Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(12):602-608
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001200003
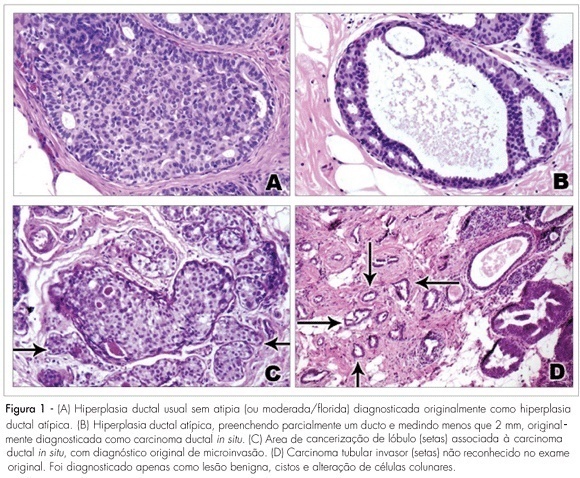
PURPOSE: to evaluate the agreement between histopathologic diagnoses of breast lesions made by general pathologists and by a specialist in breast pathology. METHODS: a cohort retrospective study comparing histopathologic diagnoses of 329 cases of breast lesions received in consultation for a second opinion was carried out. The material received for consultation included slides (152 cases), paraffin blocks (59 cases) or slides and blocks (118 cases). Cases were reviewed and the original diagnoses and diagnoses from a specialist in breast pathology were compared. The main diagnoses, nuclear grade of ductal carcinoma in situ, and the histopathologic grade of invasive mammary carcinomas were evaluated. The kappa index and percentual concordance were used in the statistical analyses. RESULTS: a moderate agreement was observed between the original histopathologic diagnoses and the second opinion (kappa index=0.48; percentual concordance=59.9%). The diagnosis of malignancy was confirmed in 185/225 cases (82.2%) and diagnosis of benign lesions was confirmed in 89/104 cases (85.6%). The highest agreement was observed in the diagnosis of invasive mammary carcinomas (81%) and the highest disagreement was observed among diagnoses of ductal carcinoma in situ with microinvasion (74%), lobular carcinoma in situ (70%), and atypical epithelial hyperplasias (61%). There was a moderate agreement in the nuclear grade of ductal carcinoma in situ (kappa index=0.52; percentual concordance=68.8%), and good concordance in the histologic grade of invasive carcinomas (kappa index=0.61; percentual concordance=74.3). CONCLUSIONS: the results show higher concordance rate in the diagnosis of invasive carcinomas and lower concordance in the diagnosis of ductal carcinoma in situ with microinvasion and premalignant breast lesions, especially lobular neoplasia in situ, and atypical epithelial hyperplasias.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(4):177-181
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000400004
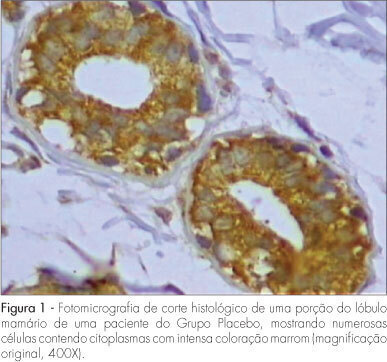
PURPOSE: to evaluate the expression of Bax antigen in the normal mammary epithelium of premenopausal women treated with raloxifene. METHODS: a randomized double-blind study was conducted in 33 ovulatory premenopausal women with fibroadenoma. Patients were divided into two groups: Placebo, (n=18) and Raloxifene 60 mg, (n=15). The medication was used for 22 days, beginning on the first day of the menstrual cycle. An excisional biopsy was carried out on the 23rd day of the menstrual cycle and a sample of normal breast tissue adjacent to the fibroadenoma was collected and submitted to immunohistochemical study using anti-Bax polyclonal antibody to evaluate the expression of Bax protein. Immunoreaction for Bax was evaluated taking into consideration intensity and fraction of stained cells, whose combination resulted in a final score ranging from 0 to 6. Cases with a final score >3 were classified as positive for Bax. The c2 test was used for statistical analysis (p<0.05). RESULTS: the percentage of positivity of Bax protein expression was 66.7 and 73.3% in Groups A and B, respectively. There was no significant difference in Bax expression between the two groups (p=0.678). CONCLUSIONS: raloxifene, administered for 22 days in the dose of 60 mg/day, did not alter the expression of Bax protein in the breast normal tissue of premenopausal women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(2):67-74
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000200004
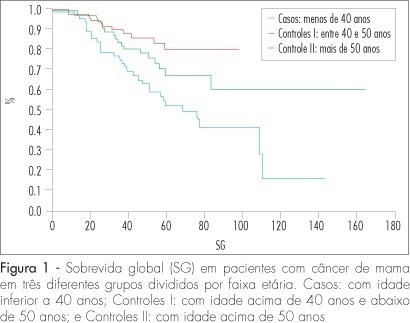
PURPOSE: to compare the epidemiologic and clinical characteristics, and the follow-up of breast cancer in women diagnosed under and over 40 years of age. METHODS: a retrospective study, case-control type, with analysis of information obtained from medical records of patients attended from January 1994 to June 2004. Cases of intraductal carcinoma and at stage IV were excluded. Three groups were formed: patients under 40 years old at the diagnosis (n=72); patients between 40 and 50 (n=68) and patients over 50 (n=75). Data about age at the moment of diagnosis, lesion largest diameter, clinical stage, type, histological grade, presence of hormonal receptors and state of the lymph nodes were collected and analyzed. The chi2 test was used for qualitative variables. For quantitative variables without normal distribution (such as number of axillary nodes with metastasis and follow-up duration), the Kruskal-Wallis' test was used. For delineating the curves of free-of-disease and global survival, the log-rank test was used. RESULTS: there was no difference among the groups in the stage distribution, concerning the tumoral differentiation grade or in the distribution of histological types, and in the estrogen receptor and c-erb-B2 expression. Difference was found in the RP expression, which was less frequent in the group of patients under 40, than in the group of patients over 50 (36.2% versus 58.4%) respectively. There was no difference among the groups in the mean tumoral diameter (5.1, 4.7 and 5 cm, respectively). There was also no difference among the groups, concerning the rate of axillary lymph node metastasis (63.9, 46.9 and 50%, respectively). The average follow-up was 54 months for all the groups. Disease recurrence occurred in 22.6% of patients under 40 years old, in 60% of patients between 40 and 50, and in 22.6% of patients over 50, with a significant difference among groups (p<0.0001). Death caused by the disease was higher among patients under 40 (46.9%) than among patients between 40 and 50 (26.9%) and over 50 (22.6%), p=0.0019. The logistic analysis showed that "age under 40" and the "presence of more than one metastatic axillary node" were independent death risk factors. CONCLUSIONS: age under 40 is an independent risk factor for breast cancer. The traditional prognostic indicators, such as stage, tumoral diameter, axillary involvement and presence of hormonal receptors are not associated with the disease evolution.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(1):42-47
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000100008
Breast cancer is the principal cause of death from cancer in women. Molecular studies of breast cancer, based in the identification of the molecular profiling techniques through cDNA microarray, had allowed defining at least five distinct sub-group: luminal A, luminal B, HER-2-overexpression, basal and " normal" type breast-like. The technique of tissue microarrays (TMA), described for the first time in 1998, allows to study, in some samples of breast cancer, distinguished by differences in their gene expression patterns, which provide a distinctive molecular portrait for each tumor and the basis for and improved breast cancer molecular taxonomy. Another important implication is that genetic profiling may lead to the identification of new target for therapy and better predictive markers are needed to guide difficult treatment decisions. Additionally, the current pathology classification system is suboptimal, since patients with identical tumor types and stage of disease present different responses to therapy and different overall outcomes. Basal breast tumor represents one of the most intriguing subtypes and is frequently associated with poor prognosis and absence of putative therapeutic targets. Then, the purpose of this review was to resume the most recent knowledge about the breast carcinoma classification and characterization.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(12):608-613
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001200002
PURPOSE: to assess the accuracy (rate of correct predictions) of stereotactic core needle biopsy (CNB) of risk category BI-RADS® 4 breast lesions. METHODS: a retrospective analysis of category BI-RADS® 4 breast lesions that had been submitted to a stereotactic core-needle biopsy from June 1998 to June 2003. Patients with histological benign results consistent with the radiographic image were referred to mammographic follow-up. Patients with malign diagnosis and papillary lesions were submitted to standard specific treatment. Excisional biopsies were performed when results were benign, but in disagreement with the mammographic image. It was considered as a gold-standard attendance: (1) the mammographic follow-up of low suspicion lesions with benign results at CNB, which stayed unchanged for, at least, three years, and (2) surgical resection when specimen results were malign or benign, but with a high suspicion on mammography. Sensitivity (S) specificity (E) and overall accuracy of stereotactic CNB were statistically analyzed. RESULTS: among the 118 non-palpable lesions of category BI-RADS® 4 submitted to CNB, the results obtained were: 27 malign cases, 81 benign, and ten lesions with atypical or papillary lesions. The statistical analysis comprised 108 patients (atypical and papillary lesions were excluded). CNB sensitivity was 87.1% and specificity 100%. The positive predictive value was 100% and the negative, 95.1%. False negatives occurred in 3.7% (4/108) of cases. The prevalence of malign diagnostics in the BI-RADS® 4 lesions of this sample was 29.7 (31/118).The accuracy of this method in this casuistic was 96.3%. CONCLUSIONS: these results support stereotactic CNB as an extremely reliable alternative to open biopsy, in the diagnosis and definition of breast lesions. In positive results, it is possible to indicate the appropriate therapy, and, in negative (when mammography shows low suspicion), it allows a follow up.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(12):625-632
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001200005
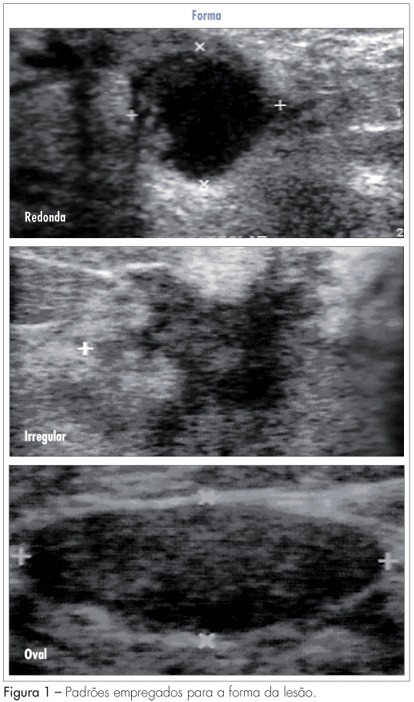
PURPOSE: to analyze which characteristics proposed by the BIRADS lexicon for ultrasound have the greatest impact on distinguishing between benign and malignant lesions. METHODS: ultrasonography features from the third edition of the BIRADS were studied in 384 nodes submitted to percutaneous biopsy from February 2003 to December 2006, at the Medical School of Botucatu. For the ultrasonography, the equipment Logic 5 with a 7.5-12 MHz multifrequential linear transducer was used. The ultrasonography analysis of the node considered the features proposed by the BIRADS lexicon for ultrasound. The data were submitted to statistical analysis by the logistic regression model. RESULTS: the benign lesions represented 42.4% and the malignant, 57.6%. The logistic regression analysis found an odds ratio (OR) for cancer of 7.69 times when the surrounding tissue was altered, of 6.25 times when there were microcalcifications in the lesions interior, of 1.95 when the acoustic effect is shadowing, of 25.0 times when there was the echogenic halo, and of 7.14 times when the orientation was non-parallel. CONCLUSIONS: among the features studied, the lesion limit, represented by the presence or not of the halogenic halo, is the most important differentiator of the benign from the malignant masses.