Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(12):703-709
To investigate the action of testosterone (T), isolated or associated with estradiol benzoate (EB), on the proliferation markers and apoptosis of breasts of ovariectomized rats.
A total of 48 castrated female Wistar rats were divided into 6 groups, and each of them were submitted to one of the following treatments for 5 weeks: 1) control; 2) EB 50 mcg/day + T 50 mcg/day; 3) T 50mcg/day; 4) EB 50 mcg +T 300 mcg/day; 5) T 300 mcg/day; and 6) EB 50 mcg/day. After the treatment, the mammary tissue was submitted to a histological analysis and immunoexpression evaluation of proliferation markers (proliferating cell nuclear antigen, PCNA) and apoptosis (caspase-3).
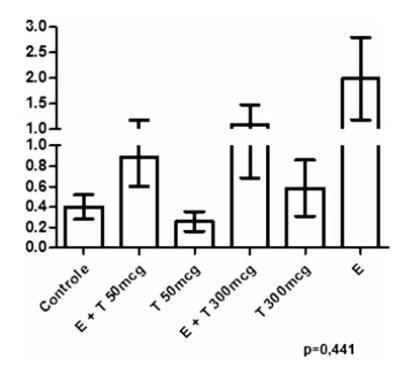
There was a statistically significant difference among the groups regarding microcalcifications and secretory activity, with higher prevalence in the groups treated with EB. There was no difference among the groups regarding atrophy, but a higher prevalence of atrophy was found in the groups that received T versus those that received EB +T. There was a difference among the groups regarding the PCNA (p = 0.028), with higher expression in the group submitted to EB +T 300 mcg/day. Regarding caspase-3, there was no difference among the groups; however, in the group submitted to EB +T 300 mcg/day, the expression was higher than in the isolated T group.
Isolated T did not have a proliferative effect on the mammary tissue, contrary to EB. Testosterone in combination with EB may or may not decrease the proliferation, depending on the dose of T.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(12):733-739
To determine the role of caspase-3, apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF), and Bcell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) expressions in term premature rupture of membrane (PROM).
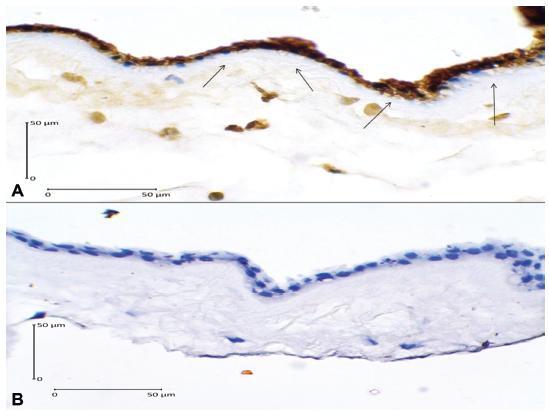
An analytic observational study with case-control design was conducted, involving 52 subjects (37-42 weeks of gestation) who were divided into 2 groups: 26 cases of term delivery with PROM, and 26 controls of term delivery without PROM. The expressions of caspase-3, AIF, and Bcl-2 in the amniotic membrane were determined by immunohistochemistry. Data were analyzed using the chi-squared test. The risk of PROM was expressed by odds ratio (OR).
There were no significant differences in age, parity and body mass index between the two groups (p > 0.05). High caspase-3 and AIF expressions increased the risk of PROM 17.64 times (OR = 17.64; 95% CI = 4.44-70.07; p = 0.001) and 9.45 times (OR = 9.45; 95% CI= 2.62-34.07; p = 0.001), respectively, while low Bcl-2 expression increased 10.39 times (OR = 10.39; 95% CI = 2.73-39.56; p = 0.001)the risk of PROM .
High caspase-3 and AIF expressions and low Bcl-2 expression were risk factors for term PROM. Caspase-dependent and independent pathways of apoptosis were involved in the mechanism of PROM in term pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(8):450-457
The present study aims to investigate the association between caspase-8 (CASP8) (rs13416436 and rs2037815) and Fas cell surface death receptor (FAS) (rs3740286 and rs4064) polymorphisms with endometriosis in Brazilian women.
In the present case-control study, 45 women with a diagnosis of endometriosis and 78 normal healthy women as a control group were included. The genotyping was determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with Taqman hydrolysis probes (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Darmstadt, Germany). Genotypic and allelic frequencies were analyzed using Chi-squared (χ2) test. In order to determine the inheritance models and haplotypes ,SNPStats (Institut Català d’Oncologia, Barcelona, Spain) was used. Levels of 5% (p = 0.05) were considered statistically significant.
No significant difference was observed in genotypic or allelic frequencies between control and endometriosis groups for rs13416436 and rs2037815 (CASP8 gene). On the other hand, a significant difference between rs3740286 and rs4064 (FAS gene) was found. Regarding polymorphisms in the FAS gene, a statistically significant differencewas found in co-dominant and dominantmodels. Only the haplotype containing the rs3740286A and rs4064G alleles in the FAS gene were statistically significant.
The polymorphisms in the CASP8 gene were not associated with endometriosis. The results indicate an association between FAS gene polymorphisms and the risk of developing endometriosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(6):283-290
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005292
To determine the basic expression of ABC transporters in an epithelial ovarian cancer cell line, and to investigate whether low concentrations of acetaminophen and ibuprofen inhibited the growth of this cell line in vitro.
TOV-21 G cells were exposed to different concentrations of acetaminophen (1.5 to 15 μg/mL) and ibuprofen (2.0 to 20 μg/mL) for 24 to 48 hours. The cellular growth was assessed using a cell viability assay. Cellular morphology was determined by fluorescence microscopy. The gene expression profile of ABC transporters was determined by assessing a panel including 42 genes of the ABC transporter superfamily.
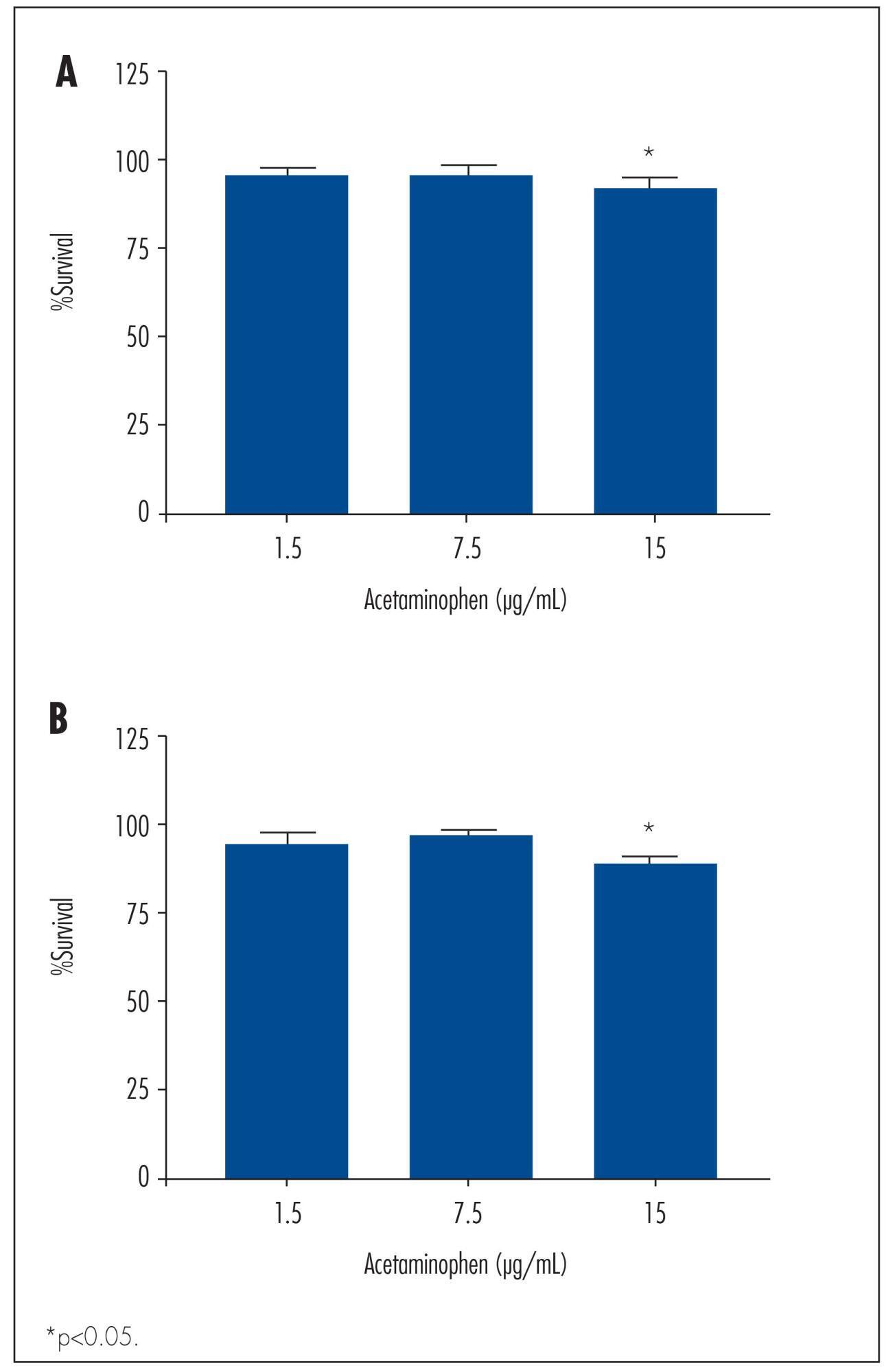
We observed a significant decrease in TOV-21 G cell growth after exposure to 15 μg/mL of acetaminophen for 24 (p=0.02) and 48 hours (p=0.01), or to 20 μg/mL of ibuprofen for 48 hours (p=0.04). Assessing the morphology of TOV-21 G cells did not reveal evidence of extensive apoptosis. TOV-21 G cells had a reduced expression of the genes ABCA1, ABCC3, ABCC4, ABCD3, ABCD4 and ABCE1 within the ABC transporter superfamily.
This study provides in vitro evidence of inhibitory effects of growth in therapeutic concentrations of acetaminophen and ibuprofen on TOV-21 G cells. Additionally, TOV-21 G cells presented a reduced expression of the ABCA1, ABCC3, ABCC4, ABCD3, ABCD4 and ABCE1 transporters.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(8):374-380
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000800003
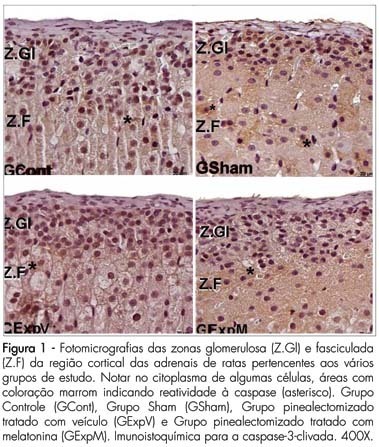
PURPOSE: to evaluate the reactivity of VEGF-A and cleaved caspase-3 in the adrenal gland cortex of female pinealectomized rats treated with melatonin. METHODS: forty adult female rats were divided into 4 groups (G) of 10 animals: GI - no surgical intervention, with vehicle administration; GII - sham pinealectomized with vehicle administration; GIII - pinealectomized with vehicle administration; GIV - pinealectomized with melatonin administration (10 µg/animal) during the night. After 60 days of treatment, all animals were anesthetized, and the adrenal glands were removed and fixed in 10% formaldehyde (phosphate buffered) for histological processing and paraffin embedding. Sections (5 µm thick) were collected on silanized slides and submitted to imunnohistochemical methods for the detection of cleaved caspase-3 (apoptosis) and of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF-A) in the adrenal cortex. The data obtained were submitted to analysis of variance (ANOVA) complemented by the Tukey-Kramer test (p<0.05). RESULTS: reactivity to cleaved Caspase-3 was noted in the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal glands in all studied groups. There were no significant differences in the zona glomerulosa; however, the zona fasciculata (15.51±3.12*, p<0.05) and the zona reticularis (8.11±1.90*, p<0.05) presented the smallest percentage of apoptosis in the pinealectomized group (GIII). The reactivity to the VEGF-A was stronger in the zona glomerulosa and weaker in the zona reticularis in all groups. We found a stronger VEGF-A reactivity in the zona fasciculata in the pinealectomized group (GIII). CONCLUSIONS: the pineal gland affects the arrangement of the zona glomerulosa and reticularis of the adrenal glands, which are related to the production of sex hormones.