Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(6):325-332
07-17-2020
To evaluate the insertion of the hysteroscopic intratubal sterilization device for female sterilization concerning the technique and the feasibility.
Retrospective study with data collection of medical records of 904 patients who underwent device insertion between January and September 2016 in a public hospital in Rio de Janeiro (Brazil) with data analysis and descriptive statistics.
In 85.8% of the cases, the uterine cavity was normal, and themost commonlydescribed findings upon hysteroscopy were synechiae (9.5%). The procedure lasted an average of 3.56minutes (range: 1 to 10minutes), and the pain was considered inexistent or mild in 58,6% of the cases, mild or moderate in 32,8%, and severe or agonizing in less than 1% (0.8%) of the cases, based on a verbal scale ranging from 0 to 10. The rate of successful insertions was of 85.0%, and successful tubal placement was achieved in 99.5% of the cases. There were no severe complications related to the procedure, but transient vasovagal reactions occurred in 5 women (0.6%).
Female sterilization performed by hysteroscopy is a safe, feasible, fast, and well-tolerated procedure. The rates of successful insertions and tubal placements were high. There were few and mild adverse effects during the procedure, and there were no severe complications on the short term.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(6):294-308
06-01-2017
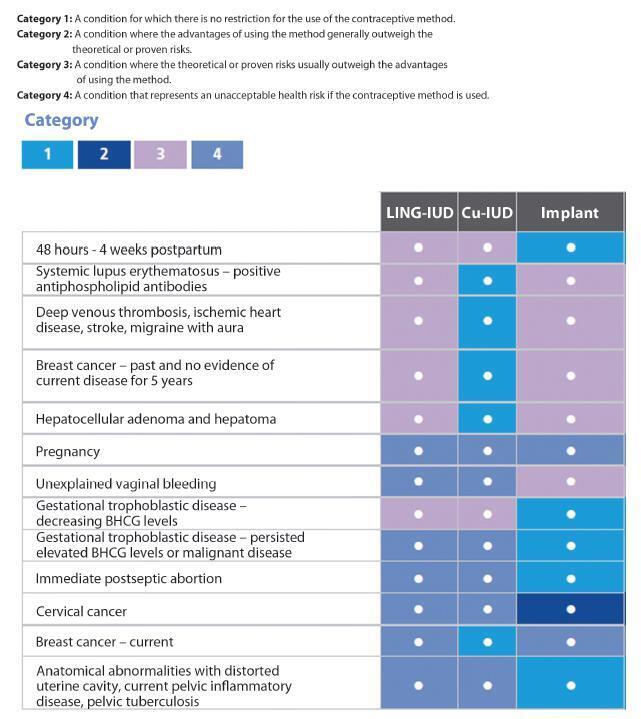
Unwanted pregnancy is a major public health problem both in developed and developing countries. Although the reduction in the rates of these pregnancies requires multifactorial approaches, increasing access to long-acting contraceptive methods can contribute significantly to change this scenario. In Brazil, gynecologists and obstetricians play a key role in contraceptive counseling, being decisive in the choice of long-acting reversible methods, characterized by intrauterine devices (IUDs) and the contraceptive implant. The vast scope due to the reduced number of situations to indicate long-acting methods should be emphasized in routine contraceptive counseling. On the other hand, gynecologists and obstetricians should adapt the techniques of insertion of long-acting methods, and engage in facilitating conditions to access these contraceptives through public and private health systems in Brazil. This study is part of a project called Diretrizes e Recomendações FEBRASGO (Guidelines and Recommendations of the FEBRASGO - Brazilian Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Associations from the Portuguese acronym). It aims to review the main characteristics of long-acting contraceptives and critically consider the current situation and future prospects to improve access to these methods, proposing practical recommendations of interest in the routine of gynecologists and obstetricians.