Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(6):287-292
06-01-2016
betatrophin has been reported to boost β cell expansion in insulin resistant states. Pregnancy is a well-recognized physiological state of insulin resistance. Betatrophin levels in pregnant women and their relationships with metabolic variables remain to be elucidated.
A total of 49 pregnant women and 31 age-matched unpregnant women with normal glucose regulation (UP-NGR) were included. Among these subjects, according to results from 75 g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), 22 women were diagnosed as having gestational diabetes mellitus ( GDM ).
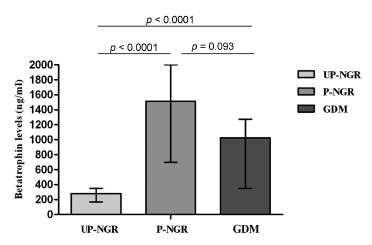
Our study found that pregnant women, regardless of their glucose regulation status, had remarkably higher triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), fasting insulin (FINS), homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) and homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function (HOMA-β). However, GDM patients had much lower HOMA-β compared with those of pregnant women with normal glucose regulation (P-NGR). Participants of the P-NGR group had almost 4 times higher levels of betatrophin than those of the UP-NGR group. Although betatrophin levels were lower in the GDM group than those of the P-NGR group, the difference did not reach statistical significance. Spearman correlation analysis showed that betatrophin levels were positively and significantly associated with total cholesterol, triglycerides, highdensity lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c), FINS and HOMA-β. However, adjustments of TC, TG and HDL-c eliminated the association between HOMA-β and betatrophin.
Pregnant women have significantly higher betatrophin levels in comparison to unpregnant women. Betatrophin levels are positively and significantly associated with β cell function and lipid levels. Furthermore, lipids may contribute to