-
Case Report
Primary Amenorrhea Associated with Hyperprolactinemia in Polyglandular Autoimmune Syndrome Type II: A Case Report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(7):425-429
07-01-2018
Summary
Case ReportPrimary Amenorrhea Associated with Hyperprolactinemia in Polyglandular Autoimmune Syndrome Type II: A Case Report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(7):425-429
07-01-2018Views90Abstract
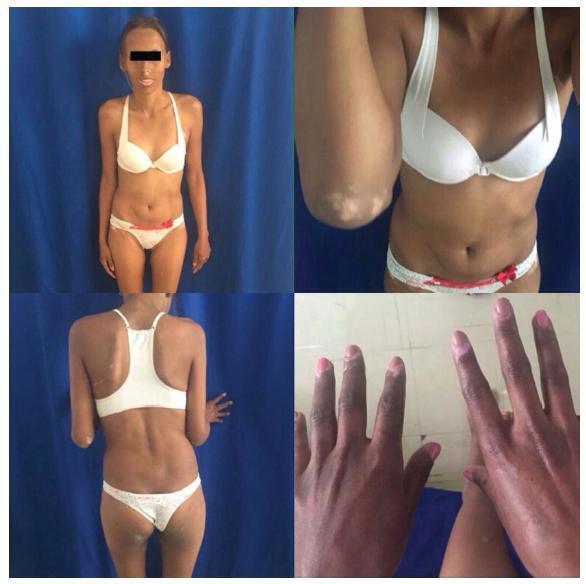
Polyglandular autoimmune syndrome type II (PGA-II) is a rare immunoendocrinopathy syndrome characterized by the occurrence of autoimmune Addison disease along with diabetes mellitus type 1 and/or autoimmune thyroid disease. Here, we report the case of a 23-year-old female with PGA-II who was followed up at the dermatology and endocrinology clinics of the Universidade Federal do Triângulo Mineiro, located in the state of Minas Gerais, Brazil. First, the patient presented diffuse skin hyperpigmentation, vitiligo; and in sequence, due to vomiting, appetite and weight loss, hypoglycemia, amenorrhea, and galactorrhea, the patient was then diagnosed with PGA-II. The patient also presented intense hyperprolactinemia due to primary hypothyroidism. The late diagnosis of PGA-II is frequent because the disorder is uncommon and has non-specific clinical manifestations. This report emphasizes the significance of a timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment to reduce morbidity and mortality associated with these diseases, especially Addison disease. The present study reports a rare case of a patient with PGA-II with primary amenorrhea associated with hyperprolactinemia.
Key-words Amenorrheaautoimmune polyendocrinopathiesautoimmune polyglandular syndromeHyperprolactinemiatype IIvitiligoSee morePlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 1
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 1157
- Abstract Views: 189
- Captures
- Readers: 12
-
Artigos Originais
Macroprolactinemia and intermediate hyperprolactinemia: clinical manifestations and image
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(2):92-96
03-15-2012
Summary
Artigos OriginaisMacroprolactinemia and intermediate hyperprolactinemia: clinical manifestations and image
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(2):92-96
03-15-2012DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000200009
Views99See morePURPOSE: To characterize patients with indeterminate values of hyperprolactinemia (PEG test for the identification of macroprolactinemias with recovery between 30 and 65%) (PRLi) or macroprolactinemia (PRLm), in relation to clinical characteristics, such as the presence or absence of symptoms, as well as their intensity and variation, and the presence or absence of central nervous system tumors. METHODS: This is a cross-sectional retrospective survey of records of 24 patients with hyperprolactinemia, in reproductive ages, with prolactin >25 ng/dL. Eleven women with PRLm and 13 with PRLi were included. Records from the two groups were extracted for analysis: age, parity, body mass index, presence of galactorrhea, infertility, and central nervous system tumor. Anthropometrics data were expressed as mean and standard deviation. To compare groups regarding the presence of central nervous system tumor, galactorrhea, as well as infertility we used the Student's t-test. RESULTS: Galactorrhea was more prevalent in patients with PRLi (p=0.01). Seventy percent of women with PRLi presented pituitary tumor (microprolactinoma), whereas this finding was evident in 17% of the PRLm Group (p=0.04). Among the patients with and PRLm PRLi, nine were not investigated with the image of the central nervous system because they have low levels of prolactin (five carriers and four PRLm PRLi). There were no significant differences regarding the occurrence of infertility or irregular menstrual cycles between groups. DISCUSSION: Women with intermediate hyperprolactinemia present more galactorrhea symptoms as well as central nervous system tumors than women with macroprolactinemia.
-
Artigos Originais
Hyperprolactinemia effects on the female mice uterus during proestrous
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(8):385-390
10-09-2009
Summary
Artigos OriginaisHyperprolactinemia effects on the female mice uterus during proestrous
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(8):385-390
10-09-2009DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000800003
Views126See morePURPOSE: to evaluate the effect of hyperprolactinemia induced by metoclopramide on the endometrium and myometrium of female mice in the proestrus phase. METHODS: 24 female mice were randomly divided in two groups: CtrG/control and ExpG/treated with metoclopramide (6.7 mg/g daily). After 50 days, the animals were sacrificed in the proestrus phase, and the blood was collected to determine the levels of estradiol, progesterone and prolactin. The uterine horns were removed, fixed in 10% formaldehyde and processed before being included in paraffin. Slices of 4 µm were stained by hematoxylin and eosin (H/E). In the morphological analysis, a Carl Zeiss light microscope, with objectives varying from 4 to 400 X was used for each histological slice characterization. In the morphometrical analysis, the superficial epithelium, the lamina propria and the myometrium thickness were evaluated, with the help of an image analyzer (AxionVision - Carl Zeiss) attached to the light microscope (Carl Zeiss). The statistical analysis was done by ANOVA, followed by the Wilcoxon test. P-value was considered as significant, when <0.05. RESULTS: our findings have shown an increase in the seric levels of prolactin (295.6±38.0 ng/mL) and significant decrease in the progesterone levels (11.3±0.9 ng/mL) in the ExpG, as compared to the CtrG (45.5±5.2 ng/mL and 18.2±1.6 ng/mL, respectively; p<0.001). Concerning the seric level of estradiol, significant differences between the groups were not obtained (ExpG=119.1±12.3 pg/mL and CtrG=122.7±8.4 pg/mL; p=0.418). The morphological study has shown that the uterus from the ExpG presented the endometrium with more developed superficial epithelium and lamina propria, as compared to the CtrG, the same happening with the myometrium. The thickness morphometrical values of the luminal epithelium (8.0±1.1 µm) and endometrium (116.2±21.1x10² µm) from the CtrG were lower than the ones from the ExpG (10.2±0.8 µm and 163.2±23.3x10² µm, respectively) with p<0.05. Nevertheless, data obtained in the myometrium have not shown significant differences between the groups (CtrG=152.2±25.2x10² µm and ExpG=140.8±18.0x10² µm). CONCLUSIONS: data have shown that hyperprolactinemia induced by metoclopramide determines endometrial proliferation and interferes with the ovarian function, mainly in the progesterone production.
-
Artigos Originais
Effects of metoclopramide-induced hyperprolactinemia on the lacrimal gland: experimental study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(9):524-528
01-30-2005
Summary
Artigos OriginaisEffects of metoclopramide-induced hyperprolactinemia on the lacrimal gland: experimental study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(9):524-528
01-30-2005DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000900004
Views107See morePURPOSE: to evaluate the morphological changes in murine lacrimal glands by metoclopramide-induced hyperprolactinemia during the proestrus phase or pregnancy. METHODS: forty adult mice were divided into two groups: CTR1 (control) and MET1 (treated with metoclopramide). After fifty days, half of the mice were sacrificed. The remaining animals were mated, and then labeled as pregnant controls (CTR2). Part of these animals were treated with metoclopramide and constituted the metoclopramide-treated pregnant (MET2) group. The CTR2 and MET2 groups were sacrificed on the 6th day of pregnancy. The blood was collected for determination of the hormonal levels of estradiol and progesterone by a chemoluminescent method. The lacrimal glands were then removed, fixed in 10% formaldehyde and stained with HE. The morphometric analysis was performed using the Axion Vision program (Carl Zeiss) to measure acinar nuclear and cellular volumes. RESULTS: the nuclear and cellular volumes of the lacrimal glands in the MET1-(152.2±8.7; 6.3±1.6 µm³) and MET2-(278.3±7.9; 27.5±0.9 µm³) treated groups were lower than those in CTR1 (204.2±7.4; 21.9±1.3 µm³) and CTR2 (329.4±2.2; 35.5±2.0 µm³), respectively. There was a significant hormonal level reduction in the animals that received metoclopramide compared to controls (CTR1: estradiol = 156.6±42.2 pg/ml; progesterone = 39.4±5.1 ng/ml; MET1: estradiol = 108.0±33.1 pg/ml; progesterone = 28.0±6.4 ng/ml; CTR2: estradiol = 354.0±56.0 pg/ml; progesterone = 251.0±56.0 ng/ml; MET2: estradiol = 293.0±43.0 pg/ml, progesterone = 184.0±33.0 ng/ml). CONCLUSION: metoclopramide-induced hyperprolactinemia produced morphological signs of reduction of cellular activity in lacrimal glands during the proestrus phase and pregnancy. It is hypothesized that this effect might be related to the hyperprolactinemia-induced decrease in the hormonal production of estrogen and progesterone.
-
Relato de Casos
Macroprolactinoma resistant to dopamine agonists: a case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(8):663-667
11-23-2004
Summary
Relato de CasosMacroprolactinoma resistant to dopamine agonists: a case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(8):663-667
11-23-2004DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000800011
Views92See moreMacroprolactinomas are benign prolactin-secreting pituitary tumors, causing amenorrhea, galactorrhea and gonadal dysfunction. Clinical treatment with dopamine agonists is the first-choice therapy. Surgery is indicated for the rare cases that are resistant to clinical treatment, when there is intolerance to the medication, or intratumoral hemorrhage is detected. We describe the case of a female patient with macroprolactinoma submitted to two surgical procedures and resistant to clinical treatment, with unusual evolution.