Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(4):204-209
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000400007
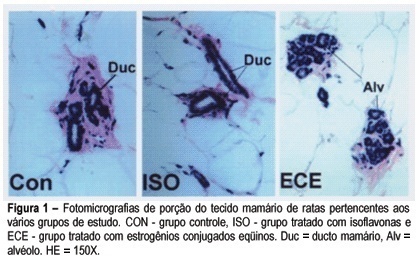
PURPOSE: to analyze the effects of isoflavones and estrogens on the morphology, morphometry and VEGF expression of the adult female rat mammary gland. METHODS: Forty-five adult female rats were oophorectomized; 28 days after surgery they were divided into 3 groups of 15 animals each: CON - control (treated with propylenoglycol); ISO - isoflavones (100 mg/kg) and CEE - conjugated equine estrogens (50 µg/Kg). Drugs or vehicle were given orally once a day for 60 days. After this, the animals were killed and the first pair of inguinal mammary glands was immediately removed; part of the material was processed for routine histological study and the remaining tissue was frozen for further analyses of the expression of VEGF mRNA by means of the RT-PCR technique. RESULTS: We observed that mammary ducts were atrophic in the control (CON) and isoflavone-treated (ISO) groups. In these groups the mammary glands were composed of a large concentration of adipose tissue with some ducts and rare alveolar structures. In the CEE group the ducts were well developed with many buds and alveolar structures. The number of mammary gland alveoli was higher in CEE than in the other groups (CON = 1.4 ± 2.1; ISO = 1.6 ± 3.8; CEE = 12.3 ± 7.1 alveoli/mm²; p<0.05%); also, the cell volume was higher (CON = 14.9 ± 4.9; ISO = 11.4 ± 6.9; CEE = 27.4 ± 9.7 µm³, p< 0.05%). The same was observed with regard to the number of blood vessels (CON = 16.4 ± 1.5; ISO = 18.4 ± 2.1; CEE = 37.1 ± 4.1 vessels/mm², p< 0.05). The expression of VEGF in the CEE group was higher than in the other groups, which did not significantly differ from each other in this respect. CONCLUSION: Our data did not show any proliferation effect in the mammary tissue of adult oophorectomized rats treated with isoflavones (100 mg/kg) during 60 days.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(1):1-6
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000100002
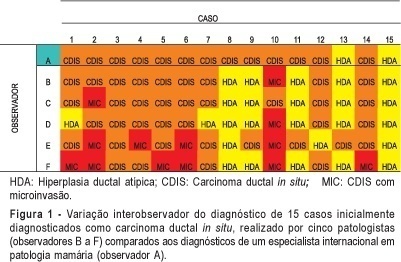
PURPOSE: to perform a critical evaluation of the histopathological diagnosis of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) of the breast, through the analysis of interobserver variation related to diagnosis, architectural pattern, nuclear grade, and histological grade. METHODS: eighty-five cases with an initial diagnosis of DCIS were reviewed by the same pathologist, specialist in breast pathology, who selected 15 cases for interobserver analysis. The analysis was carried out by five pathologists and an international expert in breast pathology, who received the same slides and a protocol for classifying the lesions as atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH), DCIS, or ductal carcinoma in situ with microinvasion (DCIS-MIC). If the diagnosis was DCIS, the pathologists should classify it according to the dominant architectural pattern, nuclear grade, and histological grade. The results were analyzed using percent concordance and the kappa test. RESULTS: there was a great interobserver diagnostic variation. In one case we had all diagnoses, from ADH, DCIS to DCIS-MIC. The kappa test for the comparison among the five observers' and the expert's diagnoses showed minimum interobservers' concordance (<0.40). Regarding DCIS classification related to the dominant architectural pattern and the histological grade, the kappa test values were considered poor among the pathologists. The best results were obtained for the nuclear grading, with a kappa index up to 0.80, considered as good concordance. CONCLUSION: the low index of interobserver concordance in diagnosis and classification of DCIS of the breast indicates the difficulty in using the most common diagnostic criteria of the literature and the need for specific training of non-specialist pathologists in breast pathology for the diagnosis of these lesions.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(3):227-232
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000300009
PURPOSE: to identify the risk factors associated with the occurrence of surgical site infection (SSI) in surgeries for the treatment of breast cancer. METHODS: the study was conducted on 140 women submitted to treatment of invasive breast cancer during the period from January 2001 to December 2002. SSI was defined as infection occurring up to 30 days after surgery and was related to the operation, according to the standard criteria adopted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), USA. SSI were considered to be superficial when they involved only the skin and subcutaneous tissue and deep when they involved deep tissues at the site of incision, such as fascia and muscles. The risk factors related to patient were age, hormonal status, staging, body mass index (BMI) and hemoglobin, and the factors related to surgery were type of operation, time of hospitalization, duration of surgery, and formation of seroma and hematoma. Data concerning numerical nonparametric variables were analyzed by the Mann-Whitney test and quantitative variables were analyzed by the Fisher exact test. RESULTS: of the 140 patients studied, 29 (20.7%) presented SSI, which were superficial in 19 (13.6%) and deep in 10 (71%); 111 patients did not present SSI and represented the control group. The risk factors associated with the patient and the disease were locally advanced stage (odds ratio = 27; 95% CI: 1.1-6.5) and obesity, represented by a mean BMI of 32.2 kg/m² in the patients with SSI and a mean BMI of 27.2 kg/m² in the control group (p<0.0001). The factors related to treatment of the disease were the use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy (odds ratio = 2.7 (95% CI: 1.1-6.5), the duration of surgery, whose median value was 165 minutes for the patients who developed the infection and 137 minutes for the control group (p=0.02), and the number of days of use of the postoperative drain, whose median value was 6 days for the patients with SSI and 5 days for the control group (p=0.048). CONCLUSION: on the basis of the identification of risk factors such as advanced stage, neoadjuvant chemotherapy and obesity, preoperative care for these patients should be emphasized. The use of an accurate surgical technique may reduce the impact of other factors such as surgical time and time of use of the drain.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(9):655-659
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000900006
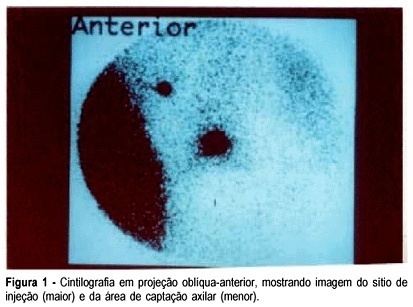
PURPOSE: to assess the simultaneous approach of radioguided occult lesion localization and sentinel lymph node biopsy in women with breast cancer. METHOD: forty-five patients with nonpalpable breast cancer were enrolled in a prospective study. The employed radiocolloid was 99mTc-labelled dextran. The injection was performed peritumorally under sonographic or stereotactic guidance using a 18 gauge needle. Lymphoscintigraph images for the visualization of both the site of injection and sentinel lymph node were obtained in a conventional gamma-camera, with the ipsilateral arm positioned in a 90º angle. Excision biopsy of the tumor and sentinel lymph node were performed with a gamma-detecting probe. RESULTS: the procedure was always successful in permitting the localization of occult breast lesions. It was necessary to enlarge surgical margins in five cases. Concerning the sentinel lymph node we achieved localization in 93% of the cases. No complications were observed. CONCLUSION: the results seems to demonstrate that a combined radioguided occult lesion localization and sentinel lymph node biopsy using the same radiopharmaceutical represents a useful and practicable strategy in the management of early breast cancer.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(7):429-433
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000700005
Purpose: to study the monoclonal antibody MIB-1 in the normal breast epithelium adjacent to a fibroadenoma in women in the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle treated with tamoxifen. Patients and methods: the proliferative activity of the mammary epithelium adjacent to the fibroadenoma was studied by immunohistochemistry based on immunoexpression of the monoclonal antibody MIB-1. The study was randomized and double blind and was conducted on 44 women with fibroadenomas, divided into 3 groups: A (n = 16; placebo), B (n = 15; tamoxifen, 10 mg), and C (n = 13; tamoxifen, 20 mg). Tamoxifen was administered for 22 days starting on the 2nd day of the menstrual cycle and a biopsy was taken on the 23rd day. Results: the mean percentage of stained nuclei per 1000 cells was 9.2 in group A, 4.5 in group B, and 3.2 in group C. Fisher's test revealed that tamoxifen significantly reduced the immunoexpression of MIB-1 at the doses of 10 and 20 mg compared to the placebo group (p<0.0001), with no significant differences between doses in terms of proliferative activity (p = 0.21). Conclusion: we conclude that tamoxifen significantly reduced the proliferative activity of the mammary epithelium at the doses of 10 and 20 mg/day.
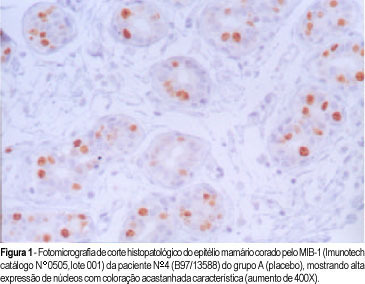
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(3):211-214
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000300011
The authors present a case of lymphangiosarcoma in the upper left limb of a 52-year-old patient previously submitted to a left-sided modified radical mastectomy followed by radiotherapy due to breast cancer six years earlier. This rare syndrome is associated with chronic lymphedema as a consequence of radical mastectomy followed by radiotherapy. Approximately 400 cases have been reported in the literature. The infrequent occurrence of this disease and the rather innocuous appearance of the tumor often lead to late diagnosis and treatment. In the present case, the diagnosis was based on an incision biopsy of the lesion and confirmed immunohistochemically using endothelial markers, antibodies (anti-CD31), vimentin and muscle actin. The patient's limb was amputated and no local or distant recurrence has so far been observed during 18 months of follow-up.
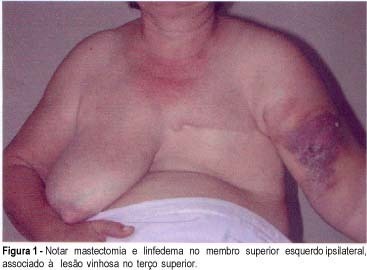
Summary
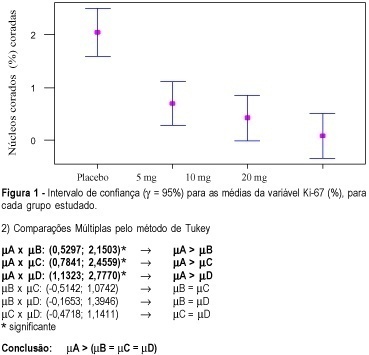
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(3):185-191
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000300007
PURPOSE: to quantitatively analyze the immunoreaction of monoclonal antibody Ki-67 in the mammary epithelium adjacent to fibroadenoma of premenopausal women treated with tamoxifen, for 50 days, at doses of 5, 10 and 20 mg/day. METHODS: we studied, prospectively, the effects of tamoxifen administered for 50 days, at doses of 5, 10 e 20 mg/day, by the immunoreaction of the Ki-67 (clone Ki-S5) monoclonal antibody on mammary epithelium adjacent to fibroadenoma in premenopausal women. We studied 58 patients in a double-blind trial who were divided into four groups: Group A (n=13; placebo), Group B (n=16; 5 mg/day tamoxifen), Group C (n=14; 10 mg/day) and Group D (n=15; 20 mg/day). All patients received the medication from the first day on of the menstrual cycle and biopsy was performed on the last day of the treatment. Cells stained and not stained by the immunoreagent were counted by optical microscopy (400X) with a digital image capturing system and image analysis. RESULTS: the average percentage of stained nuclei was calculated for all groups: Group A was 2.0 with a standard error (SE) of 0.3. In Group B it was 0.7 (SE=0.2); in Group C it was 0.4 (SE=0,2) and in Group D it was 0.1 (SE=0). Statistical analysis showed significant reductions between the groups (p<0.001), and Tukey's pairwise comparison test confirmed that there was a significant increase in the immunoreaction of the monoclonal Ki-67 antibody in groups B, C and D. CONCLUSIONS: tamoxifen, administered at doses of 5, 10 and 20 mg/day for 50 days, significantly reduced the immunoreaction of monoclonal Ki-67 in the mammary epithelium of premenopausal patients and there was no significant difference between the groups that received 5, 10 and 20 mg/day tamoxifen.