Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 07-30-2021;43(5):414-416
The diagnosis of genital ulcers remains a challenge in clinical practice. Lipschütz ulcer is a non-sexually transmitted rare and, probably, underdiagnosed condition, characterized by the sudden onset of vulvar edema along with painful necrotic ulcerations. Despite its unknown incidence, this seems to be an uncommon entity, with sparse cases reported in the literature. We report the case of an 11-year-old girl who presented at the emergency department with vulvar ulcers. She denied any sexual intercourse. The investigation excluded sexually transmitted infections, so, knowledge of different etiologies of non-venereal ulcers became essential. The differential diagnoses are extensive and include inflammatory processes, drug reactions, trauma, and malignant tumors. Lipschütz ulcer is a diagnosis of exclusion. With the presentation of this case report, the authors aim to describe the etiology, clinical course, and outcomes of this rare disease, to allow differential diagnosis of genital ulceration.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 11-07-2019;41(10):607-612
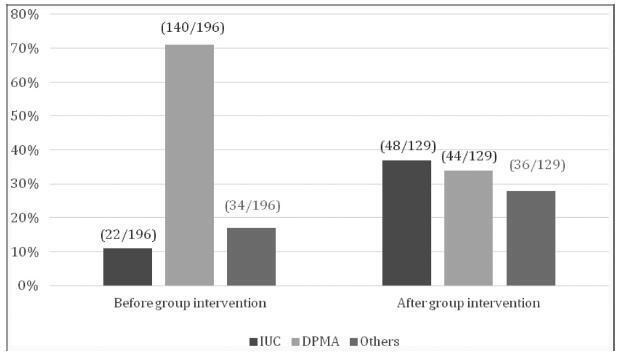
Almost 80% of adolescent pregnancies are unplanned, and between 28 and 63% of adolescent mothers had a repeated pregnancy within 18 months. Among girls with repeated pregnancies, two-thirds reported that the pregnancy was unplanned. We aim to assess contraceptive use by adolescent mothers with increasing choice for long-acting reversible contraception (LARC) methods in postpartum consultation after a semistructured group intervention involving adolescent mothers.
Retrospective observational study conducted at the Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Campinas, state of São Paulo, Brazil, involving new antenatal and postpartum education groups for adolescents. At postpartum consultations, the adolescents chose their contraceptive. The datawas compared with previous series followed in a period before the implementation of the education group - a historical control group.
We included 129 adolescent after childbirth from January 1st, 2015 through July 31st, 2017. Out of this total, 63% had ever used contraceptive methods before pregnancy, and the most frequent method was combined oral contraceptives (33%) followed by condoms (21%). At the first postpartum consultation, the most common contraceptive chosen was intrauterine contraception (IUC) (37.2%) and depot-medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA) (34.1%).When comparing the rates before and after the education interventions, there was a 3-fold increase in the use of IUCs.
Antenatal and postpartum education have shown a significant increase in the choice for LARC methods among adolescent mothers, with very high acceptability after a period using the method. The educational groups performed during the antenatal care and beyond the gestational period are easy to be applied worldwide with low dependence on funding.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 06-27-2019;41(5):291-297
To evaluate the level of information possessed by pregnant adolescents regarding the human papillomavirus (HPV).
Descriptive study developed in the adolescent prenatal outpatient clinic of a tertiary hospital fromthe state of São Paulo, Brazil. Data were collected between June and December 2017 following approval from the ethics and research committee (CAAE: 1.887.892/2017). Pregnant adolescents, ≤18 years old, who attended the abovementioned outpatient section, composed the sample. Those diagnosed with a psychiatric disorder and those with hearing or cognitive disabilities were excluded. After acceptance to participate in the present study, the pregnant adolescents signed an Informed Consent Form. Regarding the statistical analysis, the chi-squared test and the Fisher exact test were used.
Regarding the knowledge about HPV, 123 (80.92%) of the participants had already heard about the subject; for 77 (50.66%), their schools had been the source of the information; 101 (66.45%) did not know how they could be infected by the virus. Age variation did not influence their knowledge on how to prevent themselves from HPV (p = 0.2562). The variable vaccine is associated with HPV prevention (p < 0.0001).
The pregnant adolescents composing the sample have shown to have knowledge about HPV. However, they do not prevent themselves from it appropriately, given that little more than half of the sample was vaccinated, had not reported an understanding that the use of preservatives and vaccination are effective means of prevention, and did not correlate HPV with uterine cervical cancer.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 08-05-2011;33(4):176-181
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000400005
PURPOSE: to evaluate changes in the nutritional status of lactating adolescents in different postpartum weeks. METHOD: this is an analytical, observational, longitudinal study. Lactating adolescents were followed-up from the 5th to the 15th postpartum week (PPW). The nutritional status was evaluated in the 5th, 10th and 15th PPW by the Body Mass Index (BMI/age). A colorimetric method was used to determine hemoglobin level and microcentrifugation to define hematocrit. ANOVA with repeated measures was used to compare means, followed by the Tukey post-test. The level of significance was 5%. RESULTS: modification in nutritional status was observed from the pregestational period to the 15th PPW, with a reduction in the frequency of lactating adolescents with low weight (from 21% to 9%) and a rise in the frequency of overweight (21% to 27%) and eutrophic (58% to 64%) adolescents. Although mean hemoglobin (12.3±1.7 g/dL) and hematocrit (39.0±4.0%) levels were normal, a high frequency of anemia (30%) was observed throughout the study period. CONCLUSION: the present results show that the body weight of lactating adolescents rises during the lactation period and could lead to a higher frequency of obesity among adolescents. Anemia is still a nutritional problem, not only during pregnancy, but also during the postpartum period. It is necessary to prevent and treat probable subclinical nutritional deficiencies at this biological time.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 09-28-2010;32(6):267-272
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000600003
PURPOSE: to assess the alpha-tocopherol concentration in the serum and colostrum of adolescent and adult mothers and to determine the nutritional adequacy of vitamin E in the colostrum offered to infants. METHODS: in total, 72 pregnant women participated in the study, 25 adolescents and 47 adults. An amount of 5 mL of blood and 2 mL of colostrum were collected under fasting conditions for the analysis of alpha-tocopherol levels. The samples were analyzed by means of high performance liquid chromatography. Nutritional adequacy of colostrum for vitamin E was calculated as the product of the estimated volume of milk intake by the concentration of alpha-tocopherol in colostrum and by direct comparison of this product with the reference value for nutrient intake (4 mg/day). RESULTS: the levels of alpha-tocopherol in the serum of adolescents and adults were 30.8±9.8 and 34.1±9.5 µmol/L (mean±SD), respectively, and in colostrum, the adolescents showed a concentration of 32.9±15.8 µmol/L and the adults, a concentration of 30.4±18.0 µmol/L. No significant difference was found between concentrations of alpha-tocopherol in serum or in colostrum between adolescents and adults. CONCLUSIONS: Both adolescents and adult women had a satisfactory vitamin E nutritional status reflected in the colostrum, whose values were able to meet the nutritional requirements of infants, suggesting that the maternal age does not influence the levels of alpha-tocopherol in human colostrum.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 06-30-2009;31(4):171-176
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000400003
PURPOSE: to apply geoprocessing techniques for the spatial birth profile analysis of each municipality. METHODS: ecological and exploratory study, using data from the Health Information System about born alive babies in 2004, and using geoprocessing techniques. The spatial autocorrelations of the variables: cesarean section, mother's schooling, low birth weight, Apgar score at five minutes, prematurity, number of medical appointments and adolescent mothers, besides the map with the index of human development were estimated. For the detection of spatial events aggregates, Moran's I M statistics, through the program Terra View 3.13 (developed by INPE and available to the public) was used. Spatial maps with those variables were built, and Pearson's correlation coefficients, estimated. RESULTS: results have shown that the rate of born alive babies, from mothers with school level over primary school and from cesarean sections, presented a spatial pattern visually identifiable and significant spatial self-correlation. Low birth weight, prematurity, Apgar score, number of pre-natal appointments and adolescent mothers have presented a random spatial pattern, showing that, in this analysis scale, those markers have not discriminated the risk groups, despite their unquestionable predictive value for children's morbidity-mortality at individual level. There has been a positive correlation between cesarean section and schooling, and between cesarean section and human development index; and a negative correlation between adolescent mothers and human development index, with statistical significance (p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: this methodology has allowed us to identify spatial clusters for the variables cesarean section and mother's schooling, besides deepening our knowledge on birth profile in the municipalities, presenting good potential on how to direct actions for specific areas.
