Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(10):446-454
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005264
To reduce the percentage of cesareans among pregnant women at UNIMED Jaboticabal by redesigning the care delivery model.
Descriptive study conducted at an institution in São Paulo State starting in 2012 to propose the redesign of the care mode based on Continued Improvement Science adapted to the health area. To measure the results of changes we selected nine indicators and their targets.
The percentage of natural births reached the target of 40% after seven months of implementation of the interventions. The percentage of natural births reached 66% among pregnant women in SUS. The perinatal mortality rate decreased by 25% from 2012 to 2014, and the prematurity rate was 3 per 100 live births in 2014. The percentage of pregnant women from UNIMED with six or more prenatal consultations reached 95%. The hospital costs for childbirth care decreased by 27% compared to 2012 and 2013. This reduction was not sustainable and the per capita cost returned to the same level in 2014. The remuneration of all obstetricians increased by 72% from 2012 to 2014.Unimed's costs attributed to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) decreased by 61% from 2012 to 2013. The cost was the same for 2013 as it was for 2014 while the admission rate among newborns at UNIMED decreased by 55%. The percentage of pregnant women participating in courses to prepare for birth did not reach the goal set at 80%. The percentage of pregnant women satisfied and very satisfied with care delivery reached 86%.
This project achieved its objectives by reducing the percentage of C-sections among pregnant women of UNIMED Jaboticabal representing a concrete example of achieving the Triple Aim in health: to improve the experience of care and the health outcomes of populations and individuals and to perform these two tasks at a lower cost.
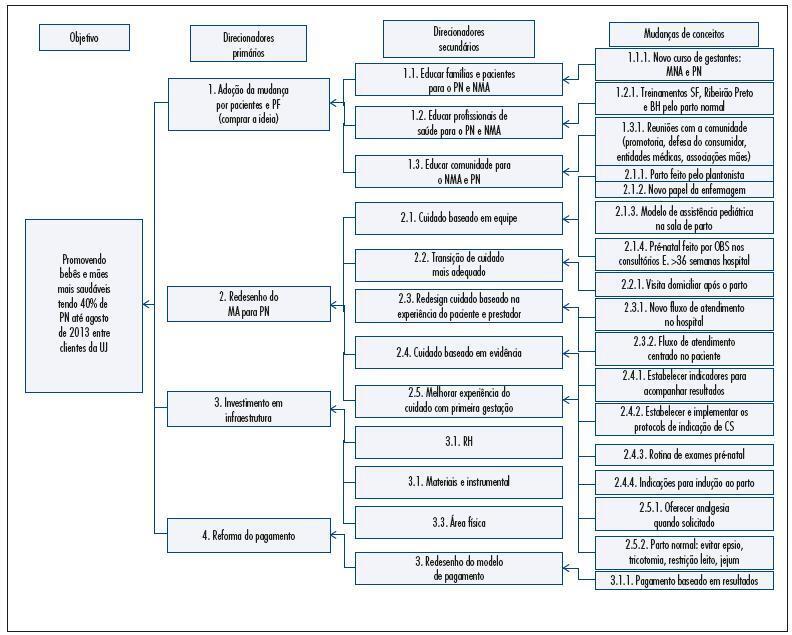
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(4):159-163
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150004973
To analyze the relationship between route of delivery and other aspects of pregnancy and the occurrence of intracranial hemorrhage in newborns of very low weight at a teaching hospital in South Brazil.
A case-control study was conducted. Medical records of all patients who were born weighing ≤1,500 g and who were submitted to transfontanellar ultrasonography were analyzed from January 2011 to September 2014. The cases were newborns with diagnosis of intracranial hemorrhage, while newborns with regular exams were used as controls. Differences between groups were analyzed by the Student t test and by χ2 or Fisher exact tests, and association was determined using the odds ratio with a 95% confidence interval and α=5%.
A total of 222 newborns with birth weight ≤1,500 g were recorded; of these, 113 were submitted to transfontanellar ultrasonography and were included in the study. Sixty-nine (61.1%) newborns were diagnosed with intracranial hemorrhage (cases) and 44 (38.9%) showed no abnormal results (controls). Most cases had grade I hemorrhage (96.8%) originating from the germinative matrix (95.7%). The predominant route of delivery was caesarean section (81.2% of the cases and 72.7% of the controls). Five deaths were recorded (3 cases and 2 controls). Gestational age ranged from 24 to 37 weeks. Median birth weight was 1,205 g (range: 675-1,500 g). The median time of hospitalization was 52 days, ranging from 5 to 163 days.
Grade I intracranial hemorrhage from the germinative matrix was the most frequent. No differences were found between cases and controls for the variables studied. The small number of infants submitted to transfontanellar ultrasonography limited the sample size and the results of the study.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(11):519-524
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140005100
To validate a questionnaire to be applied in order to learn and describe the perceptions of specialists in obstetrics and gynecology about their experience and self-confidence in the emergency care for vaginal delivery.
This was a prospective study for the validation of an instrument that contains statements about emergency obstetrical care: breech delivery (n=23), shoulder dystocia (n=20), postpartum haemorrhage (n=24), forceps delivery (n=32), and vacuum extractor (n=5). Participants gave their opinions on each item by applying the Likert scale (0=strongly disagree, 1=partially disagree, 2=indifferent, 3=partially agree and 4=strongly agree). The questionnaire was applied to 12 specialists in obstetrics and gynecology and it was expected to be found a level of comprehension exceeding 80%. A five-point scale was used to assess the understanding of each question (from 0=did not understand anything to 5=understood perfectly and I have no doubt). A score above 4 was considered to indicate sufficient understanding. The instrument used was specially designed to suit the specific demands. The analysis of internal reliability was done using the Cronbach alpha coefficient. For external validation, we calculated the proportion of items with full understanding for each subscale. For research purposes, the alpha should be greater than 0.7.
Participants had a mean age of 33.3 years, with 5.0 standard deviation (SD), and an average interval time since graduation from medical school of 5.8 years (SD=1.3 years). All were specialists with residency in obstetrics and gynecology. The mean proportion of participants who fully understood the items in each emergency was 97.3% for breech delivery, 96.7% for shoulder dystocia, 99.7% for postpartum hemorrhage, 97.4% for forceps delivery, and 98.3% for the use of a vacuum extractor. The results of Cronbach's alpha for the items in each emergency studied were: 0.85 for breech delivery, with 0.72 lower limit of 95% confidence interval ((%%CI), 0.74 for shoulder dystocia (lower limit of 95%CI=0.51), 0.79 for postpartum hemorrhage (lower limit of 95%CI=0.61), 0.96 for forceps delivery (lower limit of 95%CI=0.92), and 0.90 for the vacuum extractor (lower limit of 95%CI=0.79).
The validated questionnaire is useful for learning and describing the perception of physicians about their experience and self-confidence in emergency care for vaginal births.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(11):516-522
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013001100007
PURPOSE: To analyze the impact of vaginal delivery after a previous cesarean section on perinatal outcomes. METHODS: Case-control study with selection of incident cases and consecutive controls. Maternal and perinatal variables were analyzed. We compared secundiparas who had a vaginal delivery after a previous cesarean delivery (VBAC) (n=375) with secundiparas who had a second cesarean section (CS) (n=375). Inclusion criteria were: secundiparas who underwent a cesarean section in the previous pregnancy; singleton and term pregnancy; fetus in vertex presentation, with no congenital malformation; absence of placenta previa or any kind of bleeding in the third quarter of pregnancy. RESULTS: The rate of vaginal delivery was 45.6%, and 20 (5.3%) women had forceps deliveries. We found a significant association between VBAC and mothers younger than 19 years (p<0.01), Caucasian ethnicity (p<0.05), mean number of prenatal care visits (p<0.001), time of premature rupture of membranes (p<0.01), labor duration shorter than 12 hours (p<0.04), Apgar score lower than seven at 5th minute (p<0.05), fetal birth trauma (p<0.01), and anoxia (p<0.006). In the group of newborns delivered by cesarean section, we found a higher frequency of transient tachypnea (p<0.014), respiratory disorders (p<0.048), and longer time of stay in the neonatal intensive care unit (p<0.016). There was only one case of uterine rupture in the VBAC group. The rate of neonatal mortality was similar in both groups. CONCLUSIONS: Vaginal delivery in secundiparas who had previous cesarean sections was associated with a significant increase in neonatal morbidity. Further studies are needed to develop strategies aimed at improving perinatal results and professional guidelines, so that health care professionals will be able to provide their patients with better counseling regarding the choice of the most appropriate route of delivery.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(6):281-285
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000600008
PURPOSE: It was to describe and compare the preference of nulliparous and primiparous women for a particular mode of delivery and to determine whether the previous experience of childbirth influences the delivery process. METHODS: We conducted a prospective cross-sectional study. One-hundred interviews were held with 56 nulliparous and 44 primiparous women using previously prepared questionnaires. The quantitative and categorical data were evaluated by the chi-square or Fisher's Exact Test. RESULTS: 60.7% of nulliparous women and 70.5% of primiparous women reported to prefer vaginal delivery. When analyzing the answers about receiving sufficient information about the type of delivery, the presence or absence of influence on the choice of route of delivery and the preferred route of delivery by the partner, there were no statistically significant differences between the two groups. The level of significance used for the tests was 0.05. CONCLUSIONS: This study permitted us to conclude that the previous experience of delivery does not influence the expectation of the delivery process or the choice for a specific mode of delivery. When choosing the route of delivery, women seek to ensure the health of mother and neonate, as well as to avoid the process of pain and suffering.