-
Original Article
Assessıng the predıctıve accuracy of blood-based bıomarkers ın neonatal outcomes for pregestatıonal dıabetes mellıtus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo17
04-30-2025
Summary
Original ArticleAssessıng the predıctıve accuracy of blood-based bıomarkers ın neonatal outcomes for pregestatıonal dıabetes mellıtus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo17
04-30-2025Views13Abstract
Objective:
This retrospective study aimed to investigate blood-based immune-inflammatory biomarkers (IIBs) in predicting neonatal outcomes in pregnancies with pregestational diabetes mellitus (PGDM).PIV[(neutrophil×platelet×monocyte)/lymphocyte)], SII (neutrophil×platelet/lymphocyte), and NLR neutrophil/lymphocyte) values were evaluated in all three trimesters, and their correlation with neonatal outcomes was examined.
Methods:
We included 82 cases of PGDM pregnancies delivered after 32 weeks. Maternal age, gravidity, parity, types of diabetes, and route of delivery were noted. For neonatal outcomes, we recorded gestational age at birth, birth weight percentile, existence of fetal growth restriction, LGA, neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) requirement, Apgar Score <7 at 1, 5, or 10 minutes, need for positive pressure ventilation (PPV), need for mechanical ventilation, hypoglycaemia, hyperbilirubinemia and the need for phototherapy. PIV, SII and NLR values were calculated in each trimester and their association with adverse neonatal outcomes was analyzed.
Results:
We could not detect any consistent and significant correlation between SII and PIV values and adverse neonatal outcomes for each trimester. There was a correlation between 3rd trimester NLR and adverse neonatal outcomes, including APGAR <7, the requirement for PPV and mechanical ventilation (p=0.056, 0.013 and 0.060, respectively).
Conclusion:
While SII and PIV values did not consistently correlate with adverse neonatal outcomes throughout each trimester in PGDM pregnancies, 3rd-trimester NLR showed a notable association with the requirement for PPV with statistical significance and with Apgar Score <7 and the requirement for mechanical ventilation without statistical significance. NLR in the third trimester may hold potential as a predictive marker for specific adverse neonatal outcomes in PGDM pregnancies, warranting further investigation.
Key-words biomarkersDiabetes mellitusGestational ageHypoglycemiaInfant, newbornIntensive care units, neonatalLymphocytesMaternal ageMonocytesNeuthrophilsPregancyPregnancy in diabetesRespiration, artificialSee more -
Review Article
Efficacy of vitamin C supplementation during pregnancy in the prevention of preterm birth: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo1
03-18-2025
Summary
Review ArticleEfficacy of vitamin C supplementation during pregnancy in the prevention of preterm birth: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo1
03-18-2025Views89Abstract
Objective:
Preterm birth is a leading global cause of neonatal mortality and morbidity, with oxidative stress playing a role in its pathogenesis. Vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant, may help reduce this risk. This study assessed the effectiveness of vitamin C supplementation, both alone and with vitamin E, in preventing preterm birth compared to a placebo.
Data source:
Databases were systematically searched in PubMed, Cochrane and Embase in December 2023 and updated in May 2024.
Study Selection:
Included RCTs evaluated vitamin C's effect on preterm birth and related neonatal outcomes.
Data collect:
Statistical analyses used a random-effects model for pooled risk ratios (RR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI). Heterogeneity was assessed with the I² statistic.
Data synthesis:
Seventeen RCTs (21,567 patients) were analyzed. Vitamin C supplementation showed no significant difference compared to placebo for preterm birth (RR 1.04; 95% CI 0.96, 1.14). No significant differences were observed for neonatal death (RR 0.77; 95% CI 0.55, 1.08), NICU admission (RR 1.03; 95% CI 0.95, 1.13), preterm PROM (RR 1.04; 95% CI 0.63, 1.71), or birth weight (MD 52.41; 95% CI −19.65, 124.47). A slight decrease in gestational age was observed (MD 0.26; 95% CI −0.02, 0.55).
Conclusion:
Vitamin C supplementation alone or in combination with vitamin E does not significantly prevent preterm birth or improve related neonatal outcomes.
Key-words Ascorbic acidFetal membranes, premature ruptureGestational ageIntensive care units, neonatalPregnancyPremature birthVitamin C supplementationVitamin ESee more
-
Original Article
Maternal erythrocytosis as a risk factor for small for gestational age at term in high altitude
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo98
01-23-2025
Summary
Original ArticleMaternal erythrocytosis as a risk factor for small for gestational age at term in high altitude
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo98
01-23-2025Views238Abstract
Objective
To determine if maternal erythrocytosis is a risk factor for small-for-gestational age at term at 3,400-m altitude in pregnant women without intercurrent disease.
Methods
Analytical study of retrospective cohorts at Cusco, a city at 3,400-m altitude. Our participants were 224 and 483 pregnant women with and without exposure to maternal erythrocytosis, respectively. A logistic regression with the goodness of fit to the proposed model was also performed with the Hosmer and Lemeshow test, evaluating the small-for-gestational-age results with or without exposure to hemoglobin >14.5 g/dl.
Results
The incidence of small-for-gestational-age was 6.9% for this entire cohort. The maternal erythrocytosis during gestation without any maternal morbidity at 3,400-m altitude has an ORa=0.691 (p=0.271) for small-for-gestational-age at term. Inadequate prenatal control has an ORa=2.115 (p=0.016) for small-for-gestational-age compared to adequate prenatal control.
Conclusion
Maternal erythrocytosis in pregnant women without any morbidity is not a risk factor for small-for-gestational-age at 3,400 m-altitude.
Key-words AltitudeFetal growth retardationGestational agehemoglobinHypoxiaMorbidityNeonatal mortalityPolycythemiaPregnancyPregnant womenRisk factorssmall for gestational ageSee more -
Original Article
Mode of delivery according to Robson classification and perinatal outcomes in restricted and small for gestational age fetuses
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo30
07-26-2024
Summary
Original ArticleMode of delivery according to Robson classification and perinatal outcomes in restricted and small for gestational age fetuses
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo30
07-26-2024Views168Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the mode of delivery according to Robson classification (RC) and the perinatal outcomes in fetal growth restriction (FGR) and small for gestational age (SGA) fetuses.
Methods
Retrospective cohort study by analyzing medical records of singleton pregnancies from two consecutive years (2018 and 2019). FGR was defined according to Delphi Consensus. The Robson groups were divided into two intervals (1–5.1 and 5.2–10).
Results
Total of 852 cases were included: FGR (n = 85), SGA (n = 20) and control (n=747). FGR showed higher percentages of newborns < 1,500 grams (p<0.001) and higher overall cesarean section (CS) rates (p<0.001). FGR had the highest rates of neonatal resuscitation and neonatal intensive care unit admission (p<0.001). SGA and control presented higher percentage of patients classified in 1 - 5.1 RC groups, while FGR had higher percentage in 5.2 - 10 RC groups (p<0.001). FGR, SGA and control did not differ in the mode of delivery in the 1-5.1 RC groups as all groups showed a higher percentage of vaginal deliveries (p=0.476).
Conclusion
Fetuses with FGR had higher CS rates and worse perinatal outcomes than SGA and control fetuses. Most FGR fetuses were delivered by cesarean section and were allocated in 5.2 to 10 RC groups, while most SGA and control fetuses were allocated in 1 to 5.1 RC groups. Vaginal delivery occurred in nearly 60% of FGR allocated in 1-5.1 RC groups without a significant increase in perinatal morbidity. Therefore, the vaginal route should be considered in FGR fetuses.
Key-words Cesarean sectionFetal growth retardationFetusGestational ageInfant, newbornInfant, small for gestational agePregnancy outcomerobson classificationSee more -
Original Articles
Placental Growth Measures in Relation to Birth Weight in a Latin American Population
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(8):373-380
08-01-2016
Summary
Original ArticlesPlacental Growth Measures in Relation to Birth Weight in a Latin American Population
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(8):373-380
08-01-2016Views179See moreAbstract
Introduction
The placenta, translates how the fetus experiences the maternal environment and is a principal influence on birth weight (BW).
Objective
To explore the relationship between placental growth measures (PGMs) and BW in a public maternity hospital.
Methods
Observational retrospective study of 870 singleton live born infants at Hospital Maternidad Sardá, Universidad de Buenos Aires, Argentina, between January 2011 and August 2012 with complete data of PGMs. Details of history, clinical and obstetrical maternal data, labor and delivery and neonatal outcome data, including placental measures derived from the records, were evaluated. The following manual measurements of the placenta according to standard methods were performed: placental weight (PW, g), larger and smaller diameters (cm), eccentricity, width (cm), shape, area (cm2), BW/PW ratio (BPR) and PW/BW ratio (PBR), and efficiency. Associations between BW and PGMs were examined using multiple linear regression.
Results
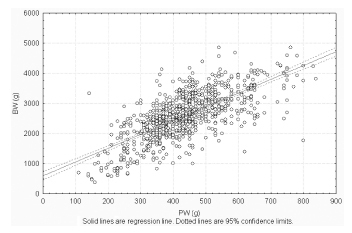
Birth weight was correlated with placental weight (R2 =0.49, p < 0.001), whereas gestational age was moderately correlated with placental weight (R2 =0.64, p < 0.001). By gestational age, there was a positive trend for PW and BPR, but an inverse relationship with PBR (p < 0.001). Placental weight alone accounted for 49% of birth weight variability (p < 0,001), whereas all PGMs accounted for 52% (p < 0,001). Combined, PGMs, maternal characteristics (parity, pre-eclampsia, tobacco use), gestational age and gender explained 77.8% of BW variations (p < 0,001). Among preterm births, 59% of BW variances were accounted for by PGMs, compared with 44% at term. All placental measures except BPR were consistently higher in females than in males, which was also not significant. Indices of placental efficiency showed weakly clinical relevance.
Conclusions
Reliable measures of placental growth estimate 53.6% of BW variances and project this outcome to a greater degree in preterm births than at term. These findings would contribute to the understanding of the maternal-placental programming of chronic diseases.
-
Artigos Originais
Maternal age and adverse perinatal outcomes in a birth cohort (BRISA) from a Northeastern Brazilian city
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(12):562-568
11-21-2014
Summary
Artigos OriginaisMaternal age and adverse perinatal outcomes in a birth cohort (BRISA) from a Northeastern Brazilian city
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(12):562-568
11-21-2014DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005161
Views112PURPOSE:
To verify the existence of associations between different maternal ages and the perinatal outcomes of preterm birth and intrauterine growth restriction in the city of São Luís, Maranhão, Northeastern Brazil.
METHODS:
A cross-sectional study using a sample of 5,063 hospital births was conducted in São Luís, from January to December 2010. The participants comprise the birth cohort for the study "Etiological factors of preterm birth and consequences of perinatal factors for infant health: birth cohorts from two Brazilian cities" (BRISA). Frequencies and 95% confidence intervals were used to describe the results. Multiple logistic regression models were applied to assess the adjusted odds ratio (OR) of maternal age associated with the following outcomes: preterm birth and intrauterine growth restriction.
RESULTS:
The percentage of early teenage pregnancy (12–15 years old) was 2.2%, and of late (16–19 years old) was 16.4%, while pregnancy at an advanced maternal age (>35 years) was 5.9%. Multivariate analyses showed a statistically significant increase in preterm births among females aged 12–15 years old (OR=1.6; p=0.04) compared with those aged 20–35 years. There was also a higher rate in preterm births among females aged 16–19 years old (OR=1.3; p=0.01). Among those with advanced maternal age (>35 years old), the increase in the prevalence of preterm birth had only borderline statistical significance (OR=1.4; p=0.05). There was no statistically significant association between maternal age and increased prevalence of intrauterine growth restriction.
Key-words Fetal growth retardationGestational ageMaternal agePregnancy outcomePremature birth/etiologySee more -
Artigos Originais
Fetal brain fissures development a three-dimensional ultrasonography study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(3):111-117
07-27-2011
Summary
Artigos OriginaisFetal brain fissures development a three-dimensional ultrasonography study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(3):111-117
07-27-2011DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000300002
Views156PURPOSE: to assess the distance of the fetal cerebral fissures from the inner edge of the skull by three-dimensional ultrasonography (3DUS). METHODS: this cross-sectional study included 80 women with normal pregnancies between 21st and 34th weeks. The distances between the Sylvian, parieto-occiptal, hippocampus and calcarine fissures and the internal surface of the fetal skull were measured. For the evaluation of the distance of the first three fissures, an axial three-dimensional scan was obtained (at the level of the lateral ventricles). To obtain the calcarine fissure measurement, a coronal scan was used (at the level of the occipital lobes). First degree regressions were performed to assess the correlation between fissure measurements and gestational age, using the determination coefficient (R²) for adjustment. The 5th, 50th and 95th percentiles were calculated for each fissure measurement. Pearson's correlation coefficient (r) was used to assess the correlation between fissure measurements and the biparietal diameter (BPD) and head circumference (HC). RESULTS: all fissure measurements were linearly correlated with gestational age (Sylvian: R²=0.5; parieto-occiptal: R²= 0.7; hippocampus: R²= 0.3 and calcarine: R²= 0.3). Mean fissure measurement ranged from 7.0 to 14.0 mm, 15.9 to 28.7 mm, 15.4 to 25.4 mm and 15.7 to 24.8 mm for the Sylvian, parieto-occiptal, hippocampus and calcarine fissures, respectively. The Sylvian and parieto-occiptal fissure measurements had the highest correlations with the BPD (r=0.8 and 0.7, respectively) and HC (r=0.7 and 0.8, respectively). CONCLUSION: the distance from the fetal cerebral fissures to the inner edge of the skull measured by 3DUS was positively correlated with gestational age.
Key-words BrainFetusGestational ageReference valuesUltrasonography, prenatal Imaging, three dimensionalSee more -
Artigos Originais
Teenage pregnancy outcome
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(12):620-625
02-06-2008
Summary
Artigos OriginaisTeenage pregnancy outcome
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(12):620-625
02-06-2008DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001200006
Views129See morePURPOSE: to compare delivery and pregnancy follow-up among adolescent and non-adolescent pregnant women whose delivery occurred in a tertiary hospital from Região de Lisboa (Portugal). METHODS: retrospective study with 10,656 deliveries. Pregnancy follow-up, delivery type, need of episiotomy and severe lacerations, Apgar index at the fifth minute and the delivery weight have been evaluated. The pregnant women were divided into two groups, over and under 20 years old. The group with women under 20 was further subdivided in pregnant women under or over 16. The χ2 test has been used for statistical analysis. RESULTS: adolescents presented worse follow-up: first appointment after 12 weeks (46.4 versus 26.3%) and less than four appointments (8.1 versus 3.1%), less dystocia (21.5 versus 35.1%), less caesarian sections (10.6 versus 20.7%), and lower need for inducing labor (16.5 versus 26.5%). There was no significant difference concerning gestational age at delivery and ratio of low weight newborns. Among adolescents, the ones under 16 had more low weight newborns (12 versus 7.4%) and more deliveries between 34 and 37 weeks (10.8 versus 4.2%). CONCLUSIONS: in a hospital attending adolescents with social and psychological support, the fact of them having had a worse follow-up in the pre-natal phase, their performance has not been worse. Nevertheless, special attention might be given to pregnant women under 16.


