Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo25
04-09-2024
Fertility preservation is a priority in oncology for female cancer patients. However, there is a lack of communication between infertility specialists and oncologists. This study aimed to evaluate infertility specialists’ perceptions and experiences regarding fertility preservation.
Conduct an online survey to profile infertility specialists. Participants were infertility affiliated with the Brazilian Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Associations (FEBRASGO). The specialists received an online survey, which response rate were 30.9%, most of whom were in southern and southeastern. The survey consisted on 14 questions about the infertility specialists’ location, techniques in clinical practice, treatment successful rate, patients idea, etc.
The average experience in human reproduction were 15.5 ± 10.2 years (mean ± standard deviation, range 1-40). Among reproductive-aged female cancer patients recommended for fertility preservation, 60.3 ± 28.8% (range 10-100%) underwent preservation procedures. Main barriers were cost (41%), oncologists’ knowledge or acceptance (35%) and accessibility (9%). Most infertility specialists (58%) considered 40 years the limit for fertility preservation. Leukemia, lymphoma, breast and ovarian cancers were prioritized for fertility preservation, while lung, thyroid, gastric, and brain cancers were less relevant.
This is the first Brazilian study about infertility specialists’ perceptions on oncology patients access to fertility preservation. These patients primarily receive treatment in the public health system, while infertility specialists mainly work in the private healthcare. This healthcare mode is currently fragmented, but integrating these experts is enhancing patient access to fertility preservation. Studies on this topic are still warranted.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo33
04-09-2024
Evaluate histological changes in testicular parameters after hormone treatment in transgender women.
Cross-section study with patients who underwent gonadectomy at Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre from 2011 to 2019. Hormone treatment type, route of administration, age at initiation and duration were recorded. Atrophy parameters were observed: testicular volume, tubular diameter, basal membrane length, presence of spermatogonia and spermatids (diploid and haploid spermatozoid precursors).
Eighty-six patients were included. Duration of hormone treatment is associated with testicular atrophy and spermatogenesis arrest. Other characteristics of hormone treatment such as age of initiation, route of administration and type of treatment were not associated with testicular histological changes. Testicular volume may predict spermatogenesis arrest. Basal membrane length and tubular diameter ratio is an interesting predictor of germ cell presence.
Cross-sex hormone treatment affects testicular germ cell presence. Basal membrane length and tubular diameter ratio reduces inter variability of measurements and better exemplify how atrophic seminiferous tubules are. Fertility preservation should be addressed by healthcare providers in order to recognize gender affirming treatment impact on transgender health.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(3):251-257
02-09-2022
To evaluate the reproductive and histological characteristics of fresh cultured ovarian tissue from transgender male patients.
An in vitro pilot study in which samples were collected during sex reassignment surgery for transgender male patients. The ovarian cortex was cut into fragments of 2 mm, 3mm, and 4 mm, and placed in a 96-well plate suitable for cultivation at days 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8, when the histology was analyzed.
Stromal hyperplasia was observed in all samples, and it was not associated with the obtainment of primordial or primary follicles. Peripheral reduction in cell count was also a recurrent finding. Primordial and primary follicles were identified with a heterogeneous pattern in fragments from the same patient and from different patients, and follicles in more advanced stages of development (secondary and antral) were not found. There was an association between the diameter of the ovarian fragments and the identification of primary follicles (p=0.036). The number of days in culture was associated with histological signs of tissue damaging in the fragments (p=0.002). The total number of follicles identified in the samples with 2mm in diameter was significantly lower than in those that measured 4mm in diameter (p=0.031).
A diameter of 4mm is suitable for ovarian tissue culture with the benefit of ease of handling. Even after prolonged exposure to testosterone, the ovarian fragments presented primordial and primary follicles, maintaining viability throughout the days they were exposed to the culture. Freezing the ovarian cortex of transgender patients who will undergo surgery for gender reassignment would be an interesting option, in the future, for the preservation of fertility.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):225-231
01-19-2021
We report a case of ultrasound-guided ex vivo oocyte retrieval for fertility preservation in a woman with bilateral borderline ovarian tumor, for whom conventional transvaginal oocyte retrieval was deemed unsafe because of the increased risk of malignant cell spillage. Ovarian stimulation with gonadotropins was performed. Surgery was scheduled according to the ovarian response to exogenous gonadotropic stimulation; oophorectomized specimens were obtained by laparoscopy, and oocyte retrieval was performed ~ 37 hours after the ovulatory trigger. The sum of 20 ovarian follicles were aspirated, and 16 oocytes were obtained.We performed vitrification of 12 metaphase II oocytes and 3 oocytes matured in vitro. Our result emphasizes the viability of ex vivo mature oocyte retrieval after controlled ovarian stimulation for those with high risk of malignant dissemination by conventional approach.
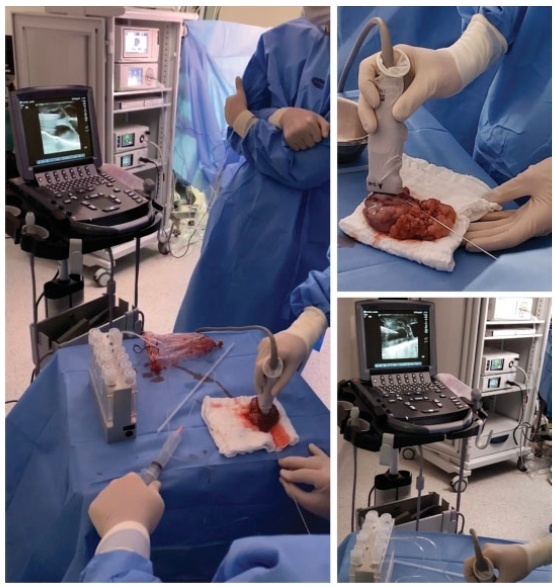
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(9):569-576
10-23-2020
To performa comprehensive review to provide practical recommendations regarding the diagnosis and treatment of benign adnexal masses, as well as information for appropriate consent, regarding possible loss of the ovarian reserve.
A comprehensive review of the literature was performed to identify the most relevant data about this subject.
In total, 48 studies addressed the necessary aspects of the review, and we described their epidemiology, diagnoses, treatment options with detailed techniques, and perspectives regarding future fertility.
Adnexal masses are extremely common. The application of diagnosis algorithms is mandatory to exclude malignancy. A great number of cases can bemanaged with surveillance. Surgery, when necessary, should be performed with adequate techniques. However, even in the hands of experienced surgeons, there is a significant decrease in ovarian reserves, especially in cases of endometriomas. There is an evident necessity of studies that focus on the long-term impact on fertility.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(11):614-621
11-01-2017
The present study aimed to evaluate the impact of vitrification on the viability of follicles using a three-dimensional (3D) in vitro culture.
Bovine ovarian tissue samples (n = 5) obtained from slaughterhouses were utilized. The cortex was cut into small fragments of 2 x 3 x 0.5 mm using a tissue slicer. From these fragments, secondary follicles were first isolated by mechanical and enzymatic methods, then encapsulated in alginate gel and individually cultured for 20 days. Additional fragments of the same ovarian tissue were vitrified in a solution containing 25% glycerol and 25% ethylene glycol. After warming, the follicles underwent the same follicular isolation process that was performed for the fresh follicles.
A total of 61 follicles were isolated, 51 from fresh ovarian tissue, and 10 from vitrified tissue. After the culture, the vitrified and fresh follicles showed 20% and 43.1% survival rates respectively (p = 0.290),with no significant differences. At the end of the culture, therewere no significant differences in follicular diameter between the vitrified (422.93 ± 85.05 μm) and fresh (412.99 ± 102.55 μm) groups (p = 0.725). Fresh follicles showed higher mean rate of antrum formation when compared with vitrified follicles (47.1% and 20.0% respectively), but without significant difference (p = 0.167).
The follicles were able to develop, grow and form antrum in the 3D system after vitrification, despite the lower results obtained with the fresh tissue.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(2):78-83
02-07-2013
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000200007
PURPOSE: To understand the reproductive and sexual life of women treated for breast cancer. METHODS: A total of 139 women with a diagnosis made at least 6 months ago were interviewed after being randomly selected in a rehabilitation service. The interviews were carried out between 2006 and 2010. The inclusion criteria were: to have used a rehabilitation service between 2006 and 2010, to be a Unified Health System user, to have been a patient at a regional hospital and to be resident in the area of DRS XIII-Ribeirão Preto, state of São Paulo. The interviewees were visited at home where a face to face questionnaire regarding sociodemographic features and questions about the disease and reproductive and sexual life was administered. For the last one, the Female Sexual Function Index instrument was used. Data were analyzed statistically by the χ² test, Fisher exact test, Student's t test, multivariate analysis by logistic regression, factorial analysis and the Cronbach's alpha. RESULTS: Most patients had between 2 to 3 children and 80% used some contraceptive. About half of them had had sexual intercourse in the last month, 45.3% had interrupted sexual intercourse during treatment and 25.9% did not. There were reports of decreasing sexual activity, although half of the interviewees had re-started sexual life during the first six months after treatment. About half presented sexual dissatisfaction. An active sexual life is associated with being younger than 40 years of age and to have a partner. No association was found between active sexual life and diagnosis and types of treatment. CONCLUSION: Sexual activity of women treated for breast cancer is not associated with the treatments, but with age and with the opportunity of having sex.