Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1083-1089
03-24-2022
To compare the efficacy of quadratus lumborum (QL) block and intrathecal morphine (M) for postcesarean delivery analgesia.
Thirty-one pregnant women with ≥ 37 weeks of gestation submitted to elective cesarean section were included in the study. They were randomly allocated to either the QL group (12.5 mg 0.5% bupivacaine for spinal anesthesia and 0.3 ml/kg 0.2% bupivacaine for QL block) or the M group (12.5 mg bupivacaine 0.5% and 100 mcg of morphine in spinal anesthesia). The visual analog scale of pain, consumption of morphine and tramadol for pain relief in 48 hours, and side effects were recorded.
Median pain score and/or pain variation were higher in the morphine group than in the QL group (p = 0.02). There was no significant difference in the consumption of morphine or tramadol between groups over time. Side effects such as pruritus, nausea, and vomiting were observed only in the morphine group.
Quadratus lumborum block and intrathecal morphine are effective for analgesia after cesarean section. Patients undergoing QL block had lower postoperative pain scores without the undesirable side effects of opioids such as nausea, vomiting, and pruritus.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(4):250-255
03-30-2021
To investigate the effect of closure types of the anterior abdominal wall layers in cesarean section (CS) surgery on early postoperative findings.
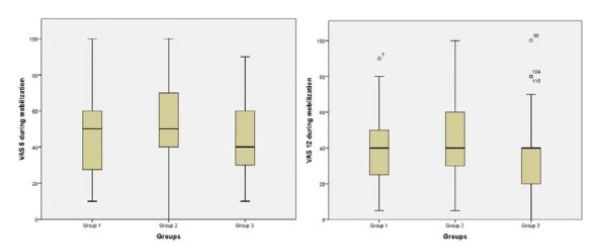
The present study was designed as a prospective cross-sectional study and was conducted at a university hospital between October 2018 and February 2019. A total of 180 patients who underwent CS for various reasons were enrolled in the study. Each patient was randomly assigned to one of three groups: Both parietal peritoneum and rectus abdominis muscle left open (group 1), parietal peritoneum closure only (group 2), and closure of the parietal peritoneum and reapproximation of rectus muscle (group 3). All patients were compared in terms of postoperative pain scores (while lying down and duringmobilization), analgesia requirement, and return of bowel motility.
The postoperative pain scores were similar at the 2nd, 6th, 12th, and 18th hours while lying down. During mobilization, the postoperative pain scores at 6 and 12 hours were significantly higher in group 2 than in group 3. Diclofenac use was significantly higher in patients in group 1 than in those in group 2. Meperidine requirements were similar among the groups. There was no difference between the groups’ first flatus and stool passage times.
In the group with only parietal peritoneum closure, the pain scores at the 6th and 12th hours were higher. Rectus abdominismuscle reapproximations were found not to increase the pain score. The closure of the anterior abdominal wall had no effect on the return of bowel motility.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(2):84-89
02-01-2019
To compare low doses of pethidine with dipyrone in labor analgesia.
In a randomized prospective study conducted by Universidade de Fortaleza, in the state of Ceará, Brazil, between May and December 2016, 200 full-term parturients, with very painful uterine contractions and exhibiting uterine cervix dilatation ≥ 5 cm, were selected to receive a single intravenous dose of either 0.25 mg/kg of pethidine (n = 100) or of 25 mg/kg of dipyrone (n = 100). Pain was assessed using the visual analogue scale. The data were analyzed using the Student t-test, the chi-square test and the likelihood ratio.
There was a significant improvement in pain in 35% of the parturients. Both drugs presented a similar analgesic effect 1 hour after the intervention (p = 0.692). There was no analgesic effect during the evaluation of the second hour after the intervention with pethidine or dipyrone. There were no adverse effects, such as maternal drowsiness, nausea or vomiting, related to the drugs used.
Pethidine in low doses and dipyrone presented equivalent analgesia during labor. Public Registry of Clinical Trials.