Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo48
Evaluate the prevalence of macrosomic newborns (birth weight above 4000 grams) in a high-risk maternity from 2014 to 2019, as well as the maternal characteristics involved, risk factors, mode of delivery and associated outcomes, comparing newborns weighing 4000-4500 grams and those weighing above 4500 grams.
This is an observational study, case-control type, carried out by searching for data in hospital’s own system and clinical records. The criteria for inclusion in the study were all patients monitored at the service who had newborns with birth weight equal than or greater than 4000 grams in the period from January 2014 to December 2019, being subsequently divided into two subgroups (newborns with 4000 to 4500 grams and newborns above 4500 grams). After being collected, the variables were transcribed into a database, arranged in frequency tables. For treatment and statistical analysis of the data, Excel and R software were used. This tool was used to create graphs and tables that helped in the interpretation of the results. The statistical analysis of the variables collected included both simple descriptive analyzes as well as inferential statistics, with univariate, bivariate and multivariate analysis.
From 2014 to 2019, 3.3% of deliveries were macrosomic newborns. The average gestational age in the birth was 39.4 weeks. The most common mode of delivery (65%) was cesarean section. Diabetes mellitus was present in 30% of the deliveries studied and glycemic control was absent in most patients. Among the vaginal deliveries, only 6% were instrumented and there was shoulder dystocia in 21% of the cases. The majority (62%) of newborns had some complication, with jaundice (35%) being the most common.
Birth weight above 4000 grams had a statistically significant impact on the occurrence of neonatal complications, such as hypoglycemia, respiratory distress and 5th minute APGAR less than 7, especially if birth weight was above 4500 grams. Gestational age was also shown to be statistically significant associated with neonatal complications, the lower, the greater the risk. Thus, macrosomia is strongly linked to complications, especially neonatal complications.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(4):174-180
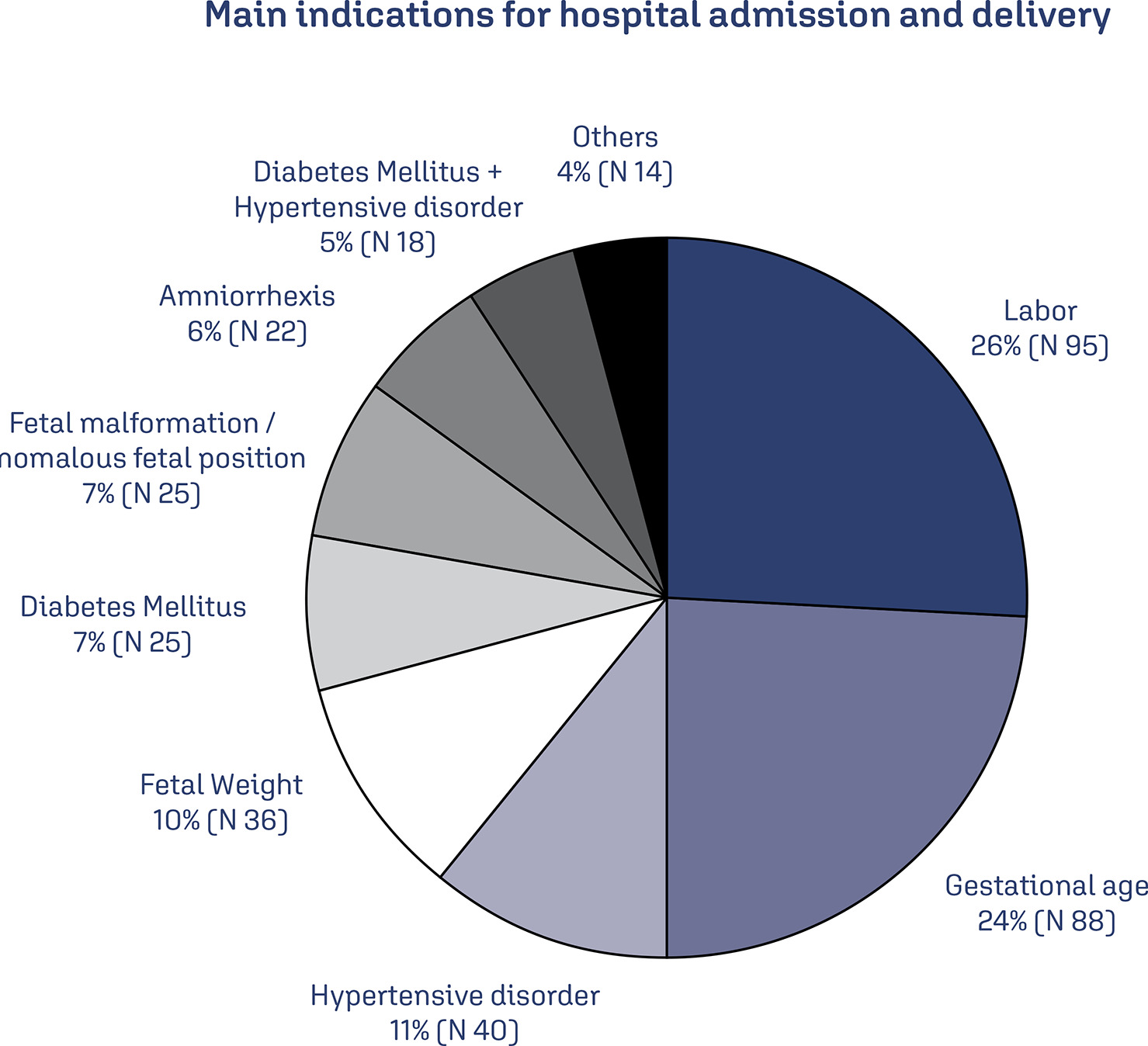
To develop reference curves of estimated fetal weight for a local population in Curitiba, South of Brazil, and compare them with the curves established for other populations.
An observational, cross-sectional, retrospective study was conducted. A reference model for estimated fetal weight was developed using a local sample of 2,211 singleton pregnancies with low risk of growth disorders and well-defined gestational age. This model was compared graphically with the Hadlock and Intergrowth 21st curves.
Reference curves for estimated fetal weight were developed for a local population. The coefficient of determination was R2 = 99.11%, indicating that 99.11% of the fetal weight variations were explained by the model. Compared with Hadlock curves, the 50th, 90th, and 97th percentiles in this model were lower, whereas the 10th percentile nearly overlapped, and the 3rd percentile was slightly higher in the proposed model. The percentiles were higher in the proposed model compared with the Intergrowth 21st curves, particularly for the 3rd, 10th, and 50th percentiles.
We provide a local reference curve for estimated fetal weight. The proposed model was different from other models, and these differences might be due to the use of different populations for model construction.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(10):580-586
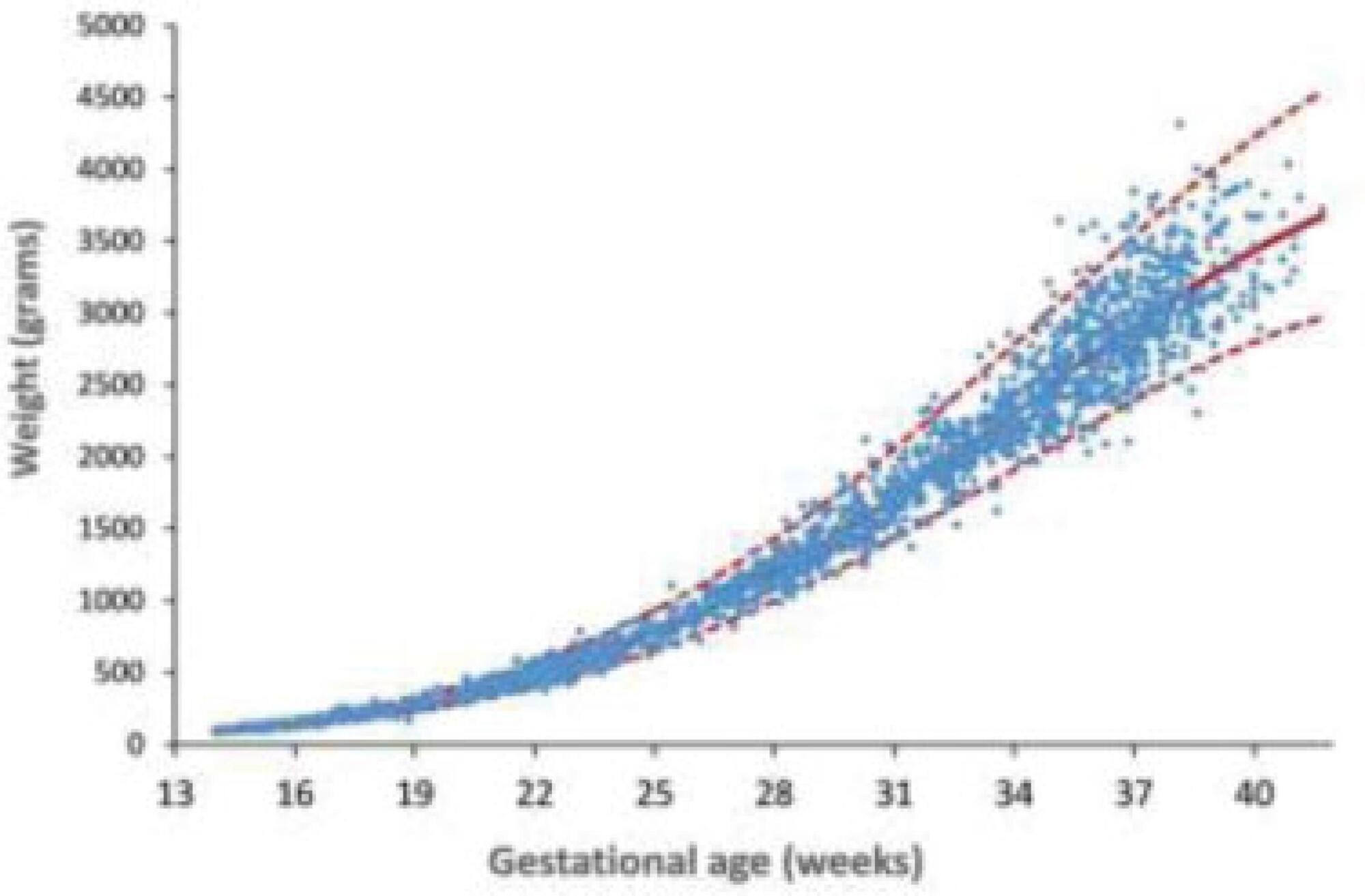
To assess 11 formulae commonly used to estimate fetal weight in a population of premature fetuses who had abnormal Doppler velocimetry due to early-onset placental insufficiency. The performance of each formula was evaluated in subgroups of fetuses with expected growth and intrauterine growth restriction.
Data were collected fromfetuses andmothers who delivered at three Brazilian hospitals between November 2002 and December 2013.We used the following formulae: Campbell; Hadlock I, II, III, IV and V; Shepard; Warsof; Weiner I and II; and Woo III.
We analyzed 194 fetuses. Of these, 116 (59.8%) were considered appropriate for gestational age (AGA), and 103 (53.1%) were male. The amniotic fluid volume was reduced in 87 (44.8%) fetuses, and the umbilical artery Doppler revealed absence or inversion of diastolic flow in 122 (62.9%) cases, and the analysis of the ductus venosus revealed abnormal flow in 60 (34.8%) fetuses. The Hadlock formulae using three or four fetal biometric parameters had low absolute percentage error in the estimated fetal weight among preterm fetuses with abnormal Doppler studies who were born within 5 days of the ultrasound evaluation. The results were not influenced by the clinical and ultrasound parameters often found in early-onset placental insufficiency.
In this study, the formulae with the best performance for fetal weight estimation in the analyzed population were Hadlock I and IV, which use four and three fetal biometric parameters respectively to estimate the weight of preterm fetuses with abnormal Doppler studies.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(1):11-19
To evaluate the relation between changes the body mass index (BMI) percentile, reflected in the Atalah curve, and perinatal outcomes.
A cross-sectional study with 1,279 women was performed. Data regarding gestational weight, sociodemographic characteristics and perinatal outcomes were collected through medical charts, prenatal card and interviews in the postpartum period. Women could be classified according to the Atalah curve in the following categories: low weight, adequateweight, overweight, and obese. The BMIwas calculated at the first and at the last prenatal care visits, and these values were compared.
An increase in the BMI category according to the Atalah classification occurred in 19.9% of pregnant women, and an increase of 3.4, 5.8 and 6.4 points of BMI were found for women respectively classified in the adequate weight, overweight and obese categories at the first prenatal visit. Women with high school education presented a lower chance of increasing their BMI (odds ratio [OR] 0:47 [0.24- 0.95]). Women who evolved with an increase in the the Atalah classification were associated with cesarean section (OR 1.97-2.28), fetalmacrosomia (OR 4.13-12.54) and large for gestational age newborn (OR 2.88-9.83).
Pregnant women who gained enough weight to move up in their BMI classification according to the Atalah curve had a higher chance of cesarean section and macrosomia. Women classified as obese, according to the Atalah curve, at the first prenatal visit had a high chance of cesarean section and delivering a large for gestational age newborn.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(10):455-459
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005271
To analyze the obstetrical and neonatal outcomes of pregnancies with small for gestation age fetuses after 35 weeks based on umbilical cord nucleated red blood cells count (NRBC).
NRBC per 100 white blood cells were analyzed in 61 pregnancies with small for gestation age fetuses and normal Doppler findings for the umbilical artery. The pregnancies were assigned to 2 groups: NRBC≥10 (study group, n=18) and NRBC<10 (control group, n=43). Obstetrical and neonatal outcomes were compared between these groups. The χ2 test or Student's t-test was applied for statistical analysis. The level of significance was set at 5%.
The mean±standard deviation for NRBC per 100 white blood cells was 25.0±13.5 for the study group and 3.9±2.2 for the control group. The NRBC≥10 group and NRBC<10 group were not significantly different in relation to maternal age (24.0 versus 26.0), primiparity (55.8 versus 50%), comorbidities (39.5 versus55.6%) and gestational age at birth (37.4 versus 37.0 weeks). The NRBC≥10 group showed higher rate of caesarean delivery (83.3 versus 48.8%, p=0.02), fetal distress (60 versus 0%, p<0.001) and pH<7.20 (42.9 versus 11.8%, p<0.001). The birth weight and percentile of birth weight for gestational age were significantly lower on NRBC≥10 group (2,013 versus 2,309 g; p<0.001 and 3.8 versus 5.1; p=0.004; respectively). There was no case described of 5th minute Apgar score below 7.
An NRBC higher than 10 per 100 white blood cells in umbilical cord was able to identify higher risk for caesarean delivery, fetal distress and acidosis on birth in small for gestational age fetuses with normal Doppler findings.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(6):264-268
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140004935
The aim of this study was to analize and describe some characteristics related to a false diagnosis of intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR).
We retrospectively included 48 pregnant women referred to our service with a suspected diagnosis of IUGR that was not confirmed after birth and we compared them to another group with confirmed IUGR. We then analyzed the characteristics of the false-positive results. The results of the study were divided into continuous and categorical variables for analysis. The χ2test or Fisher exact test was applied to compare proportions. The level of significance was set at p<0.05 for all tests.
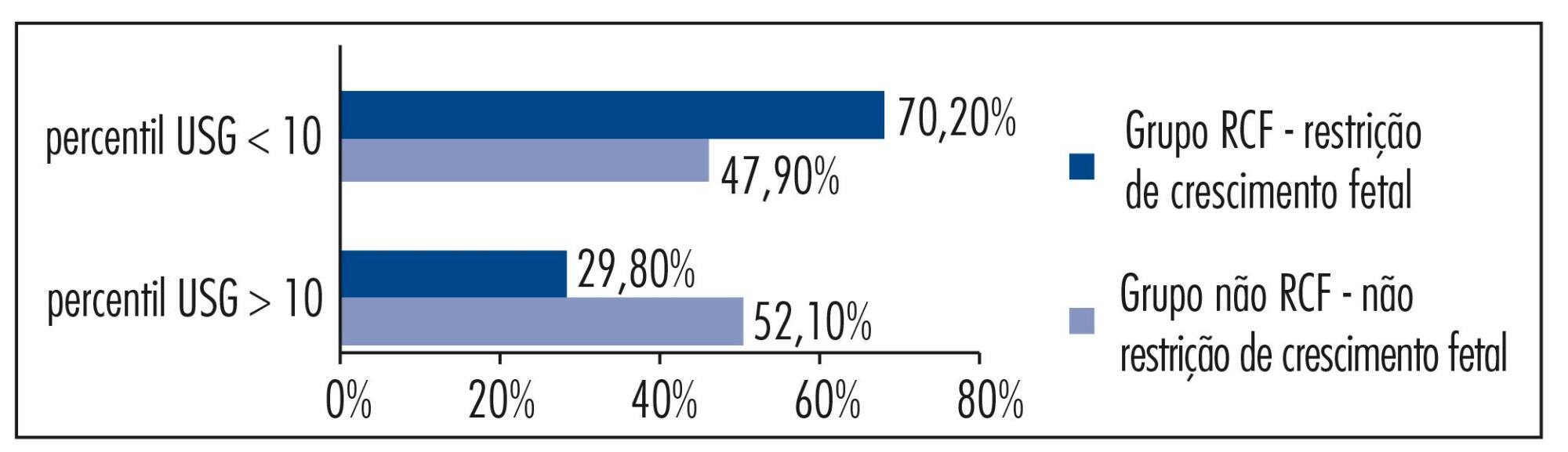
In our sample, pregnant women with a false diagnosis of IUGR had the following characteristics: they were referred earlier (mean gestational age of 32.8 weeks); were submitted to 2 to 6 ultrasound examinations before been registered in our service; in 25% of cases ultrasound examination was performed before 12 weeks; in 66.7% of cases the symphysis-fundal height measurement was normal; in 52.1% of cases they had at least 1 sonographic exam above the 10th percentile; on average, the last ultrasound examination (performed on average at 36 weeks) was above the 18th percentile; the women were submitted to a mean number of 5 ultrasound examinations and to a mean number of 4.6 vitality exams.
The false diagnosis of IUGR involves high hospital costs and higher demand for specialists. The symphysis-fundal height measurement must be valued, and the diagnosis of IUGR must be confirmed with ultrasonography in the last weeks of pregnancy before any obstetric management is taken.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(1):23-28
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000100006
To evaluate changes in body and internal organ weight of autopsied children in the perinatal period and their relationship with the cause of death.
One hundred and fifty three cases of perinatal autopsies performed at a university hospital in Southeastern Brazil ere included. Information about cause of perinatal death, date of autopsy, gestational age, perinatal weight and organ weight was obtained from the autopsy protocols and medical records of the mother and/or the newborn. Four groups of causes of death were defined: congenital malformations, perinatal hypoxia/anoxia, ascending infection and hyaline membrane. Brain, liver, lungs, heart, spleen, thymus and adrenals were analyzed.
The weight of children with perinatal hypoxia/anoxi (1,834.6±1,090.1 g versus 1,488 g), hyaline membranes (1,607.2±820.1 g versus 1,125 g) and ascending infection (1,567.4±1,018.9 g versus 1,230 g) was higher than expected for the population. Lung weight was higher in cases with ascending infection (36.6±22.6 g versus 11 g) and lower in cases with congenital malformations (22.0±9.5 g versus 40 g). Spleen weight was higher in children with ascending infection (8.6±8.9 g versus 3.75 g ) and adrenal weight was lower in cases with congenital malformations (3.9±2.1 g versus 5.5 g). Thymus weight was lower in cases with miscellaneous causes (3.7±1.2 g versus 7.5 g) and spleen weight was lower in patients with lung immaturity (0.4±0.1 g versus 1.7 g). All results showed significant differences.
This study demonstrates that variations in the weight of children and the weight of their organs are related to the types of cause of perinatal death. These data may contribute to a better interpretation of autopsy findings and their anatomical and clinical relationship.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(10):466-472
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012001000006
PURPOSES: To elaborate models for the estimation of fetal weight and longitudinal reference intervals of estimated fetal weight (EFW) using a sample of the Brazilian population. METHODS: Prospective observational study. Two groups of patients were evaluated: Group EFW (estimation of fetal weight): to elaborate (EFW-El) and validate (EFW-Val) a model for the prediction of fetal weight; Group LRI (longitudinal reference intervals): To elaborate (LRI-El) and validate (LRF-Val) conditional (longitudinal) percentiles of EFW. Polynomial regression analysis was applied to the data from subgroup EFW-El to elaborate a model for the estimation of fetal weight. The performance of this model was compared to those of previously published formulas. Linear mixed models were used for the elaboration of longitudinal reference intervals of EFW using data from subgroup LRI-El. Data obtained from subgroup LRI-Val were used to validate these intervals. RESULTS: Group EFW consisted of 458 patients (EFW-El: 367; EFW-Val: 91) and Group LRI consisted of 315 patients (LRI-El: 265; LRI-Val: 50). The model obtained for EFW was: EFW=-8.277+2.146xBPDxACxFL-2.449xFLxBPD². The performances of other models were significantly worse than those obtained with our formula. Equations for the prediction of conditional percentiles of EFW were derived from the longitudinal observation of patients of subgroup LRI-El and validated with data from subgroup LRI-Val. CONCLUSIONS: We described a method for customization of longitudinal reference intervals of EFW obtained using formulas generated from a sample of the Brazilian population.
