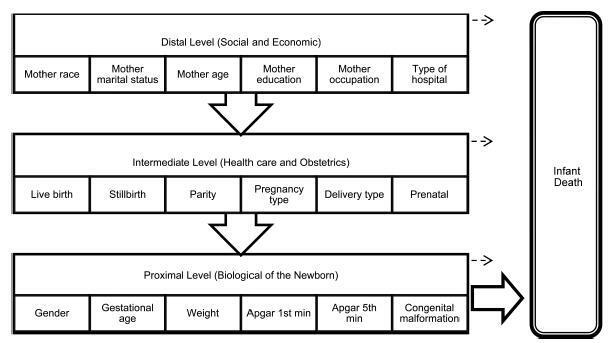
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(7):303-309
07-01-2014
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005012
To identify spatial patterns of neonatal mortality distribution in the micro regions of São Paulo State and verify the role of avoidable causes in the composition of this health indicator.
This ecological exploratory study used neonatal mortality information obtained from Information System and Information Technology Department of the Brazilian National Healthcare System (DATASUS) in the period between the years 2007 and 2011. The digital set of micro regions of São Paulo State was obtained from Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE). Moran Indexes were calculated for the neonatal mortality total rate and rate from avoidable causes; thematic maps were constructed with these rates, as well as the difference between them; and the Box Map was built.
The overall neonatal mortality rate was 8.42/1,000 live births and neonatal mortality rate from avoidable causes of 6.19/1,000 live births. Moran coefficients (I) for these rates were significant (p-value<0.05) - for the total rate of neonatal mortality I=0.11 and for mortality from preventable causes I=0.19 -, and neonatal deaths were concentrated in southwest region and the Vale do Paraíba. If preventable causes were abolished, there would be a significant reduction in the average rate of overall neonatal mortality, from 8.42 to 2.23 deaths/1,000 live births, representing a decline of 73%.
This study demonstrated that neonatal mortality rate would be close to the rates of developed countries if avoidable causes were abolished.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(4):171-176
06-30-2009
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000400003
PURPOSE: to apply geoprocessing techniques for the spatial birth profile analysis of each municipality. METHODS: ecological and exploratory study, using data from the Health Information System about born alive babies in 2004, and using geoprocessing techniques. The spatial autocorrelations of the variables: cesarean section, mother's schooling, low birth weight, Apgar score at five minutes, prematurity, number of medical appointments and adolescent mothers, besides the map with the index of human development were estimated. For the detection of spatial events aggregates, Moran's I M statistics, through the program Terra View 3.13 (developed by INPE and available to the public) was used. Spatial maps with those variables were built, and Pearson's correlation coefficients, estimated. RESULTS: results have shown that the rate of born alive babies, from mothers with school level over primary school and from cesarean sections, presented a spatial pattern visually identifiable and significant spatial self-correlation. Low birth weight, prematurity, Apgar score, number of pre-natal appointments and adolescent mothers have presented a random spatial pattern, showing that, in this analysis scale, those markers have not discriminated the risk groups, despite their unquestionable predictive value for children's morbidity-mortality at individual level. There has been a positive correlation between cesarean section and schooling, and between cesarean section and human development index; and a negative correlation between adolescent mothers and human development index, with statistical significance (p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: this methodology has allowed us to identify spatial clusters for the variables cesarean section and mother's schooling, besides deepening our knowledge on birth profile in the municipalities, presenting good potential on how to direct actions for specific areas.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(3):130-136
03-06-2005
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000300006
PURPOSE: to analyze birth weight in a cohort of newborns for the year 2000, in Goiânia, by determining the coefficient of mortality and neonatal survival probability, stratified by categories of birth weight, and also, through the identification of factors associated with low birth weight (LBW). METHODS: a retrospective cohort study, made possible by the linkage of data from the ISM (Information System on Mortality) and ISLB (Information System on Live Births) files. Coefficients of neonatal mortality were calculated for the categories of birth weight and a neonatal survival probability chart was constructed with the help of linear regression analysis. Risk factors for LBW were identified by univariate analysis (RR) and logistic regression analysis, and the level of significance was set at 5%. RESULTS: the incidence of LBW was 6.9% and 140 (66.8%) neonatal deaths took place in this group. Thirty percent of these deaths occurred in the 1,500-2,500 g weight bracket. The following risk factors were identified for LBW: preterm pregnancy, presence of congenital malformations, mothers at the extreme ages for reproduction, mothers living in the northwestern region of the city, insufficient prenatal appointments with the doctor, delivery in a public hospital, and female babies. CONCLUSION: Goiânia had an incidence of LBW which is comparable to that of developed countries and coefficients of neonatal mortality by category of weight were below those found for those countries. These results recommend that we pay attention to: prematurity, public hospitals, and the northwestern region of Goiânia.