-
Review Article
Are There Changes in the Fatty Acid Profile of Breast Milk with Supplementation of Omega-3 Sources? A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(3):128-141
03-01-2017
Summary
Review ArticleAre There Changes in the Fatty Acid Profile of Breast Milk with Supplementation of Omega-3 Sources? A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(3):128-141
03-01-2017Views134See moreAbstract
Purpose
To evaluate the effect of supplementation with omega-3 sources on the fatty acid composition of human milk.
Methods
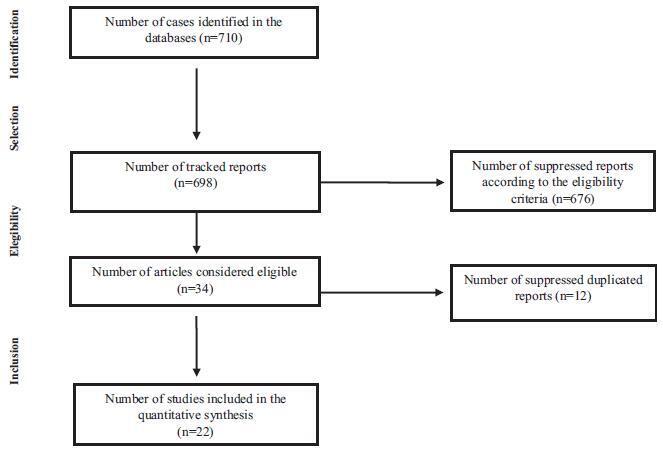
The review consisted of the search for articles published in PubMed, Biblioteca Virtual de Saúde (Virtual Health Library[VHL]) andWeb of Science databases using the following keywords: fatty acids, omega-3, human milk and supplementation; for this purpose, we have used the program of research to integrate the services for the maintenance of autonomy (PRISMA) checklist. The following selection criteria were used: articles in English, Portuguese, Spanish or Italian, published between 2000 and 2015, and about studies performed in humans. We found 710 articles that met the established criteria; however, only 22 of them were selected to be part of this study.
Results
All studies found a positive relationship between the consumption of omega- 3 sources and their concentration in humanmilk. The differences in the findings are due to the distinct methods used, such as the specific time of the omega-3 supplementation, the type of omega-3 source offered, as well as the sample size.
Conclusion
Although the studies were different in several methodological aspects, it was possible to observe the importance of omega-3 supplementation during gestation and/or the puerperium.
-
Case Report
Lactation Induction in a Commissioned Mother by Surrogacy: Effects on Prolactin Levels, Milk Secretion and Mother Satisfaction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):86-89
02-01-2017
Summary
Case ReportLactation Induction in a Commissioned Mother by Surrogacy: Effects on Prolactin Levels, Milk Secretion and Mother Satisfaction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):86-89
02-01-2017Views100See moreAbstract
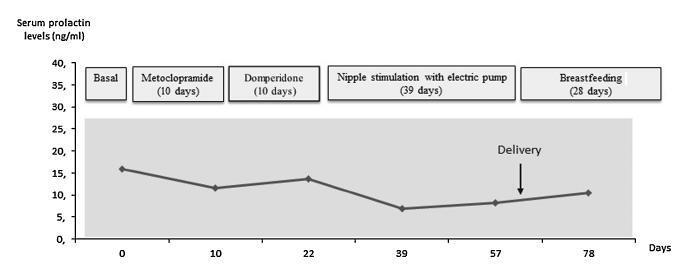
Case report of a 39-year-old intended mother of a surrogate pregnancy who underwent induction of lactation by sequential exposure to galactagogue drugs (metoclopramide and domperidone), nipple mechanical stimulation with an electric pump, and suction by the newborn. The study aimed to analyze the effect of each step of the protocol on serum prolactin levels, milk secretion and mother satisfaction, in the set of surrogacy. Serum prolactin levels and milk production had no significant changes. Nevertheless, themother was able to breastfeed for four weeks, and expressed great satisfaction with the experience. As a conclusion, within the context of a surrogate pregnancy, breastfeeding seems to bring emotional benefits not necessarily related to an increase in milk production.
-
Artigos Originais
The influence of breastfeeding in postpartum oral glucose tolerance test in women with recent gestational diabetes mellitus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):565-570
12-01-2015
Summary
Artigos OriginaisThe influence of breastfeeding in postpartum oral glucose tolerance test in women with recent gestational diabetes mellitus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):565-570
12-01-2015DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005488
Views79See moreAbstract
PURPOSE:
To determine the influence of breastfeeding on the results of a postpartum oral glucose tolerance test in women recently diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus.
METHODS:
The data were obtained from the electronic medical records of the Endocrinopathy Sector during pregnancy, HCMED laboratory system ofHospital das Clínicas of São Paulo , and by telephone. According to the inclusion criteria adopted, 132 patients were eligible for the study. For statistical analysis, the patients were divided into two groups according to whether or not they breastfed. The results were analyzed by the Student t-test and by the Mann-Whitney, Chi-square and Fisher's exact tests, depending on the variable analyzed, with the level of significance set at p<0.05.
RESULTS:
Of the 132 patients included in the study, 114 breastfed and 18 did not. Most of the patients in both groups were overweight or obese. The breastfeeding group had a lower pre-pregnancy Body Mass Index than the non-breastfeeding group (p=0.006). Insulin was introduced earlier in the group that did not breastfeed (23.21±4.33 versus 28.84±6.17; p=0.04). The group that did not breastfeed had a higher mean postpartum fasting glucose value in the oral glucose tolerance test than the group that breastfed (91.3±8.7 versus 86.5±9.3; p=0.01). Breastfeeding acted as a protective factor against the development of glucose intolerance in the postpartum oral glucose tolerance test (OR=0.27; 95%CI 0.09-0.8). By logistic regression, breastfeeding was shown to be an independent protective factor.
CONCLUSION:
There was a statistically significant relationship between breastfeeding and a decreased risk of developing glucose intolerance. Breastfeeding should be encouraged because it is an effective, low cost intervention easily accessible to all patients during the postpartum period.
-
Trabalhos Originais
Puerperal Mastitis: Study of Predisposing Factors
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(10):627-632
07-23-2000
Summary
Trabalhos OriginaisPuerperal Mastitis: Study of Predisposing Factors
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(10):627-632
07-23-2000DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000001000005
Views56Purpose: to investigate clinical and bacteriological aspects, follow-up and treatment of mastitis in our clinic. Methods: this study was performed at Cleriston Andrade General Hospital. Patients were interviewed regarding personal data, prenatal care, care received during delivery and puerperium and clinical aspects. Their mastitides were classified by Vinha's criteria. The patients with abscesses had them drained for bacteriological study. Culture medium Tryptone Soya Broth was used. Results: seventy nursing mothers were interviewed; 57% of them had given birth for the first time, 57% were between 20 and 29 years old, 51% had not finished elementary school, 63% had income less than the minimum wage, 66% of them had nobody to help with the housework. Out of the seventy females, 50% had not had their breasts examined. Approximately half of them had not been told how to breastfeed (50%) or how to express breast milk (58%). Sixty-three percent had not delivered in institutions designated by WHO as "Children's Friends Hospitals". Engorgement occurred in 46% of the cases and nipple fissures in 47%. According to Vinha's criteria, 44% had lobar, 39% ampular and 17% glandular locations. Presence of Staphylococcus aureus was detected in 55% of the cases. Conclusion: factors such as low schooling, low incomes, no assistance in housework, giving birth for the first time and lack of professional help contributed to occurrence of mastitis.
Key-words BreastfeedingPuerperal infectionSee more


