-
Review Article06-02-2021
SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Placental Pathology Infecção por SARS-CoV-2 e patologia placentária
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(6):474-479
Abstract
Review ArticleSARS-CoV-2 Infection and Placental Pathology Infecção por SARS-CoV-2 e patologia placentária
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(6):474-479
Views208See moreAbstract
Placental pathophysiology in SARS-CoV-2 infection can help researchers understand more about the infection and its impact on thematernal/neonatal outcomes. This brief review provides an overview about some aspects of the placental pathology in SARSCoV- 2 infection. In total, 11 papers were included. The current literature suggests that there are no specific histopathological characteristics in the placenta related to SARSCoV- 2 infection, but placentas frominfected women aremore likely to show findings of maternal and/or fetal malperfusion. The most common findings in placentas from infected women were fibrin deposition and intense recruitment of inflammatory infiltrates. The transplacental transmission of this virus is unlikely to occur, probably due to low expression of the receptor for SARS-CoV-2 in placental cell types. Further studies are needed to improve our knowledge about the interaction between the virus and the mother-fetus dyad and the impact on maternal and neonatal/fetal outcomes.
-
Systematic Review05-24-2021
Vertical Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):207-215
Abstract
Systematic ReviewVertical Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):207-215
Views201See moreAbstract
Objective
The evaluation of the available evidence on vertical transmission by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV)-2.
Data Sources
An electronic search was performed on June 13, 2020 on the Embase, PubMed and Scopus databases using the following search terms: (Coronavirus OR COVID-19 OR COVID19 OR SARS-CoV-2 OR SARS-CoV2 OR SARSCoV2) AND (vertical OR pregnancy OR fetal).
Selection of Studies
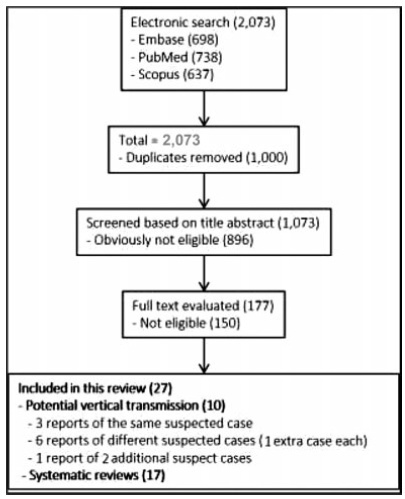
The electronic search resulted in a total of 2,073 records. Titles and abstracts were reviewed by two authors (WPM, IDESB), who checked for duplicates using the pre-established criteria for screening (studies published in English without limitation regarding the date or the status of the publication).
Data Collection
Data extraction was performed in a standardized way, and the final eligibility was assessed by reading the full text of the articles. We retrieved data regarding the delivery of the potential cases of vertical transmission, as well as themain findings and conclusions of systematic reviews.
Data Synthesis
The 2,073 records were reviewed; 1,000 duplicates and 896 clearly not eligible records were excluded. We evaluated the full text of 177 records, and identified only 9 suspected cases of possible vertical transmission. The only case with sufficient evidence of vertical transmission was reported in France.
Conclusion
The risk of vertical transmission by SARS-CoV-2 is probably very low. Despite several thousands of affected pregnant women, we have identified only one case that has fulfilled sufficient criteria to be confirmed as a case of vertical transmission. Well-designed observational studies evaluating large samples are still necessary to determine the risk of vertical transmission depending on the gestational age at infection.
-
Original Article05-24-2021
Comparison of Laboratory and Radiological Findings of Pregnant and Non-PregnantWomen with Covid-19
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):200-206
Abstract
Original ArticleComparison of Laboratory and Radiological Findings of Pregnant and Non-PregnantWomen with Covid-19
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):200-206
Views136See moreAbstract
Objective
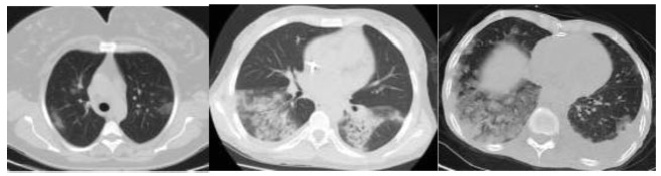
Covid-19 became a pandemic, and researchers have not been able to establish a treatment algorithm. The pregnant population is also another concern for health care professionals. There are physiological changes related to pregnancy that result in different laboratory levels, radiological findings and disease progression. The goal of the present article is to determine whether the laboratory results and radiological findings were different in non-pregnant women (NPWs) of reproductive age and pregnant women (PWs) diagnosed with the Covid-19 infection.
Methods
Out of 34 patients, 15 (44.11%) PWs and 19 (55.8%) NPWs were included in the study. Age, comorbidities, complaints, vitals, respiratory rates, computed tomography (CT) findings and stages, as well as laboratory parameters, were recorded from the hospital database.
Results
Themean age of the PWs was of 27.6 ± 0.99 years, and that of the NPWs was of 37.63 ± 2.00; when agewas compared between the groups, a statistically significant difference (p=0.001) was found. The mean systolic blood pressure of the PWs was of 116.53 ± 11.35, and that of the NPWs was of 125.53 ± 13.00, and their difference was statistically significant (p=0.05). The difference in the minimum respiratory rates of the patients was also statistically significant (p=0.05). The platelet levels observed among the PWs with Covid-19 were lower than those of the NPWs (185.40 ± 39.09 x 109/mcL and 232.00 ± 71.04 x 109/mcL respectively; p=0.05). The mean D-dimer value of the PWs was lower in comparison to that of the NPWs (p<0.05).
Conclusion
The laboratory findings and imaging studiesmay differ between pregnant and non-pregnant populations. It is important to properly interpret these studies. Future studies with a higher number of patients are required to confirm these preliminary data.
-
Review Article03-08-2021
COVID-19: Uncertainties from Conception to Birth
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(1):54-60
Abstract
Review ArticleCOVID-19: Uncertainties from Conception to Birth
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(1):54-60
Views144See moreAbstract
Scientific information on the impact of the new coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) on the health of pregnant women, fetuses and newborns is considered of limited confidence, lacking good-quality evidence, and drawing biased conclusions. As a matter of fact, the initial impressions that the evolution of COVID-19 was no different between pregnant and non-pregnant women, and that SARS-CoV-2 was not vertically transmitted, are confronted by the documentation of worsening of the disease during pregnancy, poor obstetric outcomes, and the possibility of vertical transmission. The present article aims to compile the data available on the association of COVID-19 and reproductive events, from conception to birth.
-
Review Article08-26-2020
Gynecological Surgery and COVID-19: What is the Impact and How Should I Manage it?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(7):415-419
Abstract
Review ArticleGynecological Surgery and COVID-19: What is the Impact and How Should I Manage it?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(7):415-419
Views196See moreAbstract
It is estimated that around 28 million surgeries will be postponed or canceled worldwide as a result of this pandemic, causing a delay in the diagnosis and treatment of more than 2 million cancer cases. In Brazil, both the National Health Agency (ANS) and National Health Surveillance Agency (ANVISA) advised the postponement of elective and non-essential surgeries, causing a considerable impact on the number of surgical procedures that decreased by 33.4% in this period. However, some women need treatment for various gynecological diseases that cannot be postponed. The purpose of this article is to present recommendations on surgical treatment during the COVID-19 pandemic.
-
Review Article08-26-2020
Covid-19 and Pregnancy: An Overview
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(7):420-426
Abstract
Review ArticleCovid-19 and Pregnancy: An Overview
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(7):420-426
Views180See moreAbstract
Since the World Health Organization (WHO) declared coronavirus infection (COVID-19) a Public Health Emergency of International Concern in January 2020, there have been many concerns about pregnant women and the possible effects of this emergency with catastrophic outcomes inmany countries. Information on COVID-19 and pregnancy are scarce and spread throughout a fewcase series, with no more than 50 cases in total. The present review provides a brief analysis of COVID-19, pregnancy in the COVID-19 era, and the effects of COVID-19 on pregnancy.
-
Special Article07-17-2020
Childbirth, Puerperium and Abortion Care Protocol during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(6):349-355
Abstract
Special ArticleChildbirth, Puerperium and Abortion Care Protocol during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(6):349-355
Views127See moreAbstract
The new coronavirus (severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2, SARSCoV- 2) is a virus that causes a potentially serious respiratory disease that has spread in several countries, reaching humans in all age groups, including pregnant women. The purpose of this protocol is to provide technical and scientific support to Brazilian obstetricians regarding childbirth, postpartum and abortion care during the pandemic.


