Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(5):248-256
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000500004
PURPOSE: to estimate the prevalence of HPV and its genotypes in HIV-infected and non-infected women, using the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) technique. METHODS: a sectional study with 79 enrolled women: a study group, with 41 HIV-infected women, and a control group, with 38 non-infected women attended at a Basic Health Unit. All were submitted to a serologic test for the detection of HIV and spontaneously looked for gynecological attendance at those units, for the first time. They answered a standard questionnaire and were submitted to a gynecological examination with a cervical swab and specimen for the detection of DNA-HPV and its genotypes. Statistical analysis was performed using Kruskal-Wallis, chi2 or Fisher's exact tests. Statistical significance was considered at p<0.05. RESULTS: the demographic characteristics, obstetric and gynecological previous history were similar in both groups except for previous STD, but different as to the gynecological examination and cervical cytological analysis. The presence of DNA-HPV was significantly different (p<0.05) in the two groups. Among HIV-infected patients, 73.2% presented DNA-HPV positive results, as compared with 23.8% of non-infected women (OR=8.79; 95% IC: 2.83 28.37). Concerning HPV genotypes, there was no clear predominance of a specific HPV subtype in the HIV-infected or in the HIV non-infected groups, and the frequency of unidentified types was similar in both groups. Non-significant predominance of HPV multiple infections (p>0.05) was detected in the HIV-infected women (50.0%) and the most frequently found combination was of types 6, 11 and 16. HPV simple infection occurred in 66.6% of HIV-non-infected patients. The most frequent type found in both groups was 16, representing 44% of all the simple infections in both groups. CONCLUSIONS: HIV-infected women showed higher DNA-HPV prevalence in the uterine cervix, as compared to non-infected women. There was no difference in the predominance of specific types of HPV when both groups were compared. There was a tendency to HPV multiple infections in the HIV-infected women, whereas simple infection predominated in the non-infected patients.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(2):97-102
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000200003
PURPOSE: to correlate the type of cervical lesion diagnosed by Pap smear with CD4 cell counts and HIV-RNA viral load in HIV-positive patients. METHODS: one hundred and fifteen HIV patients were evaluated retrospectively in the present study, during the period from January 2002 to April 2003, at a university hospital. Eighty-three patients presented cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) in Pap smear, in comparison with thirty-two with no lesions. Patients were divided into three groups, according to CD4 counts: CD4 more than 500 cells/mm³, between 200 and 500 cells/mm³, and less than 200 cells/mm³, and other three groups, according to HIV viral load: less than 10,000 HIV-RNA copies/mL, between 10,000 and 100,000 HIV-RNA copies/mL, or more than 100,000 HIV-RNA copies/mL. Correlation was investigated by the Fisher test. RESULTS: of the eighty-three patients with CIN, 73% presented CD4 counts less than 500 cells/mm³. In all CD4 groups, more than 50% of the patients presented CIN. According to the viral load, 71.7% of the patients with less than 10,000 HIV-RNA copies/mL presented CIN I, compared with 11.3% that showed CIN III. In the group with higher viral load (>100.000 HIV-RNA copies/mL), 61.5% showed CIN I and 30.8% presented CIN III. CONCLUSION: association between viral load and CIN was established (p=0.013), which was not observed with CD4 cell counts and CIN. Concomitant cervicovaginal infection was considered a potential confounding factor.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(6):389-395
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000600002
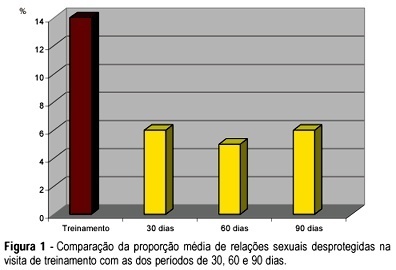
PURPOSE: to evaluate acceptability, adhesion and experience with the use of female condom (FC) among HIV-infected women. METHODS: prospective descriptive study with 76 HIV-infected women under care at CAISM/UNICAMP and Centro Corsini, both in Campinas. After a screening interview and agreeing to participate, the volunteers received a diary to register their intercourses and correspondent use of male condom (MC). After 30 days, they returned to a training visit when the FC was inserted in a pelvic model, also bringing their diary related to the previous cycle, considered a control cycle. A structured questionnaire was used at 30, 60 and 90 days, also with the respective diary on sexual intercourse and use of MC and FC kept for posterior data entry. c², Fisher's exact, McNemar and Friedman tests were applied statistical analysis of paired samples. RESULTS: there was a predominance of young women, with low schooling, living with their partner. Rate of continuity was 52% after 90 days. The use of FC in half the intercourses for each time period remained stable over the 90-day interval. There was a significant reduction in unprotected intercourses (from 14 to 6%), without use of FC or MC, at the end of the period. The initial difficulties in handling the device were overcome. Serodiscordant couples had more protected intercourses than concordant couples, but the difference did not reach statistical significance. Women reporting consistent previous use of MC had more protected sex using FC. CONCLUSIONS: the offer of the female condom was able to reduce unprotected intercourses in HIV-infected women, which were highly motivated and receptive for the new method.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(9):573-577
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000900006
Purpose: to verify the frequency of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) ¾ infected women. Methods: ninety-nine HIV-seropositive women were studied. The diagnosis of the HIV infection was established through two ELISA tests complemented by Western blot test or indirect immunofluorescence test. As control group, 104 women whose ELISA test was not positive were analyzed. The investigation of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia was achieved by association of Pap smear and colposcopy in both groups. In the cases where colposcopy revealed existence of abnormal transformation zones, NIC diagnosis was obtained through colposcopy-guided biopsy complemented or not by conization. Results: cervical intraepithelial neoplasia was found in 15 of the 99 patients (15.2%), and among them there were ten NIC I, one NIC II and four NIC III. Among the 104 women of the control group, four presented cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (3.8%), one being NIC I and three NIC III. Conclusion: the comparative analysis of the results showed that the frequency of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia was significantly higher among those patients infected with HIV.