Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(7):380-389
08-26-2020
To analyze the consumption of minimally-processed and ultraprocessed foods in relation with sociodemographic variables, maternal habits, educational activity received during prenatal care and clinical history.
A cross-sectional, analytical and descriptive study with 1,035 pregnant women who lives in the municipalities of the metropolitan region of Grande Vitória, Espírito Santo, Brazil (RMGV-ES), and who were hospitalized in establishments of the Unified Health System (SUS) due to childbirth (April-September 2010). The food frequency questionnaire, pregnant woman’s card and information from the medical records of the health facility unit were analyzed. The Chi-square test and the binary logistic regression model were used to investigate the association between the independent variables and the consumption of ultraprocessed foods.
It was identified that pregnant women ≤ 19 years of agewere 2.9 timesmore likely to consume ultraprocessed foods (confidence interval [CI] 95% 1.683-5.168, p< 0.001), while those ≥ 35 years old were less likely to consume them (odds ratio [OR] 0.265, 95% CI 0.105-0.666, p= 0.005). Maternal smoking increased the odds of consumption of ultraprocessed foods by 2.2 times (95% CI 1.202-4.199, p= 0.011) and pregnant womenwho did not obtain information on healthy food during prenatal care presented 54.1% less chances of consuming minimally-processed foods (OR 0.459, 95% CI 0.307-0.687, p< 0.001).
Smoking during the gestational period and being a teenager are factors that influence the consumption of ultraprocessed foods of pregnant women. Race/ color, head of household, age group, receiving of information about feeding in the prenatal period and not having smoked in gestation determined the consumption of minimally-processed foods.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(11):686-692
11-01-2018
The aim of the present study was to assess the anthropometric measures, food intake and food cravings during the menstrual cycle of undergraduate students of the faculty of nutrition.
A cross-sectional study was performed with 27 students from a public university in the state of Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil, who had their food intake evaluated through a 24-hour food recall, their nutritional status evaluated based on anthropometric measures, and food cravings evaluated using the Food Desire Questionnaire. Data were collected during an evaluation in the follicular phase (between the 5th and the 9th day of the menstrual cycle) and another in the luteal phase (LP) (between the 20th and the 25th day of the menstrual cycle). For food intake variables, the analysis of variance (ANOVA) test was used, followed by the Tukey test. The Mann-Whitney test was used for the analysis of food cravings, considering a significance level of 5% (p< 0.05).
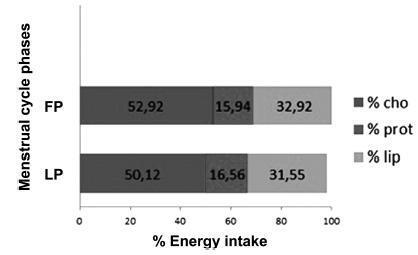
The desire for foods rich in sugar, salt, and fat, such as chocolate, pastries, snacks and desserts were higher (p< 0.05) during the premenstrual period, although it did not reflect neither a higher energy intake nor an alteration in the distribution of macronutrients. A higher intake of carbohydrates, proteins, fibers, and calcium was observed during the LP; however, without statistical difference between the groups. There were no differences either in the intake of any food group or in the anthropometric measurements (p> 0.05).
Food cravings of nutrition students differed between the phases of the menstrual cycle; however, with no difference in food intake and in anthropometric measures.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(2):87-92
07-08-2011
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000200006
PURPOSE: to determine the dietary consumption of pregnant women, by assessing the intake of macronutrients and micronutrients, and to verify the maternal weight gain during pregnancy. METHODS: a retrospective study conducted from June 2002 to June 2008 with pregnant women who received nutritional counseling during prenatal care at a university hospital, grouped according to anthropometric nutritional status classified by pregestational body mass index (BMI). The dietary intake was analyzed according to the information obtained in food frequency interviews, performed at the first evaluation of pregnant women in the service of nutrition to obtain data about eating habits, and the intake of macronutrients and micronutrients was calculated. The pregnant women received nutritional counseling, and the maternal weight gain was investigated. RESULTS: a total of 187 pregnant women who received nutritional counseling were analyzed. Twenty-three (12.2%) were underweight, 84 (45.0%) normal weight, 37 (19.8%) overweight, and 43 (23.0%) obese. The underweight pregnant women had lower consumption of lipids when compared to the normal weight group (101.4 versus 137.3 g; p=0.043). The average iron intake was higher in normal weight pregnant women (14.6 mg/d) compared to the overweight (12.2 mg/d) or obese (10.9 mg/d; p<0.001) groups. The average intake of folate was higher in normal weight pregnant women compared to obese ones (336.5 µg/d versus 234.5 µg/d; p=0.002). Excessive maternal weight gain was significantly (p=0.009) more frequent in overweight (56.7%) and obese (39.5%) pregnant women compared to underweight (17.4%) and normal weight (31.0%) women. CONCLUSIONS: The maternal weight gain above recommended levels was associated with overweight and obesity. The dietary intake of pregnant women differs according to maternal anthropometric nutritional status, with a lower daily intake of iron in overweight and obese women and a lower intake of folate in obese ones, a fact that reinforces the importance of prenatal vitamin supplementation.