Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(2):096-103
This comprehensive review compares clinical protocols of important entities regarding the management of fetal growth restriction (FGR), published since 2015. Five protocols were chosen for data extraction. There were no relevant differences regarding the diagnosis and classification of FGR between the protocols. In general, all protocols suggest that the assessment of fetal vitality must be performed in a multimodally, associating biophysical parameters (such as cardiotocography and fetal biophysical profile) with the Doppler velocimetry parameters of the umbilical artery, middle cerebral artery, and ductus venosus. All protocols reinforce that the more severe the fetal condition, the more frequent this assessment should be made. The timely gestational age and mode of delivery to terminate the pregnancy in these cases can vary much between the protocols. Therefore, this paper presents, in a didactic way, the particularities of different protocols for monitoring FGR, in order to help obstetricians to better manage the cases.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(5):289-296
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) is associated with poor perinatal prognosis and a higher risk of stillbirth, neonatal death, and cerebral palsy. Its detection and the evaluation of its severity by new Doppler velocimetric parameters, such as aortic isthmus (AoI), are of great relevance for obstetrical practice. The AoI is a vascular segment that represents a point of communication between the right and left fetal circulations. It is considered to be a functional arterial shunt that reflects the relationship between the systemic and cerebral impedances, and has recently been proposed as a tool to detect the status of hemodynamic balance and prognosis of IUGR in fetuses. In the present review, we noticed that in healthy fetuses, the AoI net flow is always antegrade, but in fetuses with IUGR the deterioration of placental function leads to progressive reduction in its flow until it becomes mostly retrograde; this point is associated with a drastic reduction in oxygen delivery to the brain. The more impaired the AoI flow is, the greater is the risk of impairment in the Doppler velocimetry of other vessels; and the alterations of the AoI Doppler seem to precede other indicators of severe hypoxemia. Although there seems to be an association between the presence of retrograde flow in the AoI and the risk of long-term neurologic disability, its role in the prediction of perinatal morbi-mortality remains unclear. The AoI Doppler seems to be a promising tool in the management of fetuses with IUGR, but more studies are needed to investigate its employment in clinical practice.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(1):7-12
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000100002
Purpose: to evaluate the accuracy of Doppler velocimetry in the diagnosis of fetal well-being. Methods: a total of 130 pregnant women assisted at the Ultrasound Unit of the Center for Integral Assistance of Women's Health, UNICAMP, between the 28th and 42nd gestational weeks was analyzed. The correlation between fetal umbilical and middle cerebral arteries, abdominal aorta, and the adverse perinatal results was established. The pregnant women selected for this study were submitted electively to cesarean sections, at the utmost four hours after the color Doppler examination. We considered as adverse perinatal results: Apgar score lower than seven at the 5th minute, neonatal intensive care unit hospitalization, intrauterine growth retardation, acute fetal distress, perinatal mortality, hypoglycemia, polycythemia, necrotizing enterocolitis, and cerebral hemorrhage. The indexes for the umbilical and middle cerebral arteries and the abdominal aorta were related, in each case, to the adverse perinatal results. Results: the systole/diastole umbilical artery ratio presented a higher sensitivity than the pulsatile and tolerance indexes. The Doppler study of the umbilical artery presented greater sensitivity than the middle cerebral artery and the abdominal aorta in detecting adverse perinatal results. Conclusion: the Doppler velocimetry of the umbilical and middle cerebral arteries presented good diagnostic capacity in evaluating fetal well-being, and a significant association with the adverse perinatal results.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(1):15-20
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000100003
PURPOSE: to analyze the values of Doppler ultrasound for blood flow velocity in the ductus venosus between the 10th and the 14th week of gestation, during the different phases of the cardiac cycle: ventricular systole (wave S), ventricular diastole (wave D), atrial systole (wave a), and angle-independent indexes. METHODS: Doppler was used in this prospective cross-sectional study to examine 276 single pregnancies. Fetus malformations, abnormal nuchal translucency, and women with clinical pathologies were excluded. A Toshiba SSH-140 ultrasound equipment was used. The derivation of Doppler frequency spectra was carried out according to standardized measurement procedures: less than 30ºinsonation angle and 50-70 Hz high-pass filter. The ductus venosus was identified in a median sagittal and ventral plane with the presence of color aliasing due to increase in blood flow velocity. The sample volume (1-2 mm³) was placed immediately at the origin of the ductus venosus. At least three clearly and subsequent waves were available for measurement of standard values. The Levene test and the Bonferroni method were used for statistical analysis. RESULTS: increase in blood flow velocity from 29 cm/s to 37 cm/s (p=0.013) was observed during ventricular systole between the 10th and the 14th week of gestation. Similarly, increase in blood flow velocity was recorded during the ventricular diastole (from 25 cm/s to 32 cm/s, p=0.026). There were no changes in wave a, pulsatility index, and S/a ratio in this period. CONCLUSION: the reference ranges established by this study may serve as the basis for Doppler ultrasound follow-up in a normal patient population. Further studies are required to determine the validity of these parameters and, in particular, for the fetus at risk.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(6):437-442
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000600009
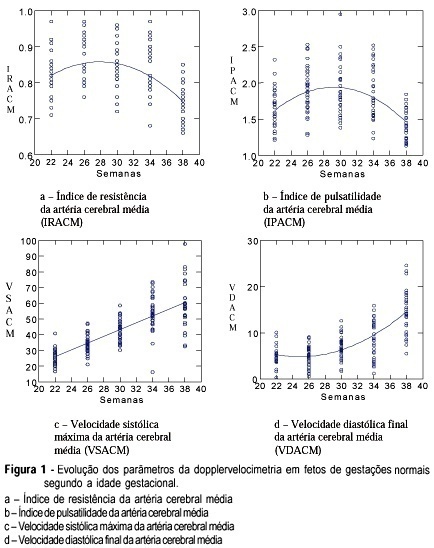
PURPOSE: to study the evolution of the resistance and pulsatility indices, maximum velocity, final diastolic velocity and time of acceleration of the middle cerebral artery of fetuses between 22 and 38 weeks of gestation. METHODS: a prospective and longitudinal observational study was conducted on 33 fetuses of normal pregnant women evaluated between 22 and 38 weeks of pregnancy. The gestational age was determined on the basis of the date of the last menstruation and/or by ultrasound examination during the first trimester. Doppler ultrasound examination was performed by a single observer using an Image Point 1800 (Hewlett Packard) apparatus equipped with a multiple frequency transducer. For the acquisition of the Doppler tracing of the middle cerebral artery, the sample indicator was calibrated for a sample volume of 1 mm³ and placed on the anterior middle cerebral artery as close as possible to the skullcap. The insonation angle was kept between 5º and 19º and the filter was adjusted to a frequency of 50-100 Hz. The newborn infants were evaluated in order to confirm that the fetuses were vigorous and adequate for gestational age. RESULTS: the results obtained for the resistance and pulsatility indices revealed a 2nd-degree equation, representing a parabola whose values for the resistance index were 0.81 during the 22nd week and 0.75 during the 38th week. The pulsatility index was 1.59 during the 22nd week and 1.45 during the 38th week. Maximum systolic velocity increased progressively along pregnancy, with values of 26.3 cm/s during the 22nd week and 57.7 cm/s during the 38th week. Final diastolic velocity increased progressively from the 26th week (5.21 cm/s) to term (14.6 cm/s). Acceleration time increased significantly only between 26 and 30 weeks, with values of 0.04 s during the 26th week and 0.05 s during the 30th week. CONCLUSION: it was concluded that the evolution of the resistance and pulsatility indices and of maximum systolic velocity were similar to those of most studies described in the literature. Acceleration time presented few modifications during the evaluated gestational weeks.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(10):659-665
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001001000008
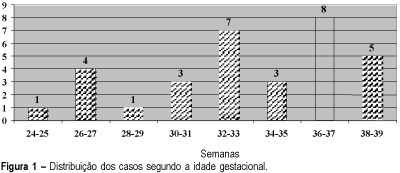
Purpose: evaluation of perinatal outcome of brain-sparing effect detected by color Doppler. Methods: brain-sparing effect was detected in 32 fetuses at the Ultrasound Service of the Center for Integral Attention to Women's Health at Campinas State University (UNICAMP). The diagnosis of brain-sparing effect was made when the ratio between middle cerebral artery and umbilical artery pulsatility indexes was below one (IPACM/IPAU <1). The measurement was obtained with color Doppler equipment Toshiba SSH-140A. Results: admission to neonatal intensive care unit (ICU) was necessary in 26 fetuses (89.6%). The number of days in ICU varied from 1 to 83 days, with a mean of 22 days. Fetal mortality rate was 3 in 32 (9.4%) and perinatal mortality was 9 in 29 (31%). Considering the gestational age by the Capurro method, the incidence of birth below 36 weeks was 21 in 32 (65.6%). Intrauterine growth restriction occurred in 71.8% of the cases and hypoglycemia in 44.8%. Conclusions: brain-sparing effect is a condition in which the fetus is at serious risk of adverse perinatal outcome and Doppler studies might be helpful in the obstetric management.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(5):291-298
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000500004
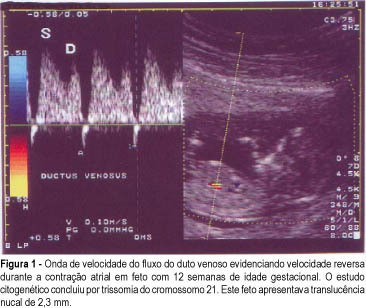
Objective: to study the value of Doppler velocimetry of the ductus venosus and of the umbilical artery and vein, in the screening for chromosomal abnormalities at 10-14 weeks of gestation. Patients and Methods: a total of 314 fetuses were studied consecutively. In 112 cases a cytogenetic study was performed on material obtained from a biopsy of the chorionic villus, and in 202 cases the postnatal phenotype was used as a basis for the result. In addition to the routine ultrasonographic examination, all the fetuses were submitted to measurement of the nuchal translucency thickness and to Doppler velocimetry of the umbilical artery and vein, particularly of the ductus venosus. For statistical analysis the Fisher exact test and the Mann-Whitney test were used. Results: twenty-three cases of chromosomal abnormalities occurred. Of these abnormal cases, the ductus venosus blood flow during atrial contraction was absent (1 case) and reverse (22 cases), sensitivity was 92%. In the group of normal fetuses (289 cases), 6 evaluations demonstrated alterations in the Doppler of the ductus venosus (specificity of 97.6%, positive and negative predictive values of 76.7% and 93.3%, respectively); the false-positive rate was 2.4%. In reference to the umbilical vein and umbilical artery, there was no statistically significant difference between the abnormal and the normal group. Conclusion: The only parameter of Doppler velocimetry of the umbilical artery and vein which contributed to the detection of aneuploidies was the accidental discovery of the reverse blood flow in both vessels. Although our favorable results demonstrated that the Doppler velocimetry of the ductus venosus is effective in detecting aneuploidies, this conclusion, however, is preliminary and needs further investigation.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(5):307-312
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000500006
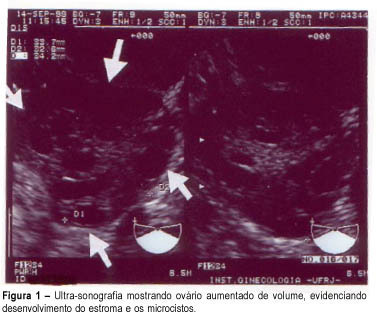
Purpose: to evaluate the effectiveness of color Doppler as a diagnosis method for polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) through blood flow variations in the ovarian stroma, in the uterine arteries and in the subendometrial tissue. Methods: thirty patients divided into two groups were selected: fifteen patients with amenorrhea or oligomenorrhea, hirsutism (Ferriman and Gallwey score >8), body mass index >25 kg/m² and echographic examination identifying increased hyperechogenic stromal and ovarian polycystosis (study group), and an identical number of patients presenting normal menstrual cycles, with no signs of hirsutism and with normal ultrasonography (control group). Transvaginal Doppler flowmetry measured systolic peak velocity or maximal velocity (Vmax) pulsatility index (PI) and resistance of ovarian stromal vessels, uterine arteries and subendometrial layer. Results: Doppler velocimetry showed significantly higher Vmax layer (p<=0,0004) in the ovarian stromal of patients with PCOS (12.2 cm/s) when compared to the control group (8.05 cm/s); the uterine artery PI was also higher in the PCOS group (3.3 cm/s) versus the control group (2.7 cm/s); other Doppler velocimetry parameters did not show significant differences. As we established a cutoff = 9 cm/s for the sample for Vmax, we obtained the percentages of 95.2 for sensitivity, 80.0 for specificity, 83.3 for positive predictive value and 94.1 for negative predictive value. Conclusion: Doppler velocimetry might constitute an additional tool to be incorporated in clinical and ultrasonographic investigation concerning the PCOS diagnosis.