Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 09-30-2019;41(9):531-538
To determine the effect of treadmill walking on maternal heart rate (MHR) and cardiotocographic parameters (basal fetal heart rate [FHR], active fetal movements [AFM], number of accelerations and decelerations, and short-term variation [STV] and long-term variation [LTV] of fetal heart rate) in pregnant women at 36 weeks.
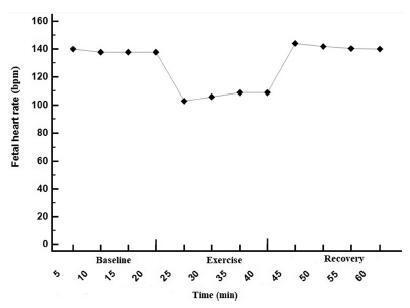
A nonrandomized, open clinical trial involving 88 healthy pregnant women submitted to moderate intensity walking and computed cardiotocography in 3 20- minute periods (resting, treadmill walking, and postexercise recovery).
The mean FHR decreased during walking (resting: 137 bpm; treadmill: 98 bpm; recovery: 140 bpm; p<0.001), with bradycardia occurring in 56% of the fetuses in the first 10minutes of exercise, and in 47% after 20minutes. Bradycardia was not detected in the other phases. The mean STV and HV were 7.9, 17.0, and 8.0 milliseconds (p<0.001) and 7.6, 10.8 and 7.6 bpm (p=0.002) in the resting, walking and recovery phases, respectively. Themean number of fetalmovements in 1 hour was 29.9, 22.2 and 45.5, respectively, in the 3 periods (p<0.001). In overweight/obese women, the mean FHR was lower (p=0.02). Following the logistic regression analysis, two variables remained significantly associated with bradycardia: maternal fitness in the 28th week of pregnancy (protective effect) and maternal weight (increased risk).
In healthy fetuses, physical exercise proved to be safe, since, although FHR and AFM decreased during treadmill walking, an increase in SVT and LTV was observed.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 12-01-2016;38(12):589-592
We speculate that genetic racial disparity exists in fetal life and can be detected by modern computerized cardiotocography (cCTG) .
This is a retrospective study comparing the results of the cCTG of pregnant patients at 37-42 weeks according to the parental ethnicity (black versus white). A cCTG was performed to analyze the variables of fetal heart rate (FHR). The cCTG variables analyzed were: percentage of signal loss; number of contractions; basal FHR; number of accelerations; number of decelerations; length of high variation episodes; short-term variability (STV); total trace duration time; and number of fetal active movements. Non-stress test (NST) parameters in the two groups were compared using the Mann-Whitney test for continuous data, and the Chi-square test for categorical variables.
We found a significantly lower number of active fetal movements (p 1/4 0.007) and longer periods of low variation (p 1/4 0.047) in the cCTG of black patients when compared with white patients.
In conclusion, identifying the factors responsible for the variance in the objective analysis of CTG results is important to improve the outcomes of patients. Our study lends further evidence as to the importance of ethnicity in clinical cCTG interpretation.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 07-23-2003;22(9):551-555
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000900003
Purpose: to evaluate the evolution in the embryo heart rate in the first trimester of pregnancy. Patients and Methods: in a prospective study 206 pregnant women were evaluated in the first trimester of pregnancy, by transvaginal color Doppler sonography, using Aloka, SSD-2000 apparatus, with a 5-MHz transvaginal transducer. All examinations were performed by the same examiner, with the determination of embryo heart rate. The patients were classified into groups according to the gestational age, in half-week intervals from the 5th week of pregnancy on. Pregnancy outcome was evaluated by ultrasonography at the end of second and third trimesters. Mean and standard deviation were determined for each evaluated gestational age. Results: it was possible to determine normal values for embryo heart rate. Mean embryo heart rate showed changes with gestational age, ranging from 110 ± 14 bpm at the 6.0th week to 150 ± 12 bpm at the 14.0th week. Conclusions: transvaginal pulsed color Doppler equipment enabled cardiovascular evaluation in early pregnancy, being a noninvasive method and innocuous to the embryo. These values would be useful in new studies on dopplervelocimetry in this period of pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 06-25-2003;23(9):567-571
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000900004
Purpose: to determine normal ranges for fetal heart rate (FHR) between the 10th and 14th week of pregnancy. Methods: a total of 1078 fetuses within a crown-rump length (CRL) from the 10th to the 14th week of pregnancy were evaluated. The fetuses were divided into 4 groups: Group I (10 weeks), Group II (11 weeks), Group III (12 weeks), Group IV (13 weeks). The fetal heart was seen using B-mode/M-mode at a sagital plane and FHR was recorded. FHR was electronically calculated using calipers within 3 consecutive cycles without fetal moveiments. Results: FRH ranged from 136 to 178 bpm among the 1078 studied fetuses. Median values and standard deviations (5 and 95 percentiles) were calculated for each group. The FHR range for each group was: 158 to 184 bpm (Group I); 155 to 175 bpm (Group II); 152 to 172 bpm (Group III) and 149 to 168 bpm (Group IV). Our main finding was a progressive reduction in FHR during the time period under consideration. Discussion: FHR evaluation in the first trimester of gestation is a simple procedure and should be analyzed not only qualitatively but also quantitatively. Published papers have shown a relation ship between FHR and fetal prognosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 06-19-2002;24(1):29-36
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000100005
Purpose: to study computerized cardiotocography performed in high-risk pregnancies, analyze the results, and correlate the criteria to perinatal results. Patients and Methods: two hundred and thirty-three high-risk pregnancies were studied prospectively, performing a total of 485 computerized cardiotocographies. The exclusion criteria included fetal anomalies and signal loss over 20% (proportion of 3.75-millisecond periods in which there were no valid pulse intervals). The perinatal results of 71 pregnancies were correlated to the last cardiotocography, performed at least seven days before birth, excluding patients with absent or reversed end diastolic velocities in the umbilical arteries. Results: thirty-three examinations with signal loss over 20% were excluded. The normal criteria were met in 404 (83.3%), and 62.1% examinations met the criteria within 20 minutes and 79% within 30 minutes. The abnormal computerized cardiotocography was related significantly (p<0.05) to adverse perinatal results, such as: preterm delivery, first minute Apgar score less than 7 (33%), neonatal intensive care admission (55.5%) and intubation of newborn at delivery (44.4%). Conclusions: computerized cardiotocography in high-risk pregnancies met the normal criteria in most of the cases, with the examination performed for 30 minutes. The cases that did not meet the criteria correlated significantly to adverse perinatal results.
