-
Review Article
Efficacy, Safety, and Acceptability of Misoprostol in the Treatment of Incomplete Miscarriage: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(12):808-817
01-11-2023
Summary
Review ArticleEfficacy, Safety, and Acceptability of Misoprostol in the Treatment of Incomplete Miscarriage: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(12):808-817
01-11-2023Views357See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the efficacy, safety, and acceptability of misoprostol in the treatment of incomplete miscarriage.
Data sources
The PubMed, Scopus, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and Clinical Trials databases (clinicaltrials.gov) were searched for the relevant articles, and search strategies were developed using a combination of thematic Medical Subject Headings terms and text words. The last search was conducted on July 4, 2022. No language restrictions were applied.
Selection of studies
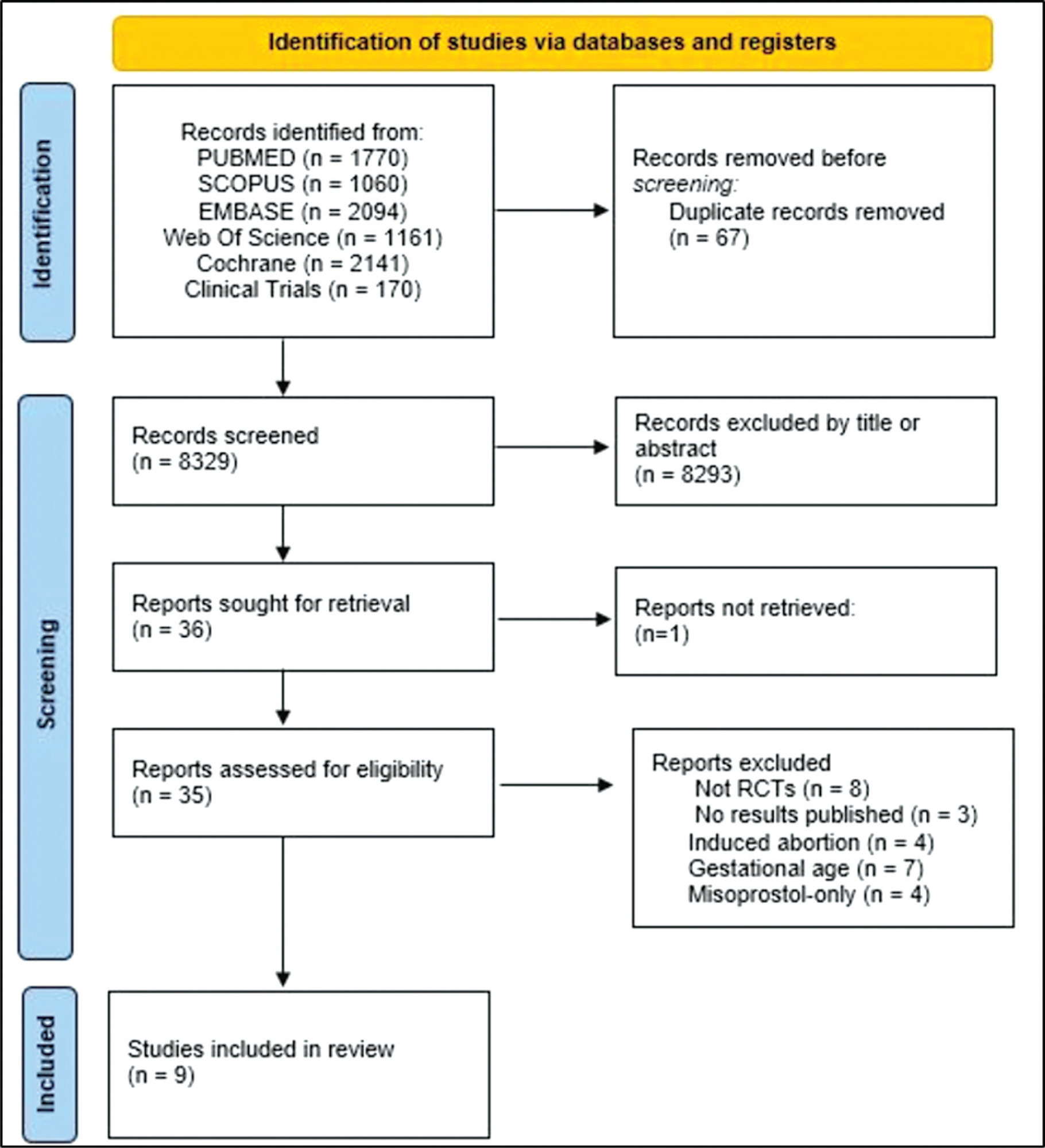
Randomized clinical trials with patients of gestational age up to 6/7 weeks with a diagnosis of incomplete abortion and who were managed with at least 1 of the 3 types of treatment studied were included. A total of 8,087 studies were screened.
Data collection
Data were synthesized using the statistical package Review Manager V.5.1 (The Cochrane Collaboration, Oxford, United Kingdom). For dichotomous outcomes, the odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were derived for each study. Heterogeneity between the trial results was evaluated using the standard test, I2 statistic.
Data synthesis
When comparing misoprostol with medical vacuum aspiration (MVA), the rate of complete abortion was higher in the MVA group (OR = 0.16; 95%CI = 0.07–0.36). Hemorrhage or heavy bleeding was more common in the misoprostol group (OR = 3.00; 95%CI = 1.96–4.59), but pain after treatment was more common in patients treated with MVA (OR = 0.65; 95%CI = 0.52–0.80). No statistically significant differences were observed in the general acceptability of the treatments.
Conclusion
Misoprostol has been determined as a safe option with good acceptance by patients.
-
Relato de Caso
Conservative management of ectopic pregnancy in cesarean scar: case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(5):233-237
07-05-2013
Summary
Relato de CasoConservative management of ectopic pregnancy in cesarean scar: case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(5):233-237
07-05-2013DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000500008
Views77Implantation of a pregnancy within a cesarean delivery scar is considered to be the rarest form of ectopic pregnancy, with a high morbidity and mortality. Pregnancy in a cesarean delivery scar may cause catastrophic complications which may result in hysterectomy and compromise the reproductive future of a woman. We report an ectopic pregnancy in cesarean scar case in a 28-year old pregnant woman that was treated with success with the association between three treatment modalities (methotrexate, uterine artery embolization and curettage) and preserve her fertility.
Key-words Case reportsCesarean sectionCicatrixCurettageMethotrexatePregnancy, ectopicUterine artery embolizationSee more -
Artigos Originais
Frequency of hydatidiform mole in tissue obtained by curettage
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(6):254-258
07-13-2012
Summary
Artigos OriginaisFrequency of hydatidiform mole in tissue obtained by curettage
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(6):254-258
07-13-2012DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000600003
Views107See morePURPOSE: To determine the frequency of hydatiform mole in tissues obtained by curettage. METHODS: A cross-sectional, prospective and descriptive conducted on patients who underwent curretage due to a diagnosis of abortion or hydatiform mole whose material was sent for pathological examination. We excluded women who did not accept to participate and refused to sign the free informed consent form. We studied the following variables: pathological findings, age, race, number of pregnancies and previous abortions, gestational age at diagnosis, quantitative serum beta fraction of human chorionic gonadotropin and ultrasound findings. The data were compared to the to histological diagnosis, considered to be the gold standard. Data were stored and analyzed in Microsoft Excel® software and the Epi-Info program, version 6.0 (STATCALC) and the results are presented as frequency (percentage) or mean±standard deviation. The χ2 test was used to determine the association between qualitative variables and the level of significance was set at p<0.005. RESULTS: A total of 515 curettage procedures were performed, 446 of which comprised the sample. The frequency of hydatiform mole was 2.2% (ten cases). The mean age of the patients with a mole was 31±10 years, most patients were white and multiparous and had no history of previous abortions, but there was no significant association between these variables. The pregnancy loss occurred early in patients with and without a mole and the most common complaints in both groups were vaginal bleeding and cramps in the lower abdomen. Quantitative determination of human chorionic gonadotropin was performed in 422 cases (413 with and 9 without a hydatiform mole). The levels of the hormone were higher than 100,000 mIU/mL in 1.9% of the patients without a hydatiform mole and in 44.45% of the patients with the disease (p=0.00004). All patients with this hormonal level had an ultrasound suspicion of hydatiform mole and one of them also had a clinical suspicion. A total of 333 patients underwent ultrasound examination. Of the patients with sonographic findings suggestive of molar pregnancy, there was confirmation in five (41.7%) cases. The other seven (58.3%) were false positives. A significant association was found between ultrasound suspected molar pregnancy and disease confirmation by histopathological analysis (p=0.0001). In 50% of cases of hydatiform mole there was no suspicion of the disease according to clinical signs and symptoms, levels of beta fraction of human chorionic gonadotropin or sonographic findings. CONCLUSIONS: The frequency of hydatidiform mole is low and the disease may not be suspected by clinical examination, ultrasonography or the serum level of the beta fraction of human chorionic gonadotropin, requiring pathological examination of tissue obtained by uterine evacuation for diagnosis.
-
Artigos Originais
Manual vacuum aspiration uterine treatment of incomplete abortion to 12 gestational weeks: an alternative to curettage
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(10):292-296
01-06-2011
Summary
Artigos OriginaisManual vacuum aspiration uterine treatment of incomplete abortion to 12 gestational weeks: an alternative to curettage
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(10):292-296
01-06-2011DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011001000004
Views144See morePURPOSE: To analyze the effectiveness and occurrence of complications, in addition to hospitalization time and blood losses. METHODS: Thirty patients were assigned alternatively and consecutively to one of two groups (15 to the Curettage Group and 15 to the Manual Vacuum Aspiration Group). The following variables were analyzed: effectiveness of the method, occurrence of complications, time before the procedure, time of execution of the procedure, time after the procedure, and total time of hospital permanence, in addition to hematocrit and hemoglobin, which were measured before and after the procedure. Patients were evaluated clinically 10 to 14 days after the procedure. Parametric and nonparametric tests were used for statistical analysis, with the level of significance set at p>0.05. RESULTS: Both methods were efficient and no complications were recorded. Blood losses were similar in the two groups, but the hospitalization time was significantly shorter for the Manual Vacuum Aspiration Group (p=0.03). CONCLUSION: Manual vacuum aspiration is as efficient and safe as uterine curettage, with the advantage of requiring shorter hospitalization, which increases the resolution of the method, improving the quality of care for these patients.
-
Artigos Originais
Misoprostol in substitution at uterine curettage in early pregnancy failure
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(6):276-280
08-19-2011
Summary
Artigos OriginaisMisoprostol in substitution at uterine curettage in early pregnancy failure
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(6):276-280
08-19-2011DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000600003
Views115PURPOSE: To evaluate the effectiveness of misoprostol administered vaginally for uterine evacuation in interrupted early pregnancies and the time between the administration and emptying correlated with gestational age. METHODS: Clinical trial with 41 patients with pregnancies interrupted between the 7th and the 12th gestational weeks. The mean age was 27.3 (±6.1) years. Mean parity was 2.2 (±1.2) deliveries. The average number of previous abortions was 0.2 (± 0.5). Misoprostol was administered vaginally in a single 800 µg dose and transvaginal ultrasound was performed after 24 hours. Abortion was considered complete when the anteroposterior diameter of the endometrial cavity measured <15 mm. Patients whose diameter remained was larger than 15 mm underwent uterine curettage. Two groups (<8 and >8 weeks of gestational age) were compared using the binomial test and Student's t test regarding outcome: frequency of complete abortion and the interval between administration of misoprostol and abortion (in minutes). The level of significance was 5%. RESULTS: The mean gestational age at diagnosis was 8.5 weeks (SD=1.5). The intervals between administration of misoprostol and uterine contractions and between the administration and abortion were 322.5±97.0 minutes and 772.5±201.0 minutes, respectively. There was complete abortion in 80.3%. The success rate was 96.2% for the first group and 53.3% for the second (p<0.01). We observed a statistically significant difference in time between administration and uterine evacuation (676.2±178.9 vs. 939.5±105.7 minutes, p<0.01). The side effects observed were hyperthermia (12.1%), nausea (7.3%), diarrhea or breast pain (2.4%). No case of genital infection was observed. CONCLUSIONS: The use of vaginal misoprostol is a safe and effective alternative to curettage for interrupted early pregnancies, being better in pregnancies up to the 8th week. The time interval until emptying was lower in pregnancies that were interrupted earlier.
Key-words Abortion, missedCurettageEvaluation of the efficacy-effectiveness of interventionsMisoprostolSee more -
Trabalhos Originais
Treatment of miscarriage in the first trimester of pregnancy: curettage versus manual vacuum aspiration
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(4):271-276
09-04-2003
Summary
Trabalhos OriginaisTreatment of miscarriage in the first trimester of pregnancy: curettage versus manual vacuum aspiration
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(4):271-276
09-04-2003DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000400008
Views72See morePURPOSE: to perform a comparative study between uterine curettage and manual vacuum aspiration (MVA) in the treatment of first-trimester miscarriages. METHODS: a hundred and two patients were included up to the 12th week of pregnancy, with diagnosis of miscarriage, admitted at Maternidade Escola Januário Cicco, between January 1998 and July 2001, and who were randomly submitted to uterine curettage or to MVA. The analyzed variables were: pain control, need of mechanical cervical dilation, uterine emptying time, incidence of complications and stay in hospital. The patients were reevaluated clinically and echographycally between 7 and 10 days after the procedures. The chi2 test was used for statistical analysis. RESULTS: general anesthesia was used in all the patients submitted to uterine curettage and in none of those who were submitted to MVA, whose pain was controlled with local anesthesia in 64% of the cases. The differences between the two methods concerning the need of mechanical cervical dilation, emptying time and incidence of complications were not significant. The stay in hospital was significantly shorter in patients submitted to MVA. CONCLUSIONS: no advantage of one method over the other was observed in regard to the technique and the incidence of complications. The unneeded use of general anesthesia and the significantly shorter stay in hospital indicate that MVA should be recommended for all services with obstetrical assistance, increasing resolvability of the cases and decreasing risks, improving the quality of assistance.
-
Trabalhos Originais
Dilatation and Curettage in the Evaluation of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: Histopathologic Findings and the Cost/Benefit Relation
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(8):495-502
07-11-2000
Summary
Trabalhos OriginaisDilatation and Curettage in the Evaluation of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: Histopathologic Findings and the Cost/Benefit Relation
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(8):495-502
07-11-2000DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000800005
Views97See morePurpose: to critically evaluate the histopathologic findings and the cost/benefit relation of dilatation and uterine curettage (D&C) in the evaluation of the abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB). Method: retrospective analysis of the histopathological findings in 542 D&C performed for AUB in the Department of Gynecology of the Faculdade de Ciências Médicas da Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (FCM-UERJ), between January 1984 and January 1994. The patients were divided into two groups: Group 1 - patients <=50 years (385 D&C) and Group 2 -- patients >50 years (157 D&C). Cases of urgency curettage were excluded from the study. All the curettages were accomplished under narcosis. The mean hospitalization lenght was three days. A histopa-thological finding of proliferative, secretory, atrophic or iatrogenic type endometrium was considered a negative pathological result. The term iatrogenic refers to the endometrium under possible influence of hormonal medication. When the histopathological finding evidenced some lesion, this was considered a positive pathological result. Results: in Group 1 there was a negative pathological result in 50.2% of the cases, positive pathological result in 39.7% of the cases, and insufficient material for diagnosis (IMD) in 10.1% of the cases. Endometrial polyp and submucosal leiomyoma were found in only 5.5% and 4.4%, respectively. Cancer was an uncommon observation in that group, endometrial adenocarcinoma (EAC) (five cases) being found in only 1.3% of the cases, in a relation of 77 D&C to one EAC. In Group 2, a negative pathological result was observed in 38.3% of the cases, positive pathological result in 38.1% of the cases and IMD in 23.6% of the cases. Endometrial polyp and submucosal leiomyoma were found only in 5.1% and 0.6%, respectively. Malignant lesions were found in 12% of the cases EAC being 9.5% (15 cases), showing a relation of one EAC to 10 D&C. Conclusions: according to the current knowledge on the etiology of AUB, this study showed that traditional diagnostic D&C has low accuracy in the evaluation of AUB and a cost/benefit relation incompatible with current medicine. Therefore, it should not be the examination of first choice. Considering, however, that EAC was found in one of each 10 D&C in women >50 years with a complaint of uterine bleeding, D&C can be indicated with more liberality in that group, if hysteroscopy with directed biopsy is not available. Nowadays, D&C does not play such a significant a role in the diagnosis of AUB as it did some years ago. However, the procedure is still indicated in some situations and it cannot be abandoned, and its indication should obey restricted criteria.


