Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(10):492-495
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009001000004
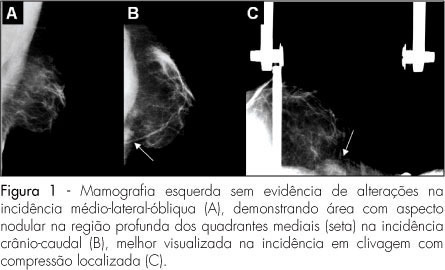
PURPOSE: to report a series of three cases of a normal variation known as sternal muscle, simulating a breast lesion. METHODS: the diagnostic suspicion was based on the clinical picture, findings in the physical examination and imaging, being confirmed by sectional imaging methods such as computerized tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). A review of the literature has been made in the data Medline and in breast radiology textbooks about the anatomic, clinical and imaging aspects of the sternal muscle. RESULTS: three female patients, without complaints, who presented nodular breast lesions in the medial quadrants projection (two in a routine mammographic exam and one in a computerized tomography). The diagnosis of sternal muscle was confirmed through breast MRI or through thoracic CT, showing an elongated image in the left parasternal region, adjacent to the breast muscle. CONCLUSIONS: the sternal muscle is an unusual variation of the muscles of the thoracic wall, present in about 2 to 8% of the population. The knowledge of this entity is crucial, as it can simulate a breast node.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(9):461-467
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000900007
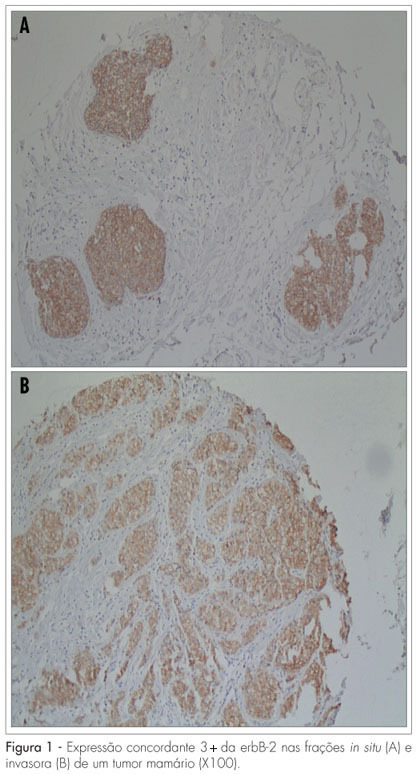
PURPOSE: to evaluate the expression of erbB-2 and of the estrogen and progesterone (ER/P) hormonal receptors in the transition regions between the in situ and the invasive fractions of ductal breast neoplasia (ISDC and IDC, respectively). METHODS: Eighty-five cases of breast neoplasia, containing contiguous ISDC and IDC areas, were selected. Histological specimens from the ISDC and the IDC areas were obtained through the tissue microarray (TMA) technique. The erbB-2 and the ER/PR expressions were evaluated through conventional immunohistochemistry. The McNemar's test was used for the comparative analysis of the expressions of erbB-2 protein and the ER/PR in the in situ and invasive regions of the tumors. The confidence intervals were set to 5% (p=0.05). Intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) were calculated to assess the cross-tabulation agreement of the erbB-2 and the ER/PR expression in the ISDC and the IDC areas. RESULTS: the erbB-2 expression has not differed between the ISDC and the IDC areas (p=0.38). Comparing the two areas in each case, there was agreement in the expression of erbB-2 (ICC=0.64), PR (ICC=0.71) and ER (ICC=0.64). Restricting the analysis to tumors with the in situ component harboring necrosis (comedo), the ICC for erbB-2 was 0.4, compared to 0.6 for the whole sample. In this select group, the ICC for PR/ER did not differ substantially from those obtained with the complete dataset: as for the ER, ICC=0.7 (versus 0.7 for the entire sample) and for PR, ICC=0.7 (versus 0.6 for the entire sample). CONCLUSIONS: our findings suggest that the erbB-2 and the ER/PR expressions do not differ in the contiguous in situ and invasive components of breast ductal tumors.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(7):361-366
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000700007
PURPOSE: to identify sensitivity alteration in the intercostal brachial nerve pathway using an extensiometer, and to observe the measurement reproducibility of the apparatus. METHODS: the Semmes-Weinstein extensiometer was used to evaluate the sensitivity along the intercostal brachial nerve pathway. Ninety-four women have participated in the study, divided into two groups: a CA Group composed of 47 women submitted to breast cancer axillary lymphadenectomy, and a comparative group composed of 47 women without breast cancer, who had not been submitted to any kind of axillary surgery. Each participant underwent anamnesis and two consecutive applications of the extensiometer. The Control Group responses to the extensiometer test were used as normality reference values. RESULTS: based on Control Group responses, the prevalence of sensitivity changes was 85.1% in the CA Group. Reproducibility of the extensiometer application was confirmed in the CA Group through the Kappa's test (p=0.8). CONCLUSIONS: in this studied sample, sensitivity alterations had high prevalence; evaluations made with the extensiometer were reproducible, and thus we consider the equipment reliable to evaluate sensitivity along the intercostal brachial nerve pathway.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(5):224-229
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000500004
PURPOSE: to identify the pattern of myoelectrical activity of muscles from the scapular region, after axillary lymphadenectomy in breast cancer. METHODS: prospective cohort study including all the women submitted to axillary lymphadenectomy for surgical treatment of breast cancer, in a breast cancer reference center, from June to August 2006. The women were evaluated before, and after 3 and 12 months from the surgery, through physical and electromyographic examinations of the serratus anterior, upper trapezius and middle deltoid muscles. RESULTS: the patients' average age was 60.3 years old (DP±14.1), and the incidence of winged scapula at the physical examination was 64.9%. At the third-months evaluation, a reduction of 28.3 µV was observed in the myoelectrical activity of the serratus anterior muscle. At the twelveth-months evaluation and between the 3rd and the 12th month, there was an increment of 23.3 µV and 43.6 µV, respectively. For the upper trapezius, the increase was of 23.1 µV at the third-months evaluation, and 23.3 µV and 43.6 µV between the 3rd and the 12th months. As compared to before the surgery, the evaluation of the middle deltoid muscle did no present significant differences. CONCLUSIONS: considering muscle activity evaluated by surface electromyography, there was a decrease in the myoelectrical activity of the serratus anterior, due to lesion of the long thoracic nerve (neuropraxia), in the immediate postoperative evaluation. The increase of the mean square root of the electromyographic signal of the upper trapezius muscle, since the preoperative evaluation, suggests a muscular compensation related to the serratus anterior muscle's deficit.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(5):219-223
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000500003
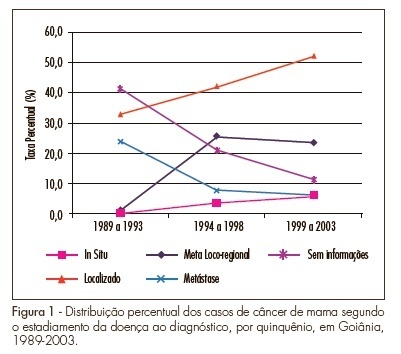
PURPOSE: To analyze the temporal changes of breast cancer staging at diagnosis among women living in Goiânia, Goiás, Brazil, between 1989 and 2003. METHODS: Retrospective and descriptive study in which the cases were identified from the Population-Based Cancer Registry of Goiânia for the period from 1989 to 2003. The variables studied were age, diagnostic method, topographic sublocation, morphology and breast cancer staging. Frequency analyses were carried out on the variables and means, and the medians for the age were determined. The SPSS® 15.0 software was used for statistical analyses. RESULTS: A total of 3,204 breast cancer cases were collected. The mean age was 56 years (sd±16 years). With regard to clinical staging, 45.6% of the cases were found to be localized in the breast, with an increased rate of 19.25% between the first and the third five-year period (p<0.001; CI 95%=0.14-0.23) and 10.2% of cases were with distant metastases. However, a reduction of 17.74% for metastatic cases in the same interval (p<0.001 e CI 95%=0.14-21) was observed. The in situ case rate was 0.2% in 1989-1993 and increased to 6.2% in 1999-2003 (p<0.001, IC95%=4.9-7.4). CONCLUSION: The diagnostic profile of breast cancer in the city of Goiânia is changing. Substantial increases in the number of early breast cancer cases are being found in relation to the number of advanced cases.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(2):61-67
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000200003
PURPOSE: to evaluate the quality of life and sexuality features of women with breast cancer, according to the type of surgery they underwent and their sociodemographic characteristics. METHODS: transversal study with 110 women treated for breast cancer, for at least one year in the Centro de Atenção Integral à Saúde da Mulher of UNICAMP. The quality of life was assessed by the WHOQOL-bref questionnaire, and the issues on sexuality, by a specific questionnaire in which Cronbach's Alpha coefficient was used to validate the concordance of responses (alpha=0.72) and the technique of factor analysis, with the criterion of self value and variance maximum rotation, resulting in two components: intrinsic or intimacy ( how the woman sees herself sexually) and extrinsic or attractiveness (how the woman believes the others see her sexually). Sociodemographic variables have been assessed according to the WHO questionnaire, and the sexuality components, through the Kruskal-Wallis followed by the Mann-Whitney's test and Spearman correlation test. RESULTS: age, schooling, type of surgery and lapse of time from the surgery did not influence the quality of life concerning physical, environmental, and psychological aspects, as well as the social relationships. Women with a stable marital relationship got higher scores in the psychological area (p=0.04) and in the area of social relationships (p=0.02). Higher socioeconomic level influenced the quality of life concerning physical appearance (p=0.01) and environment (p=0.002). Regarding the sexuality, age had influence in the extrinsic component (p=0.0158). Women with a stable marital relationship had higher scores of quality of life in both components of sexuality. Higher schooling influenced in a positive way the intrinsic factor. Women submitted to quadrantectomy or mastectomy with immediate breast reconstruction showed higher scores relating to attractiveness in comparison to mastectomized women without reconstruction. CONCLUSIONS: better socioeconomic level and better schooling, stable marital relationship and surgery with breast conservation are linked to better rates of quality of life, including sexuality.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(2):54-60
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000200002
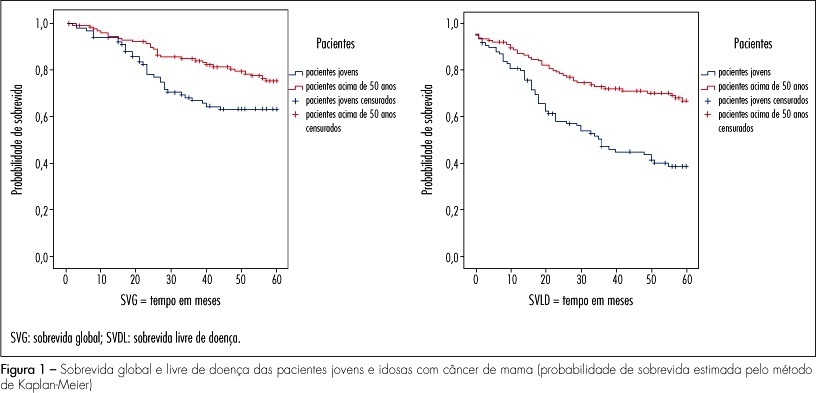
PURPOSE: the objective of this study was to evaluate the clinical, pathological and molecular characteristics in very young women and postmenopausal women with breast cancer. METHODS: we selected 106 cases of breast cancer of very young women (<35 years) and 130 cases of postmenopausal women. We evaluated clinical characteristics of patients (age at diagnosis, ethnic group, family history of breast cancer, staging, presence of distant metastases, overall and disease-free survival), pathological characteristics of tumors (tumor size, histological type and grade, axillary lymph nodes status) and expression of molecular markers (hormone receptors, HER2, p53, p63, cytokeratins 5 and 14, and EGFR), using immunohistochemistry and tissue microarray. RESULTS: when comparing clinicopathologic variables between the age groups, younger women demonstrated greater frequency of nulliparity (p=0.03), larger tumors (p<0.000), higher stage disease (p=0.01), lymph node positivity (p=0.001), and higher grade tumors (p=0.004). Most of the young patients received chemotherapy (90.8%) and radiotherapy (85.2%) and less tamoxifen therapy (31.5%) comparing with postmenopausal women. Lower estrogen receptor positivity 49.1% (p=0.01) and higher HER2 overexpression 28.7% (p=0.03) were observed in young women. In 32 young patients (29.6%) and in 20% of the posmenopausal women, the breast carcinomas were of the triple-negative phenotype (p=0.034). In 16 young women (50%) and in 10 postmenopausal women (7.7%), the tumors expressed positivity for cytokeratin 5 and/or 14, basal phenotype (p=0.064). Systemic metastases were detected in 55.3% of the young women and in 39.2% of the postmenopausal women. Breast cancer overall survival and disease-free survival in five years were, respectively, 63 and 39% for young women and 75 and 67% for postmenopausal women. CONCLUSIONS: breast cancer arising in very young women showed negative clinicobiological characteristics and more aggressive tumors.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(2):75-81
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000200005
PURPOSE: to evaluate the factors leading to delays in obtaining definitive diagnosis of suspicious lesions for breast cancer. METHODS: a cross-sectional, observational study was carried out with 104 women attending a cancer hospital with a diagnosis or suspected diagnosis of breast cancer. A semistructured questionnaire on the patients' demographic, clinical characteristics and the use of services was applied.Variables were compared using t-Student test, Mann-Whitney test, Pearson's χ2 test or Fisher's exact test, as appropriate. In order to identify the variables associated with delays in breast cancer diagnosis, the Odds Ratio (OR) were calculated together with their respective 95% confidence intervals (95%CI) and a logistic regression model was constructed. RESULTS: age of patients was 54±12.6 years (mean±standard deviation). Most of the women were white (48.1%), married (63.5%), living in the city of Rio de Janeiro (57.7%) and poorly educated (60.6%). The median time between the first sign or symptom of the disease and first consultation was one month and the mean time between first consultation and confirmation of diagnosis was 6.5 months. In 51% of the women, diagnosis was late (stages II-IV). Symptomatic presentation and longer delay between symptom onset and the first evaluation and between symptom onset and the diagnosis were found to be significant factors (p<0.05) for delays in obtaining definitive diagnosis of suspicious lesions. CONCLUSIONS: the results of this study suggest that efforts must be made to reduce the time needed to get an appointment with a doctor and to confirm a diagnosis of suspicious lesions, as well as to educate physicians and the women themselves regarding the importance of breast symptoms and the value of prompt evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment.