-
Original Article01-23-2022
Comparison of the Effects of GMCSF-Containing and Traditional Culture Media on Embryo Development and Pregnancy Success Rates
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(11):1047-1051
Abstract
Original ArticleComparison of the Effects of GMCSF-Containing and Traditional Culture Media on Embryo Development and Pregnancy Success Rates
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(11):1047-1051
Views162Abstract
Objective
The use of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF)-containing medium, which is a commercial medium that is used for cultivation of embryos in in vitro fertilization (IVF) treatments, has been suggested to increase the efficiency of this procedure in patients with previous multiple unsuccessful attempts. In this retrospective study, we analyzed GM-CSF-containing embryo culture media compared with traditional culture media in terms of development of embryos, pregnancy, and ongoing pregnancy success and live birth rates.
Methods
This is a prospective case control study conducted in a single center. A total of 131 unexplained infertility patients were included in the study. A cohort of 69 patients whose embryos were cultured in GM-CSF-containing medium and a control group of 62 age-matched patients whose embryos were cultured in conventional Sage One Step medium were included in the study. The major study outcomes were achievement of pregnancy and ongoing pregnancy rate at 12 weeks of gestation.
Results
The pregnancy and ongoing pregnancy rates of the patients whose embryos were cultured in GM-CSF-containing medium were 39.13% and 36.23%, respectively. These were higher than the rates of the control group, which were 30.65% and 29.03%, respectively, although this difference was not statistically significant. In addition, the 5th-day embryo transfer percentage in the GM-CSF group was higher than in the control group (34.78% versus 27.4%).
Conclusion
The main findings of our study were that there was no difference between the GM-CSF-enhanced medium and the control group in terms of our major study outcomes. However, blastomere inequality rate and embryo fragmentation rates were lower in the GM-CSF group.
Key-words Embryo cultureEmbryo transfergranulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factorIn vitro fertilizationSee more -
Original Article05-16-2022
One Plus One is Better than Two: An Approach Towards a Single Blastocyst Transfer Policy for All IVF Patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(6):578-585
Abstract
Original ArticleOne Plus One is Better than Two: An Approach Towards a Single Blastocyst Transfer Policy for All IVF Patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(6):578-585
Views213See moreAbstract
Objective
It is known that the single embryo transfer (SET) is the best choice to reduce multiples and associated risks. The practice of cryopreserving all embryos for posterior transfer has been increasingly performed for in vitro fertilization (IVF) patients at the risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome or preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy. However, its widespread practice is still controverse. The aim of this study was to evaluate how effective is the transfer of two sequential SET procedures compared with a double embryo transfer (DET) in freeze-only cycles.
Methods
This retrospective study reviewed 5,156 IVF cycles performed between 2011 and 2019, and 506 cycles using own oocytes and freeze-only policy with subsequent elective frozen-thawed embryo transfers (eFET) were selected for this study. Cycles having elective SET (eSET, n = 209) comprised our study group and as control group we included cycles performed with elective DET (eDET, n = 291). In the eSET group, 57 couples who had failed in the 1st eSET had a 2nd eFET, and the estimated cumulative ongoing pregnancy rate was calculated and compared with eDET.
Results
After the 1st eFET, the ongoing pregnancy rates were similar between groups (eSET: 35.4% versus eDET: 38.5%; p =0.497), but the estimated cumulative ongoing pregnancy rate after a 2nd eFET in the eSET group (eSET + SET) was significantly higher (48.8%) than in the eDET group (p < 0.001). Additionally, the eSET +SET group had a 2.7% rate of multiple gestations, which is significantly lower than the eDET group, with a 30.4% rate (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
Our study showed the association of freeze-only strategy with until up to two consecutive frozen-thawed eSETs resulted in higher success rates than a frozenthawed DET, while drastically reducing the rate of multiple pregnancies.
-
Original Article04-08-2022
Protective Effects of Platelet-rich plasma for in vitro Fertilization of Rats with Ovarian Failure Induced by Cyclophosphamide
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):161-168
Abstract
Original ArticleProtective Effects of Platelet-rich plasma for in vitro Fertilization of Rats with Ovarian Failure Induced by Cyclophosphamide
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):161-168
Views221Abstract
Objective
Premature ovarian insufficiency (POI) contributes significantly to female infertility. Cyclophosphamide (CYC has adverse effects on folliculogenesis. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is an autologous product rich in many growth factors. We evaluated the protective effect of PRP on in vitro fertilization in female rats with CYC-induced ovarian damage.
Methods
Twenty-eight adult female Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into four groups. Group 1 (control-sodium chloride 0.9%; 1 mL/kg, single-dose intraperitoneal [IP] injection); group 2 (CYC), 75mg/kg, single-dose IP injection and sodium chloride 0.9% (1mL/kg, single-dose IP injection); group 3 CYC plus PRP, CYC (75 mg/kg, single-dose and PRP (200 μl, single-dose) IP injection); and group 4 (PRP, 200 μl, singledose IP injection).
Results
In the comparisons in terms of M1 and M2 oocytes, it was observed that the CYC group presented a significantly lower amount than the control, CYC/PRP, and PRP groups. (for M1, p=0.000, p=0.029, p=0.025; for M2, p=0.009, p=0.004, p=0.000, respectively). The number of fertilized oocytes and two-celled good quality embryos was found to be statistically significant between the CYC and control groups, CYC+PRP and PRP groups (p=0.009, p=0.001, p=0.000 for oocytes, respectively. For embryos; p=0.016, p=0.002, p=0.000).
Conclusion
Platelet-rich plasma can protect the ovarian function against damage caused by CYC, and, in addition, it improves oocyte count and the development of embryos as a result of oocyte stimulation during the IVF procedure.
Key-words CyclophosphamideIn vitro fertilizationOvaryplatelet-rich plasmapremature ovarian insufficiencySee more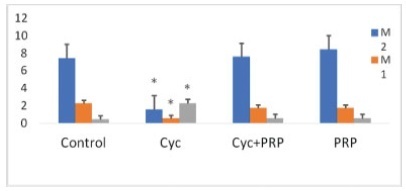
-
Original Article03-08-2021
The Graduated Embryo Score of Embryos from Infertile Women with and without Peritoneal Endometriosis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(1):28-34
Abstract
Original ArticleThe Graduated Embryo Score of Embryos from Infertile Women with and without Peritoneal Endometriosis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(1):28-34
Views152See moreAbstract
Objective
To determine embryo quality (mean graduated embryo score [GES]) in infertile patients with endometriosis undergoing in vitro fertilization with embryo transfer (IVF-ET) compared with infertile patients without endometriosis.
Methods
A case-control study was performed comparing 706 embryos (162 patients) divided into 2 groups: 472 embryos derived from patients without endometriosis (n= 109, infertile patients with tubal infertility) and 234 embryos from patients in the study group (n= 53, infertile patients with peritoneal endometriosis). All patients were subjected to IVF using an oestradiol-antagonist-recombinant follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) protocol for ovarian stimulation. Themean GESwas performed to evaluate all embryos at 3 points in time: 16 to 18 hours, 25 to 27 hours, and 64 to 67 hours. Embryo evaluation was performed according to the following parameters: fragmentation, nucleolar alignment, polar body apposition, blastomere number/morphology, and symmetry. The primary outcomemeasure was the mean GES score.We also compared fertilization, implantation, and pregnancy rates.
Results
Although the number of embryos transferred was greater in patients with endometriosis than in the control group (2.38 ± 0.66 versus 2.15 ± 0.54; p= 0.001), the meanGESwas similar inbothgroups (71 ± 19.8 versus 71.9 ± 23.5; p= 0.881). Likewise, the fertilization ratewas similar in all groups, being 61% in patients with endometriosis and 59% in the control group (p= 0.511). No significant differences were observed in the implantation (21% versus 22%; [p= 0.989]) and pregnancy rates (26.4% versus 28.4%; p= 0.989).
Conclusion
Embryo quality measured by the mean GES was not influenced by peritoneal endometriosis. Likewise, the evaluated reproductive outcomes were similar between infertile patients with and without endometriosis.
-
Case Report04-22-2020
A Rare Case of Bilateral Tubal Ectopic Pregnancy Following Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection-Embryo Transfer (ICSI-ET)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(3):165-168
Abstract
Case ReportA Rare Case of Bilateral Tubal Ectopic Pregnancy Following Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection-Embryo Transfer (ICSI-ET)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(3):165-168
Views180Abstract
Bilateral tubal ectopic pregnancy is a very rare form of ectopic pregnancy. The incidence is higher in women undergoing assisted reproductive techniques or ovulation induction. We report the case of bilateral tubal ectopic pregnancy. The patient was 30 years old and had a 3-year history of infertility; she was referred to the in-vitro fertilization (IVF) program because of tubal factor infertility. A pregnancy resulted from the transfer of two embryos during an artificial cycle. Despite the increase in β-hCG values during the follow-up, 22 days after the embryo transfer, the β-hCG levels were 2,408 U/L and the serum progesterone (P4) level was 10.53 ng/ml. After application with methotrexate, β-hCG levels did not decrease effectively. Moreover, the sonographic screening revealed a suspicious bilateral tubal focus for ectopic pregnancy. A mini-laparotomy was performed and a bilateral tubal pregnancy was found. In the case of unilateral tubal pregnancy after the transfer of two embryos, the situation of the other tube should be systematically checked and β-hCG levels should be monitored.
Key-words assisted reproductive technologybilateral tubal ectopic pregnancyIn vitro fertilizationMethotrexateSee more -
Original Article09-16-2019
Assisted Reproductive Technologies in Latin America and Europe: a Comparative Analysis of Reported Databases for 2013
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(8):493-499
Abstract
Original ArticleAssisted Reproductive Technologies in Latin America and Europe: a Comparative Analysis of Reported Databases for 2013
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(8):493-499
Views159Abstract
Objective
To compare the Latin American and European assisted reproductive technology (ART) registries regarding data accessibility and quality, treatment utilization, effectiveness, safety, and quality of services.
Methods
We performed an ecological study using data from scientific publications of Latin American and European registries that report cycles initiated during 2013 (the most recent registries available until December of 2017). The summarized data are presented as frequencies, percentages, minimum-maximum values, and absolute numbers.
Results
Reporting clinics and cycle treatments were unevenly distributed between the participating countries for both registries, although access to ART is 15 times greater in Europe. In Latin America, individual services participate voluntarily reporting started cycles until cancellation, birth or miscarriage, while in Europe it varied among countries. It makes the data available from Latin America more uniform, although lesser representative when compared with European ones, given that reporting is compulsory formost countries. The cumulative live birth rate was better in Latin America. Female age, use of intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), cycles with transfer of ≥ 3 embryos, as well as multiple pregnancy rates were greater in the Latin American Register of Assisted Reproduction (RLA, in the Portuguese acronym). Assisted reproductive technology complications, such as ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, hemorrhage, and infections were also higher in LatinAmerica, although they are extremely uncommon in both regions.
Conclusion
Both regions have points to improve in the quality of their reports. Latin America has produced a more uniform reporting, their clinical results are generally
Key-words Artificial inseminationassisted reproductive techniqueIn vitro fertilizationintracytoplasmic sperm injectionregistriesSee more -
Case Report06-27-2019
In Vitro Fertilization and Vasa Previa: A Report of Two Cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(5):348-351
Abstract
Case ReportIn Vitro Fertilization and Vasa Previa: A Report of Two Cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(5):348-351
Views184See moreAbstract
Vasa previa (VP) is a dangerous obstetric condition associated with perinatal mortality and morbidity. In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a risk factor for VP due to the high incidence of abnormal placentation. The diagnosis should be made prenatally, because fetal mortality can be extremely high. We report two cases to demonstrate the accuracy of transvaginal ultrasound in the prenatal diagnosis of VP. A 40-year-old primiparous Caucasian woman with IVF pregnancy was diagnosed with VP at 29 weeks of gestation and was hospitalized for observation at 31 weeks of gestation. She delivered a male newborn weighing 2,380 g, with an Apgar score of 10 at 5 minutes, by elective cesarean section at 34 weeks + 4 days of gestation, without complications. A 36-yearold primiparous Caucasian woman with IVF pregnancy was diagnosed with placenta previa, bilobed placenta increta and VP. The cord insertion was velamentous. She was hospitalized for observation at 26 weeks of gestation. She delivered a female newborn weighing 2,140 g, with an Apgar score of 9 at 5 minutes, by emergency cesarean section at 33 weeks + 4 days of gestation due to vaginal bleeding. The prenatal diagnosis of VP was associated with a favorable outcome in the two cases, supporting previous observations that IVF is a risk factor for VP and that all IVF pregnancies should be screened by transvaginal ultrasound.
-
Review Article10-01-2018
Effect of the Air Filtration System Replacement on Embryo Quality in the Assisted Reproduction Laboratory
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(10):625-630
Abstract
Review ArticleEffect of the Air Filtration System Replacement on Embryo Quality in the Assisted Reproduction Laboratory
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(10):625-630
Views136See moreAbstract
Improving infrastructural conditions of the in vitro fertilization laboratory, such as the air quality, has profound positive effects on embryo culture. Poor environmental conditions reduce the rate of embryo formation and, therefore, of pregnancy. This review article presents important publications regarding the impact of air quality in human reproduction laboratories on embryo quality, pregnancy success, and live births. The studies demonstrate that the replacing the air filtration system improves significantly the environmental air quality, and, consequently, improves laboratory parameters, such as the fertilization rate, the number of blastocysts, the embryo implantation rate, and the number of live births. On the other hand, improving air quality decreases the number of abortions. Therefore, environmental parameters that improve embryo quality and increase healthy child birth ratesmust be themain targets for the assisted reproduction laboratory quality control.


