Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo90
In this study, we compared indications and outcomes of 115 young (< 40 years) versus 40 elderly (> 60 years) patients undergoing nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM) as risk-reducing surgery or for breast cancer (BC) treatment.
Between January 2004 and December 2018, young and elderly patients undergoing NSM with complete data from at least 6 months of follow-up were included.
BC treatment was the main indication for NSM, observed in 85(73.9%) young versus 33(82.5%) elderly patients, followed by risk-reducing surgery in 30(26.1%) young versus 7(17.5%) elderly patients. Complication rates did not differ between the age groups. At a median follow-up of 43 months, the overall recurrence rate was higher in the younger cohort (p = 0.04). However, when stratified into local, locoregional, contralateral, and distant metastasis, no statistical difference was observed. During the follow-up, only 2(1.7%) young patients died.
Our findings elucidate a higher recurrence rate of breast cancer in younger patients undergoing NSM, which may correlate with the fact that age is an independent prognostic factor. High overall survival and low complication rates were evidenced in the two groups showing the safety of NSM for young and elderly patients.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo50
To determine the relationship between early age at menarche, late age at menopause with specific subtypes of breast cancer (BC).
A literature search was conducted in Embase, Lilacs, PubMed, Scopus, and Scielo databases, following the Joanna Briggs Institute scoping review protocol and answering the question “How early age at menarche or late age at menopause are related to different breast cancer subtypes?”.
A number of 4,003 studies were identified, of which 17 were selected. Most of the included articles found a clear relationship between early menarche, late menopause and some subtypes of BC, mainly, PR+, ER+, luminal, and HER-2 tumors. However, some studies have found a contradictory relationship and one study didn’t find any relationship between them.
A relationship between early age at menarche and advanced age at menopause was observed with some subtypes of breast cancer, since other factors must be considered in its understanding.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(4):184-188
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000400008
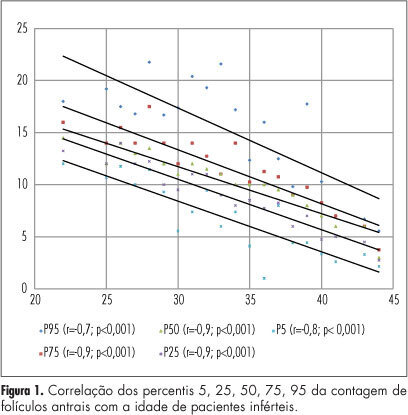
PURPOSE: To produce age-related nomograms for ovarian antral follicle count (AFC) in infertile women. METHODS: It was done a cross-sectional study of patients attended in the center of assisted reproduction Fêmina, from March 2010 to October 2011. The patients were submitted to transvaginal ultrasonography from day 2 to day 4 of their menstrual period. Patients included were between 21 to 45 years old, with regular menses, two healthy ovaries, without any evidence of endocrinopathies and who gave written informed consent. Patients excluded were smokers, with galactosemia or ovarian cysts, with antecedents of liver disease, ovarian surgeries or who were treated with chemotherapy or radiotherapy. In order to check the evolution of the AFC in relation to patient age, we used the 5th, 25th, 50th, 75th and 95th percentiles. Linear regression was carried out using these percentiles, permitting us to determine the effect of age on the CFA. RESULTS: A total of 172 patients with a mean age of 32.7 years were included in the trial. The male and tubal factors were the main causes of infertility, accounting for 65% of cases. The age-related nomogram for the 5th, 25th, 50th, 75th and 95th percentiles of AFC revealed that changes were best fitted by a linear function. The percentiles that showed the highest correlations were 25 (r=-0.9; p<0.001), 50 (r=-0.9; p<0.001) and 75 (r=-0.9; p<0.001). CONCLUSION: A nomogram was constructed correlating age with the different AFC percentiles in infertile women without endocrinopathies. This showed a linear pattern of decline in AFC with age in all percentiles. These nomograms could provide a reference guide for the clinician. However, future validation, with longitudinal data, still is needed.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(5):230-234
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000500005
PURPOSE: to evaluate the patient's age as an outcome predictor in an in vitro fertilization (IVF) program. METHODS: transversal study, which has included 302 women with ages varying from 24 to 46 years old, submitted to IVF, from May 2005 to July 2007. The patients were divided in three groups, according to their age: G<35 (n=161), G 36-39 (n=89) e G>40 (n=52). The number of collected oocytes, the fertilization rates, the number of transferred embryos, the embryonary quality and the pregnancy rate were evaluated. Statistical analysis was realized through Kruskal-Wallis variance analysis and χ2 test. RESULTS: in the G<35 group, an average of 8.8 oocytes by patient was obtained; in the G 36-49 group, 7.4; and in the G>40 group, 1.6. The number of oocytes obtained in G>40 group was significantly lower than in the other two groups (p<0.001).The fertilization rate was similar in the three groups, 61.4, 65.8 e 64.6% (p=0.2288), respectively. The percentage of good quality embryos was not statistically different among the three groups either, with rates of 57.4, 63.2 and 56.0% (p=0.2254), respectively. The average number of transferred embryos in each group was 3.1 (G<35), 2.8 (G 36-39) and 1.5 (G>40), respectively, with statistically significant decrease in the G>40 group (p<0.001). Concerning pregnancy rates, the G>40 group has presented a rate of 9.6%, a result which is significantly lower (p=0.0330) than the one presented by the G<35 and G 36-39 groups (26.1 e 27.0%, respectively), with no significant difference between themselves. CONCLUSIONS: though the embryonary quality is not different among women from different age groups, the number of collected oocytes, the number of transferred embryos and the pregnancy rate indicate that the women's age is an important predictive factor of success for the techniques of assisted reproduction and should be taken into consideration when this kind of treatment is proposed to women over 40.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(2):67-74
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000200004
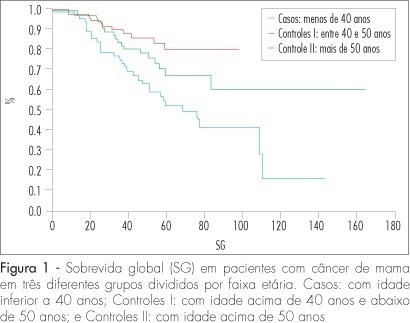
PURPOSE: to compare the epidemiologic and clinical characteristics, and the follow-up of breast cancer in women diagnosed under and over 40 years of age. METHODS: a retrospective study, case-control type, with analysis of information obtained from medical records of patients attended from January 1994 to June 2004. Cases of intraductal carcinoma and at stage IV were excluded. Three groups were formed: patients under 40 years old at the diagnosis (n=72); patients between 40 and 50 (n=68) and patients over 50 (n=75). Data about age at the moment of diagnosis, lesion largest diameter, clinical stage, type, histological grade, presence of hormonal receptors and state of the lymph nodes were collected and analyzed. The chi2 test was used for qualitative variables. For quantitative variables without normal distribution (such as number of axillary nodes with metastasis and follow-up duration), the Kruskal-Wallis' test was used. For delineating the curves of free-of-disease and global survival, the log-rank test was used. RESULTS: there was no difference among the groups in the stage distribution, concerning the tumoral differentiation grade or in the distribution of histological types, and in the estrogen receptor and c-erb-B2 expression. Difference was found in the RP expression, which was less frequent in the group of patients under 40, than in the group of patients over 50 (36.2% versus 58.4%) respectively. There was no difference among the groups in the mean tumoral diameter (5.1, 4.7 and 5 cm, respectively). There was also no difference among the groups, concerning the rate of axillary lymph node metastasis (63.9, 46.9 and 50%, respectively). The average follow-up was 54 months for all the groups. Disease recurrence occurred in 22.6% of patients under 40 years old, in 60% of patients between 40 and 50, and in 22.6% of patients over 50, with a significant difference among groups (p<0.0001). Death caused by the disease was higher among patients under 40 (46.9%) than among patients between 40 and 50 (26.9%) and over 50 (22.6%), p=0.0019. The logistic analysis showed that "age under 40" and the "presence of more than one metastatic axillary node" were independent death risk factors. CONCLUSIONS: age under 40 is an independent risk factor for breast cancer. The traditional prognostic indicators, such as stage, tumoral diameter, axillary involvement and presence of hormonal receptors are not associated with the disease evolution.