Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(10):925-929
Placenta accreta spectrum (PAS) is a cause of massive obstetric hemorrhage and maternal mortality. The application of family-centered delivery techniques (FCDTs) during surgery to treat this disease is infrequent. We evaluate the implementation of FCDTs during PAS surgeries.
This was a prospective, descriptive study that included PAS patients undergoing surgical management over a 12-month period. The patients were divided according to whether FCDTs were applied (group 1) or not (group 2), and the clinical outcomes were measured. In addition, hospital anesthesiologists were surveyed to evaluate their opinions regarding the implementation of FCDTs during the surgical management of PAS.
Thirteen patients with PAS were included. The implementation of FCDTs during birth was possible in 53.8% of the patients. The presence of a companion during surgery and skin-to-skin contact did not hinder interdisciplinary management in any case.
Implementation of FCDTs during PAS care is possible in selected patients at centers with experience in managing this disease.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(2):91-96
To analyze the factors associated with the prevalence of exclusive breastfeeding (EBF) for up to six months in mother/infant binomials cared for at a usual-risk maternity hospital.
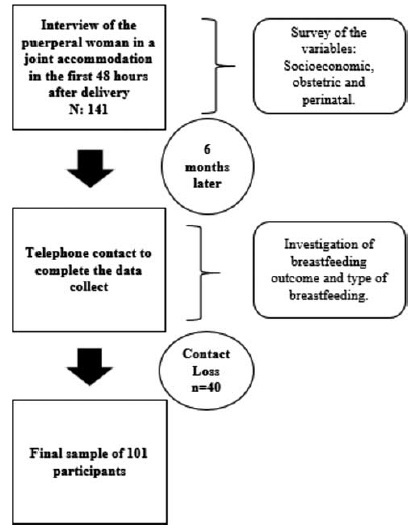
The present is a descriptive, longitudinal, prospective, quantitative study. Socioeconomic, obstetric and perinatal variables from 101 mother/infant binomials in a Public Maternity Hospital in the city of Curitiba, state of Paraná, Brazil, were investigated during hospitalization after delivery and 6 months after birth. For the statistical analysis, the Chi-squared test was used. The variables that showed values of p < 0.25 for the Chi-squared test were also submitted to an odds ratio (OR) analysis.
The prevalence (42.6%) of EBF was observed. Most women (93.1%) had had more than 6 prenatal consultations, and the variables maternity leave and support to breastfeeding were associated with EBF. Support to breastfeeding by professionals and family members increased 4-fold the chance of maintenance of EBF (OR = 0.232; 95% confidence intercal [95%CI]: 0.079 to 0.679; p = 0.008). Cracked nipples were the biggest obstacle to breastfeeding, and low milk production was the main responsible factor for weaning.
The encouragement of breastfeeding and the mother’s stay for a longer period with the child contributed to the maintenance of EBF until the sixth month of life of the infant.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(7):517-525
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000700003
PURPOSE: to evaluate the experience of implementation of the Brazilian Prenatal and Birth Humanization Program (PHPN) in 2001 and 2002, through a population descriptive study. METHODS: the study was performed through documental analysis and using data generated by SISPRENATAL, comparatively evaluating the indicators concerning criteria for prenatal follow-up in different states, regions and period. RESULTS: until the end of 2002, 3983 municipalities joined the Program (72% adhesion) and, among them, 71% reported results, constituting a data base of 720,871 women. In 2002 only 28% of the pregnant women were already registered, 25% before 120 days of pregnancy. Nearly 22% of the women had six prenatal visits, 6% had the post-partum visit and the compulsory tests performed, only 4% had also the HIV test and were vaccinated against tetanus, and 12% had two examinations performed for syphilis. There were important regional variations, generally showing better indicators for the Southeast and South regions. CONCLUSIONS: although the indicators of quality of care showed an improvement from 2001 to 2002, the recorded low percentages attest the need for permanent evaluations and new interventions with the aim of improving the quality of this care, especially in the North and Northeast regions.