-
Review Article
Efficacy of tranexamic acid application in gynecology and obstetrics procedures: a umbrella review of systematic reviews of randomized trials
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo18
04-30-2025
Summary
Review ArticleEfficacy of tranexamic acid application in gynecology and obstetrics procedures: a umbrella review of systematic reviews of randomized trials
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo18
04-30-2025Views48Abstract
Objective:
This umbrella review aimed to synthesize evidence from systematic reviews of clinical trials on the efficacy of tranexamic acid in gynecology and obstetrics procedures.
Methods:
We searched Medline, Embase, SciELO and Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews on March 11, 2024, using the term "tranexamic acid". Four reviewers independently select studies and extract data. We assessed the quality of systematic review and the quality of evidence, using AMSTAR 2 and GRADE tools, respectively.
Results:
Of 651 systematic reviews identified, 16 reviews with 96663 patients were included. The surgical procedures were cesarean section, myomectomy, hysterectomy, and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia surgery. All reviews showed a statistically significant and clinically relevant reduction in intraoperative and post-procedure blood loss, associated with intravenous or topical use of tranexamic acid. Tranexamic acid resulted in a significant reduction in the need for blood transfusions and a less pronounced drop in postoperative hematocrit and hemoglobin levels in cesarean section. Several reviews addressed the same question, but the number of included trials varied substantially, which might indicate flaws in search and selection of studies of these reviews. The quality of systematic reviews was low or critically low, and the quality of evidence was moderate.
Conclusions:
This umbrella review shows that tranexamic acid can reduce blood loss and hemorrhage in gynecology and obstetrics procedures. High quality systematic reviews are still needed.
Key-words Blood transfusionCesarean sectionEfficacyGynecologic surgical procedureshematocritHemorrhageHysterectomyObstetric surgical proceduresTranexamic acidUterine cervical dysplasiauterine myomectomySee more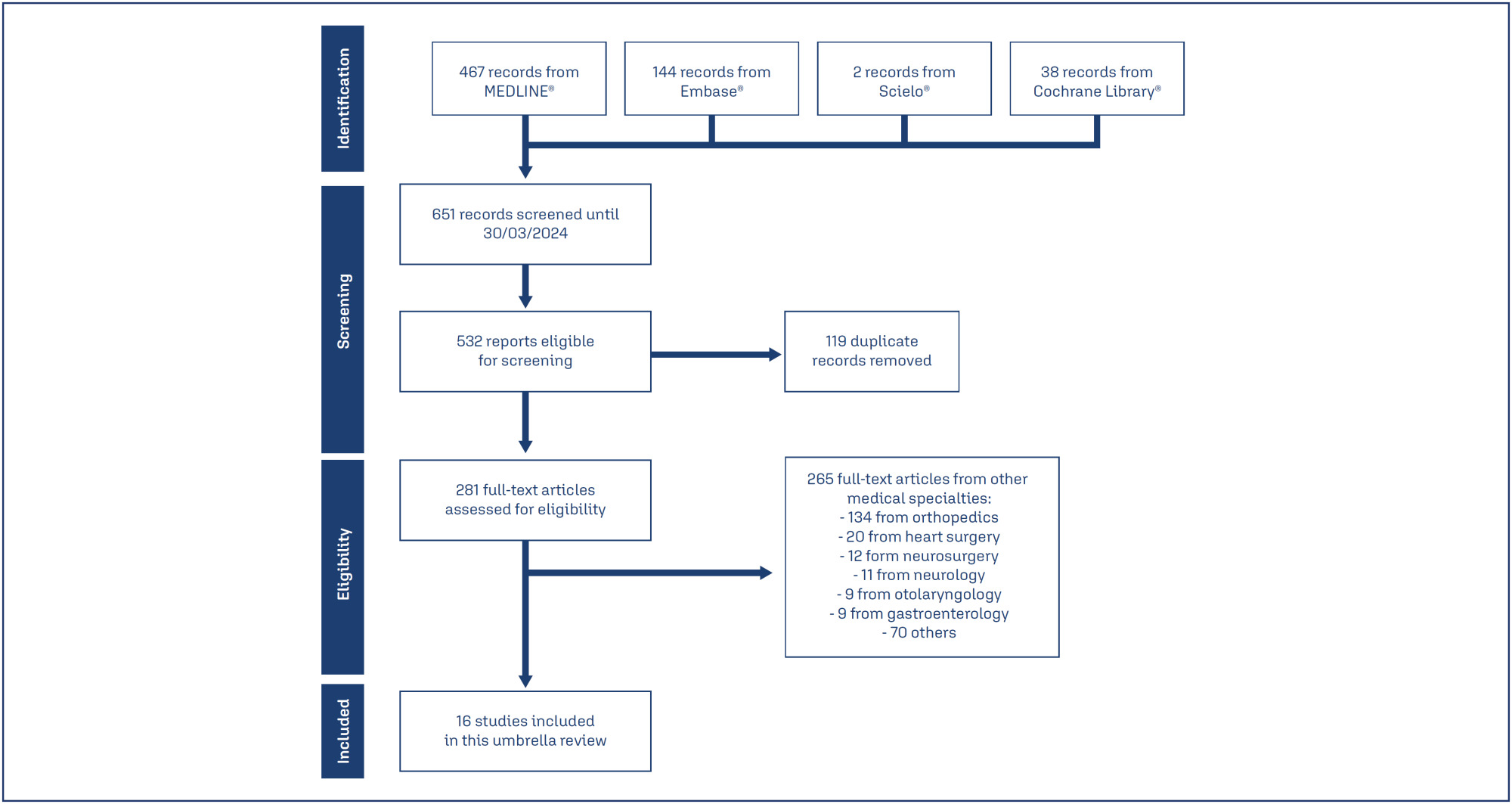
-
Original Article
The top hat procedure does not impact the management of women treated by LEEP in cervical cancer screening
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo44
06-03-2024
Summary
Original ArticleThe top hat procedure does not impact the management of women treated by LEEP in cervical cancer screening
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo44
06-03-2024Views181Abstract
Objective:
To describe Top-hat results and their association with margin status and disease relapse in a referral facility in Brazil.
Methods:
A retrospective study of 440 women submitted to LEEP to treat HSIL, in which 80 cases were complemented immediately by the top hat procedure (Top-hat Group - TH). TH Group was compared to women not submitted to Top-hat (NTH). The sample by convenience included all women that underwent LEEP from January 2017 to July 2020. The main outcome was the histological result. Other variables were margins, age, transformation zone (TZ), depth, and relapse. The analysis used the Chi-square test and logistic regression.
Results:
The TH Group was predominantly 40 and older (NTH 23.1% vs. TH 65.0%, p<0.001). No difference was found in having CIN2/CIN3 as the final diagnosis (NTH 17.0% vs. TH 21.3%, p=0.362), or in the prevalence of relapse (NTH 12.0% vs. TH 9.0%, p=0.482). Of the 80 patients submitted to top hat, the histological result was CIN2/CIN3 in eight. A negative top hat result was related to a negative endocervical margin of 83.3%. A CIN2/CIN3 Top-hat result was related to CIN2/CIN3 margin in 62.5% (p=0.009). The chance of obtaining a top hat negative result was 22.4 times higher (2.4-211.0) when the endocervical margin was negative and 14.5 times higher (1.5-140.7) when the ectocervical margin was negative.
Conclusion:
The top hat procedure did not alter the final diagnosis of LEEP. No impact on relapse was observed. The procedure should be avoided in women of reproductive age.
Key-words Cervical intraepithelial neoplasiaCervix uteriColposcopyConizationElectrosurgeryGynecologic surgical proceduresUterine cervical neoplasmsSee more -
Review Article
Patient positioning in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery: strategies to prevent injuries and improve outcomes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo46
06-03-2024
Summary
Review ArticlePatient positioning in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery: strategies to prevent injuries and improve outcomes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo46
06-03-2024Views207Abstract
Effective patient positioning is a critical factor influencing surgical outcomes, mainly in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery (MIGS) where precise positioning facilitates optimal access to the surgical field. This paper provides a comprehensive exploration of the significance of strategic patient placement in MIGS, emphasizing its role in preventing intraoperative injuries and enhancing overall surgical success. The manuscript addresses potential complications arising from suboptimal positioning and highlights the essential key points for appropriate patient positioning during MIGS, encompassing what the surgical team should or shouldn't do. In this perspective, the risk factors associated with nerve injuries, sliding, compartment syndrome, and pressure ulcers are outlined to guide clinical practice. Overall, this paper underscores the critical role of precise patient positioning in achieving successful MIGS procedures and highlights key principles for the gynecological team to ensure optimal patient outcomes.
Key-words Compartment syndromeGynecologic surgical proceduresIntraoperative complicationsMinimally invasive surgical proceduresNerve injuryPatient positioningpatient safetyPressure ulcerRisk factorsTreatment outcomeSee more -
Artigos Originais
Surgical and non-surgical treatment of vaginal agenesis: analysis of a series of cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(6):274-277
07-13-2012
Summary
Artigos OriginaisSurgical and non-surgical treatment of vaginal agenesis: analysis of a series of cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(6):274-277
07-13-2012DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000600006
Views74See morePURPOSE: This study aimed to evaluate the results of neovaginoplasty by a modified McIndoe-Bannister technique and by the non-surgical Frank technique. METHODS: This retrospective study was conducted on a convenience sample of 25 women with vaginal agenesis undergoing surgical or conservative treatment at an Infant-Pubertal Gynecology Outpatient Clinic. Data were obtained from the medical records. Fifteen women underwent the surgical McIndoe-Bannister modified technique Surgical Group, and 10 women underwent the non-surgical Frank technique Frank Group. The following parameters were considered for comparative analysis between the two samples: vaginometry, surgical and non-surgical complications, and sexual satisfaction after treatment. Sexual satisfaction was assessed by a simple question: How is your sex life? RESULTS: There were differences related to vaginal length before and after performing exercises in both Frank Group (initial vaginal length 2.4±2.0 cm versus 6.9±1.1 cm after treatment, p<0.0001) and Surgical Group (initial vaginal length 0.9±1.4 cm versus 8.0±0.8 cm after treatment, p<0.0001). Increased vaginal length was observed in Surgical Group compared to Frank Group (Frank Group=7.0±0.9 cm versus Surgical Group=8.0±0.8 cm, p=0.0005). Forty percent of Surgical Group women had surgical complications versus no complications with the Frank technique. All women reported to be satisfied with their sexual life. CONCLUSION: The present data indicate that both the surgical and Frank techniques are effective for the treatment of vaginal agenesis, resulting in the construction of a vagina that pewrmits sexual intercourse and sexual satisfaction. The favorable aspects of the Frank technique are related to its low cost and to the low rates of major complications.
-
Artigos Originais
Natural latex (Hevea brasiliensis) mold for neovaginoplasty
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(1):31-35
04-08-2008
Summary
Artigos OriginaisNatural latex (Hevea brasiliensis) mold for neovaginoplasty
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(1):31-35
04-08-2008DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000100006
Views71See morePURPOSE: to evaluate the use of natural latex mold (Hevea brasiliensis) as a modification of McIndoe and Bannister neovaginoplasty in patients presenting Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser (MKRH) syndrome. METHODS: we retrospectively included nine patients presenting MKRH syndrome, who had been submitted to McIndoe and Bannister neovaginoplasty modified by the use of natural latex mold. Neovaginal epithelization and depth, coitus occurrence and satisfaction, and surgical complications were evaluated. RESULTS: five weeks after the procedure, eight patients presented an epithelized 7 to 12 cm deep neovagina. There was one case of complete neovaginal stenosis, because of incorrect use of the mold. After at least one year, the others maintained 4 to 8 cm deep neovaginas and capacity for intercourse, with 66.7% satisfaction. One woman presented precocious rectovaginal fistula and late episodes of uretrovaginal fistulae. Two patients presented distal neovaginal stenosis in long-term follow-up. One of these and the patient with fistulae were submitted to a new procedure. CONCLUSIONS: the use of natural latex mold as a modification of classic neovaginoplasty technique allows the creation of neovaginas morphologically and functionally similar to the normal vagina in patients with vaginal agenesis.
-
Artigos Originais
The control of postpartum hemorrhage with the B-Lynch suture technique: a case series
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(3):120-125
06-21-2007
Summary
Artigos OriginaisThe control of postpartum hemorrhage with the B-Lynch suture technique: a case series
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(3):120-125
06-21-2007DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000300002
Views140PURPOSE: to present a surgical technique for patients submitted to caesarean section, which evolves to medicine refractory hemorrhage. METHODS: a case report study, of which the including criteria were failure in the pharmacological treatment to control post-partum hemorrhage, and the patients' request to preserve their uterus. Four patients submitted to caesarean section which evolved to immediate post-partum hemorrhage, refractory to the use of ocytocin, ergometrine and misoprostol, were treated with the suture technique described by B-Lynch, without modification. The uterus was transfixed in six points according to the standard procedure, with chrome catgut-2 or polyglactine-1thread. After the assistant's manual compression of the uterus, the thread was pulled by its extremities by the surgeon, and a double knot followed by two simple knots were applied before performing the hysterorraphy. RESULTS: needled chrome catgut-2 thread was used in three cases and needled poluglactine-1 in one case. In the four cases there was immediate discontinuity of the vaginal bleeding, after the suture. The four patients did not present any complication during the procedure or along the immediate and late puerperal period. CONCLUSION: this technique represents a surgical alternative to deal with post-partum hemorrhage and may represent a reduction in the maternal morbidity and mortality in our country.
Key-words Gynecologic surgical proceduresHysterectomyMaternal mortalityOxytocinPostpartum hemorrhageUterine inertiaSee more -
Artigos Originais
Hysterectomy and benign gynecological diseases: what has been performed in Medical Residency in Brazil?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(2):67-73
05-02-2007
Summary
Artigos OriginaisHysterectomy and benign gynecological diseases: what has been performed in Medical Residency in Brazil?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(2):67-73
05-02-2007DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000200002
Views73See morePURPOSE: to evaluate the teaching and the practice of hysterectomy in the Brazilian regions and to compare them with data of international literature. METHODS: questionnaires about nine issues on benign hysterectomy indications, surgical procedures, use of antibiotic prophylaxis, suture of the vaginal vault and complications were sent to the 132 Gynecological and Obstetrics Residency Services of Brazil, registered by the Ministry of the Education and Culture in 2003. Data were computed and statically analyzed, with the use of the Friedman's, Kruskal-Wallis's and chi2 tests, according to the characteristics of the variables. RESULTS: 48.5% of the questionnaires were answered or justified when there were no answers, mainly in the Southeastern region (62%). The main surgical hysterectomy procedure was the abdominal, varying from 60 to 100% (p<0.001), followed by the vaginal (10 to 40%) and the laparoscopy (6%). In 94% of the cases, laparoscopy was not employed. The main indication for hysterectomy was myomatosis (60.4%; p<0.001), followed by adenomiosis (8.3%) and abnormal uterine bleeding (7.5%). First generation cephalosporin was used for antibiotic prophylaxis in 94% of the cases. There was no significant statistical difference among the threads (simple Catgut®, chrome Catgut® or Vicryl®) used for the suture of the vaginal vault and the development of granuloma in this region, which was the main complication of the procedure (p=0,002). CONCLUSIONS: the surgical procedures, the hysterectomy indications, the threads used to suture the vaginal vault and the complications were similar in the different regions of Brazil and they agreed with the evidence reported in the international literature.


