Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(9):539-547
09-30-2019
To describe a population of pregnant women diagnosed with toxoplasmosis and their respective newborns, describing the hospital protocol for treatment and follow-up.
Retrospective cohort of pregnant women with acute toxoplasmosis infection and risk of transplacental transmission who were sent to the Fetal Medicine Group of Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre (HCPA) between - January 1, 2006 and December 31, 2016. All patients with confirmed disease were included. The diagnostic protocol and treatment were applied; a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis of the amniotic fluid was used to diagnose toxoplasmosis and determine the treatment. The newborns were followed up at the pediatric outpatient clinic specializing in congenital infection. The patients who were not followed up or were not born in the HCPA were excluded.
A total of 65 patients were confirmed to have gestational toxoplasmosis; 40 performed amniocentesis, and 6 (15%) were identified as having positive PCR in the amniotic fluid. In five of those cases, this result associated with the gestational age defined the triple therapy during pregnancy, and in one case, it defined the monotherapy (advanced gestational age). A total of 4 of these newborns were treated from birth with triple therapy for 10months, 1 was not treated (due to maternal refusal), and 1 progressed to death within the first 54 hours of life due to complications of congenital toxoplasmosis. Of the 34 remaining cases with a negative PCR, 33 were treated with monotherapy and 1 was treated with triple therapy (ultrasound findings); of these children, 9 (26.5%) presented negative immunoglobulin G (IgG), 24 (70.6%) presented positive IgG (but none presented positive immunoglobulin M [IgM]), and 1 (2,9%) presented alterations compatible with congenital disease and started treatment with the triple therapy soon after birth. Out of the total sample of 60 patients, among the 25 who did not perform amniotic fluid PCR, 5 were treated with triple therapy (ultrasound findings/prior treatment) and 20 patients were submitted to monotherapy; only two newborns underwent treatment for congenital toxoplasmosis. Among the 65 cases of gestational toxoplasmosis, 6 (9,2%) children had a diagnosis of congenital toxoplasmosis, and 2 patients with triple therapy felt severe adverse effects of the medications.
The present study suggests that research on PCR screening of the amniotic fluid may be useful to identify patients with a higher potential for fetal complications, who may benefit from the poly-antimicrobial treatment. Patients with negative PCR results must continue to prevent fetal infection with monotherapy, without risk of fetal or maternal impairment.
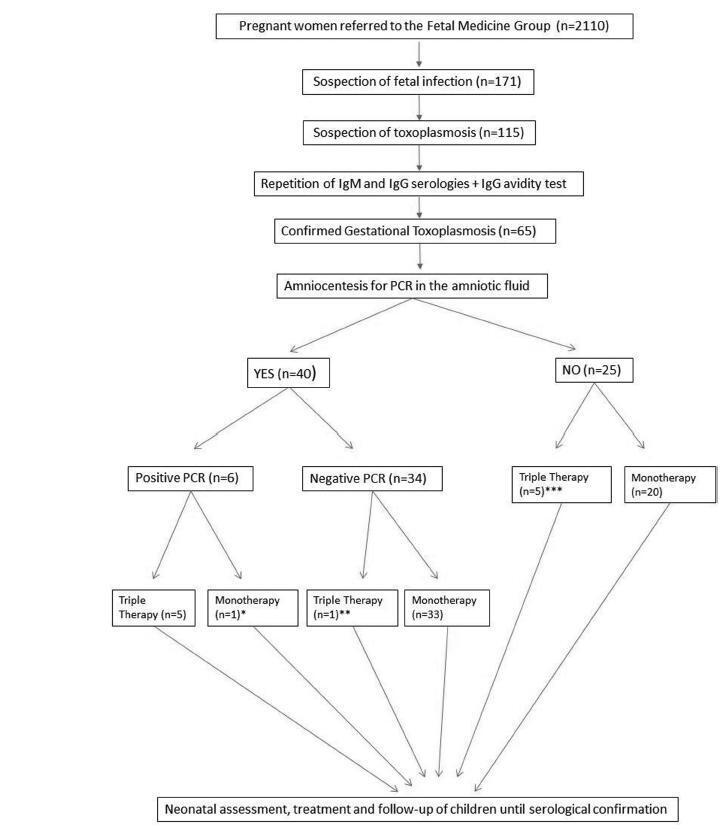
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(2):90-96
02-01-2019
The present study assessed epidemiological and obstetrical data from pregnant women with syphilis at the Hospital de Clínicas of the Universidade Federal do Triângulo Mineiro (UFTM, in the Portuguese acronym), describing this disease during pregnancy and its vertical transmission for future healthcare actions.
Records from pregnant women who had been admitted to the Obstetrics Department of the Hospital de Clínicas of the UFTM and were diagnosed with syphilis between 2007 and 2016 were reviewed. A standardized form was used to collect epidemiological, obstetric data and outcomes of congenital infection. The present research has been authorized by the Ethics Committee of the institution.
There were 268 women diagnosed with syphilis, with an average age of 23.6 years old. The majority of the patients were from Uberaba. Inadequate prenatal care was observed in 37.9% of the pregnant women. Only 34.2% of the patients completed the treatment according to the guidelines issued by the Ministry of Health of Brazil, and 19.8% of the partners of the patients underwent adequate syphilis treatment; 37 (13.8%) couples (patients and partners) underwent correct treatment. Regarding the obstetric outcomes, 4 (1.5%) patients had a miscarriage and 8 (3.4%) had fetal losses (from the fetal loss group, 7 had no adequate treatment); 61 (25.9%) patients had premature births - this prematurity has been significantly correlated to inadequate or incomplete treatment in 49 (27.9%) patients, compared with 12 (13.0%) patients with premature births and adequate treatment (p = 0.006). The average live newborn weight was 2,840 g; 25.3% had a birth weight < 2,500 g; 74.2% had congenital syphilis, a data with heavy correlation to inadequate or incomplete prenatal care, prematurity, and low birth weight.
Public awareness policies on adequate prenatal care, intensification of serological screening, and early treatment of syphilis are needed, considering the rise of cases diagnosed during gestation and its potentially preventable deleterious consequences related to congenital transmission.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(11):538-544
11-01-2016
Toxoplasmosis a parasitic zoonosis of global distribution, responsible for disorders during gestation can cause fetal death or congenital anomalies.
To evaluate the knowledge of toxoplasmosis among pregnant and postpartum women treated at the University Hospital of the city of Rio Grande, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil.
This was a cross-sectional study of 100 pregnant and postpartum women at the University Hospital. Participants answered a self-administered questionnaire and gave consent for data relating to serological examinations to be abstracted from their medical records.
The proportion of women who received information about toxoplasmosis was higher among those who received care in the private health care system (52.9%) than among those cared for in the public health care system (25.0%). Only 55.7% of women reported having some knowledge about toxoplasmosis. Of these, 53.7% received information during the prenatal period. However, most participants were unable to answer questions about preventive measures and modes of infection. Of the 100 patients in the study, only 46 underwent serologic testing for toxoplasmosis, 65.2% of whom tested negative (IgG).
Findings from this study are relevant to the training of health professionals regarding toxoplasmosis education and prevention. Improved education for health care providers and patients can lead to earlier diagnoses and reductions in adverse outcomes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(12):719-725
04-13-2005
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001200003
PURPOSE: to evaluate the prevalence, epidemiological profile (age and origin) and vertical transmission rate of HTLV I/II infection in pregnant women screened by the Pregnant Protection Program of the State of Mato Grosso do Sul Brazil. METHODS: it is a descriptive and transversal study of 32,512 pregnant women submitted to a prenatal screening from November 2002 to October 2003. HTLV I/II infection was diagnosed in all pregnant women by ELISA, confirmed by Western blot and PCR. Congenital HTLV infection was investigated by ELISA test, Western blot and PCR performed on the child's blood sample. The associations between data (age, origin and HTLV infection) were statistically analyzed by the chi2 test considering p<0.05 to reject the null hypothesis. RESULTS: a prevalence of 0.1% (37) 0.1% HTLV I/II among 32,512 pregnant women was found. The mean age of the infected women was 25.4 ± 6.4 years, and 78.4% of them were from other areas than the capital. There was no association between maternal age and the patients' origin and infection. In all the eight evaluated newborns, which represented 21.6% of the sample, HTLV I/II serum antibodies were found. Only one newborn infant was breast-fed. CONCLUSIONS : HTLV I/II prevalence among pregnant women of the State of Mato Grosso do Sul Brazil was lower than the rates reported by endemic HTLV countries. This rate was almost the same as that described for non-endemic areas and in some Brazilian reports. The vertical transmission rate of HTLV I/II was 100%, in spite of breast-feeding having been proscribed. Improving the follow-up of the pregnant women and their newborns in the State is mandatory, since only a few infants were investigated.