Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo98
01-23-2025
To determine if maternal erythrocytosis is a risk factor for small-for-gestational age at term at 3,400-m altitude in pregnant women without intercurrent disease.
Analytical study of retrospective cohorts at Cusco, a city at 3,400-m altitude. Our participants were 224 and 483 pregnant women with and without exposure to maternal erythrocytosis, respectively. A logistic regression with the goodness of fit to the proposed model was also performed with the Hosmer and Lemeshow test, evaluating the small-for-gestational-age results with or without exposure to hemoglobin >14.5 g/dl.
The incidence of small-for-gestational-age was 6.9% for this entire cohort. The maternal erythrocytosis during gestation without any maternal morbidity at 3,400-m altitude has an ORa=0.691 (p=0.271) for small-for-gestational-age at term. Inadequate prenatal control has an ORa=2.115 (p=0.016) for small-for-gestational-age compared to adequate prenatal control.
Maternal erythrocytosis in pregnant women without any morbidity is not a risk factor for small-for-gestational-age at 3,400 m-altitude.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo21
03-15-2024
We conducted a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials evaluating the clinical effects of ferric carboxymaltose therapy compared to other intravenous iron in improving hemoglobin and serum ferritin in pregnant women. We also assessed the safety of ferric carboxymaltose vs. other intravenous iron.
EMBASE, PubMed, and Web of Science were searched for trials related to ferric carboxymaltose in pregnant women, published between 2005 and 2021. We also reviewed articles from google scholar. The keywords "ferric carboxymaltose," "FCM," "intravenous," "randomized," "pregnancy," "quality of life," and "neonatal outcomes" were used to search the literature. The search was limited to pregnant women.
Studies related to ferric carboxymaltose in pregnancy were scanned. Observational studies, review articles, and case reports were excluded. Randomized studies in pregnant women involving ferric carboxymaltose and other intravenous iron formulations were shortlisted. Of 256 studies, nine randomized control trials were selected.
Two reviewers independently extracted data from nine selected trials
The final effect size for increase in hemoglobin after treatment was significant for ferric carboxymaltose vs. iron sucrose/iron polymaltose (standard mean difference 0.89g/dl [95% confidence interval 0.27,1.51]). The final effect size for the increase in ferritin after treatment was more for ferric carboxymaltose vs. iron sucrose/iron polymaltose (standard mean difference 22.53µg/L [-7.26, 52.33]). No serious adverse events were reported with ferric carboxymaltose or other intravenous iron.
Ferric carboxymaltose demonstrated better efficacy than other intravenous iron in increasing hemoglobin and ferritin levels in treating iron deficiency anemia in pregnant women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(11):1059-1069
01-23-2022
The aim of this study was to systematically review literature on the use of iron supplements (not including iron derived from diet), increased levels of hemoglobin and/or ferritin, and the risk of developing gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM).
The following databases were searched, from the study's inception to April 2021: PUBMED, Cochrane, Web of Science, Scopus, Embase, Cinahl and Lilacs.
A total of 6,956 titles and abstracts were reviewed, 9 of which met the final inclusion criteria, with 7,560 women in total.
Data extraction was performed by two independent reviewers and disagreements were resolved by a third researcher.
Methodological quality in controlled trials were assessed according to the Cochrane Collaboration tools (ROB-2 and ROBINS-1) and for the observational studies, the National Institutes of Health's (NIH) quality assessment tool was used. Among the 5 observational studies, women with a higher hemoglobin or ferritin level were more likely to develop GDM when compared with those with lower levels of these parameters. Among the 3 randomized clinical trials, none found a significant difference in the incidence of GDM among women in the intervention and control groups. However, we identified many risks of bias and great methodological differences among them.
Based on the studies included in this review, and due to the important methodological problems pointed out, more studies of good methodological quality are needed to better establish the association between iron supplementation and GDM.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):53-59
02-01-2017
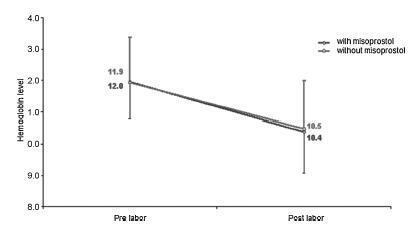
To evaluate blood loss during misoprostol-induced vaginal births and during cesarean sections after attempted misoprostol induction.
We conducted a prospective observational study in 101 pregnant women indicated for labor induction; pre- and postpartum hemoglobin levels were measured to estimate blood loss during delivery. Labor was induced by administering 25 μg vaginal misoprostol every 6 hours (with a maximum of 6 doses). The control group included 30 patients who spontaneously entered labor, and 30 patients who underwent elective cesarean section. Pre- and postpartum hemoglobin levels were evaluated using the analysis of variance for repeated measurements, showing the effects of time (pre- and postpartum) and of the group (with and withoutmisoprostol administration).
Therewere significant differences between pre- and postpartum hemoglobin levels (p < 0.0001) with regard to misoprostol-induced vaginal deliveries (1.6 ± 1.4 mg/dL), non-induced vaginal deliveries (1.4 ± 1.0 mg/dL), cesarean sections after attempted misoprostol induction (1.5 ± 1.0 mg/dL), and elective cesarean deliveries (1.8 ± 1.1 mg/dL). However, the differences were proportional between the groups with and without misoprostol administration, for both cesarean (p = 0.6845) and vaginal deliveries (p = 0.2694).
Labor induction using misoprostol did not affect blood loss during delivery.