Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(7):137-142
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000700004
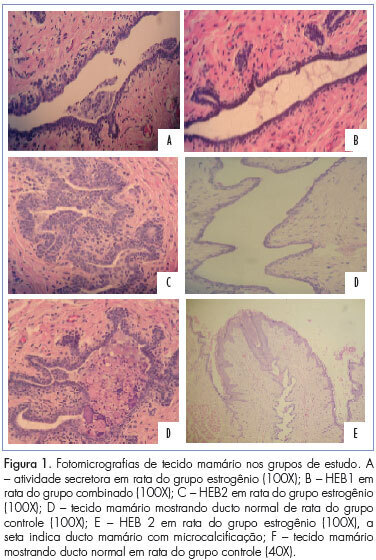
PURPOSE: To evaluate the efect of trimegestone on the histological changes of the mammary tissue of castrated rats. METHODS: Forty-five virgin female Wistar rats were used after oophorectomy. Sixty days after surgery, with hypoestrogenisms confirmed, the experimental rats were randomly assigned to three groups of 15 animals each, when then the specific treatment for each group was started. The control group (C) and experimental groups 1 and 2 respectively received 0.9% saline solution, 17-beta-estradiol and 17-beta-estradiol in combination with trimegestone for 60 consecutive days. After the end of treatment , the inguinal mammary glands were removed, stained with hematoxylin and eosin (HE) for morphometry and examined by immunohistochemistry for the quantification of anti-PCNA antibody in the mammary tissue, followed by euthanasia. The morphometric parameters evaluated were: epithelium cell-proliferation, secretor activity and mammary stroma changes. There were nine deaths during the experiment. The variables were submitted to statistical analysis adopting the 0.05 level of significance. RESULTS:Histological changes were observed in 16/36 rats, mild epithelial hyperplasia in 13/36, moderate epithelial hyperplasia in 3/36, with no cases of severe epithelial hyperplasia. Stromal fibrosis was found in 10/36 and secretory activity in 5/36 rats. All morphometric variables were significant in the estrogen group compared to control (p=0.0361), although there were no difference between the group receiving combined treatment and the controls (p=0.405). The immunohistochemical analysis showed no difference between groups. CONCLUSIONS:The hormones administered to castrated rats, i.e., 17 beta-estradiol alone or in combination with trimegestone, increased the proliferation of breast cells, but this effect appeared to be lower in the combined treatment, the same occurring regarding fibrosis of the mammary stroma.