Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(10):580-586
To assess 11 formulae commonly used to estimate fetal weight in a population of premature fetuses who had abnormal Doppler velocimetry due to early-onset placental insufficiency. The performance of each formula was evaluated in subgroups of fetuses with expected growth and intrauterine growth restriction.
Data were collected fromfetuses andmothers who delivered at three Brazilian hospitals between November 2002 and December 2013.We used the following formulae: Campbell; Hadlock I, II, III, IV and V; Shepard; Warsof; Weiner I and II; and Woo III.
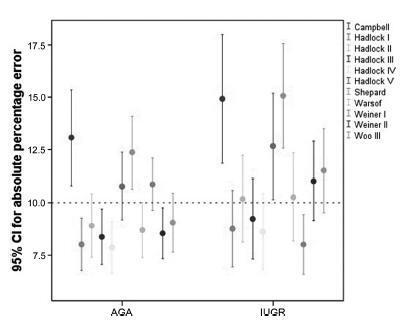
We analyzed 194 fetuses. Of these, 116 (59.8%) were considered appropriate for gestational age (AGA), and 103 (53.1%) were male. The amniotic fluid volume was reduced in 87 (44.8%) fetuses, and the umbilical artery Doppler revealed absence or inversion of diastolic flow in 122 (62.9%) cases, and the analysis of the ductus venosus revealed abnormal flow in 60 (34.8%) fetuses. The Hadlock formulae using three or four fetal biometric parameters had low absolute percentage error in the estimated fetal weight among preterm fetuses with abnormal Doppler studies who were born within 5 days of the ultrasound evaluation. The results were not influenced by the clinical and ultrasound parameters often found in early-onset placental insufficiency.
In this study, the formulae with the best performance for fetal weight estimation in the analyzed population were Hadlock I and IV, which use four and three fetal biometric parameters respectively to estimate the weight of preterm fetuses with abnormal Doppler studies.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(9):517-524
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000900005
Purpose: to determine the behavior of doppler velocimetry during the course of risk pregnancies and to compare the perinatal results obtained for concepti with retarded intrauterine growth (RIUG) with those for concepti considered adequate for gestational age (AGA). Methods: a prospective study of the evolution of doppler ultrasound was made in 38 pregnant women with of idiopathic intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR) in previous pregnancy. A relationship was established between this antecedent and the new pregnancy. The pregnant women studied were divided into two groups in agreement with their neonates birthweight. Group 1 was associated with IUGR and group 2 with adequate birth weight. IUGR was confirmed in 23.7% of the cases. Umbilical and uterine artery doppler velocimetry was performed from 20 to 40 weeks of gestation. Middle cerebral artery doppler velocimetry was analyzed after 28 weeks of gestation, twice a month, being the last valued examination before birth. Results: the uterine and umbilical artery ratio at 24 and 28 weeks of gestation, respectively, correlated with the presence of IUGR. There was no difference between the two groups regarding the presence or absence of a small notch in the uterine artery wave form and middle cerebral artery doppler velocimetry ratio, at the last examination before birth. There was a relationship between neonatal stay in hospital for more than three days and the presence of IUGR. Conclusions: doppler ultrasound should be used in the follow-up of cases with a high risk of IUGR. It allows the detection of the fetuses at high risk of hypoxia and, by interrupting the pregnancy, fetal distress-related complications may be avoided.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(10):663-668
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002001000005
PURPOSE: to evaluate the effect of intravascular transfusion on ductus venosus and inferior vena cava Doppler ultrasound indexes (SV/CA) and to relate it to hemoglobin levels before transfusion. METHODS: this is a transversal prospective study. A total of 62 intravascular transfusions were performed in 27 fetuses from pregnancies with red blood cell isoimmunization. The 62 cases were divided into two groups: (1) fetuses with hemoglobin levels before transfusion £10 g/dL and (2) fetuses with hemoglobin levels before transfusion >10 g/dL. The SV/CA and CA/SV indexes were measured using color Doppler ultrasound 6 h before and 12 h after intravascular transfusion. The index values before and after transfusion in all 62 cases were compared. Thereafter we compared these indexes before and after transfusion regarding each group. The Wilcoxon test was used and the results were considered statiscally significant when p<0.05. RESULTS: when we studied the whole group (62 cases) no significant difference was observed between the CA/SV index before and after transfusion (p=0.775). On the other hand, a significant increase in the SV/CA index was observed after transfusion (p=0.004). No significant differences were observed in both the SV/CA and CA/SV indexes before and after transfusion in the group of fetuses with hemoglobin levels before transfusion £10 g/dL (p=0.061 and p=0.345, respectively). There was a significant increase in the CA/SV index after transfusion in fetuses with hemoglobin levels before transfusion >10 g/dL (p=0.049), but the SV/CA index did not change in this group (p=0.086). CONCLUSION: venous Doppler study may be useful to understand fetal hemodynamic adjustment after intravascular transfusion. An increase in SV/CA without change in CA/SV after transfusion in anemic fetuses may be an important compensatory mechanism to increase intravascular volume. The increase in CA/SV index in fetuses with hemoglobin levels before transfusion <10 g/dL suggests a state of fetal hypervolemia.