Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo31
04-09-2024
To compare Transforming growth factor beta-1 (TGF-β1) expression in patients with and without adenomyosis.
A prospective design was performed including 49 patients submitted to hysterectomy. Immunohistochemistry was performed on anatomopathological samples staged in paraffin blocks from patients with and without adenomyosis. The sample contained 28 adenomyosis cases and 21 controls. Student's t-test and multivariate logistic regression tests were used for statistical analysis. Associations were considered significant at p < 0.05.
We found no significant association between adenomyosis and: smoking (p = 0.75), miscarriage (p = 0.29), number of previous pregnancies (p = 0.85), curettage (p = 0.81), pelvic pain (p = 0.72) and myoma (p = 0.15). However, we did find a relationship between adenomyosis and abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) (p = 0.02) and previous cesarean section (p = 0.02). The mean TGF-β1 intensity (mean ± SD) in the ectopic endometrium of women with adenomyosis showed no significant association (184.17 ± 9.4 vs.184.66 ± 16.08, p = 0.86) from the topic endometrium of women without adenomyosis.
TGF-β1 expression was not increased in the ectopic endometrium of women with adenomyosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(9):564-574
09-30-2019
To assess the efficacy of non-surgical treatment for adenomyosis.
A search was performed by two authors in the Pubmed, Scopus, and Scielo databases and in the grey literature from inception to March 2018, with no language restriction.
We have included prospective randomized studies for treating symptomaticwomen with adenomyosis (abnormal uterine bleeding and/or pelvic pain) diagnosed by ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging.
Studies were primarily selected by title and abstract. The articles that were eligible for inclusion were evaluated in their entirety, and their data was extracted for further processing and analysis.
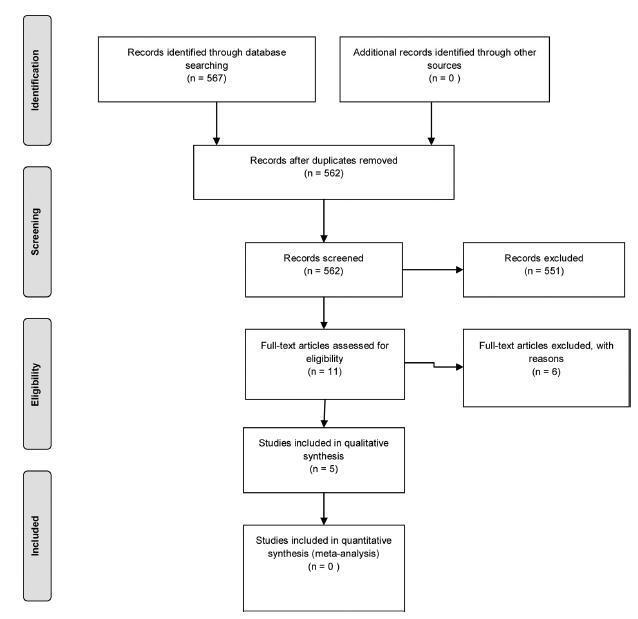
From567retrieved records only 5 remained for analysis. The intervention groups were: levonorgestrel intrauterine system (LNG-IUS)(n= 2), dienogest (n= 2), and letrozole (n= 1). Levonorgestrel intrauterine system was effective to control bleeding when compared to hysterectomy or combined oral contraceptives (COCs). One study assessed chronic pelvic pain and reported that LNG-IUS was superior to COC to reduce symptoms. Regarding dienogest, it was efficient to reduce pelvic pain when compared to placebo or goserelin, but less effective to control bleeding than gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analog. Letrozolewas as efficient asGnRHanalog to relieve dysmenorrhea and dyspareunia, but not for chronic pelvic pain. Reduction of uterine volumewas seen with aromatase inhibitors, GnRH analog, and LGN-IUD.
Levonorgestrel intrauterine system and dienogest have significantly improved the control of bleeding and pelvic pain, respectively, in women with adenomyosis. However, there is insufficient data from the retrieved studies to endorse eachmedication for this disease. Further randomized control tests (RCTs) are needed to address pharmacological treatment of adenomyosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(8):473-478
12-05-2006
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000800006
PURPOSE: to verify the effects of intrauterine levonorgestrel device (IUD) in women with adenomyosis, with implantation failure in previous in vitro fertilization (IVF) cycles. METHODS: eighty infertile women with ages up to 38 years, who had adenomyosis diagnosed by ultrasonography and MRI were selected. All the women presented antecedents of one or more tormer IVF attempts without success due to implantation failure. The women were subdivided into IUD Group, composed of 40 women with an IUD that released 20 µg of levonorgestrel/day during six months, preceding a new IVF cycle, and IVF Group, also composed of 40 women, who were directly submitted to a new IVF cycle without previous adenomyosis treatment. In the IUD Group the uterine volume, thickness and hypersignal foci of the junctional zone were assessed before and after treatment, as well as the pregnancy rates in the new IVF cycle, compared to the data obtained with the IVF Group. Statistical analyses were performed adopting the significance level of 5% (p<0,05), using the Mann-Whitney and Sudent's t tests. RESULTS: after treatment, there was a reduction of 77.7% in the cases of focal adenomyosis, in addition to a significant reduction of the uterine volume and of the mean thickness of the junctional zone from 128.8 to 93.6 ml and from 12.3 to 11.3 mm, respectively. In the IUD Group, pregnancy rate reached 30%, which was higher than, but not significantly different from that of the IVF group, which was 17.5%. CONCLUSION: the use of an IUD with levonorgestrel may be administered prior to IVF cycles in patients with adenomyosis who suffered previous implantation failure.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(9):579-584
02-13-2002
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000900003
Purpose: to evaluate the sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values of a clinical and an ecographic method for adenomyosis diagnosis. Methods: a transversal study of validation of the diagnostic method was done, including 95 women in menacme submitted to hysterectomy for various causes. Adenomyosis was diagnosed through a clinical method in women aged 40 years or older, with 2 or more deliveries, increased menstrual bleeding associated with dysmenorrhea. The ecographic diagnosis was established if at least one myometrial ill defined area of abnormal ecotexture was found, which could be hypoechoic, hyperchoic, heterogeneous or cystic. Gold standard was histopathology, defined as the finding of endometrial glands or stroma more than 2.5 cm above the endomiometrial junction. Results: the clinical method had 68.2% sensitivity, 78.1% specificity, 48.4% positive predictive value and 89.1% negative predictive value. For the echographic method this figures were, respectively, 45.5%, 84.9%, 47.6% and 83.8%. Likelihood ratio was 3.11 for the clinical and 3.03 for the echographic method. Considering only those simultaneously positive cases by both methods, sensitivity was below 30% and specificity was near 100%. Considering all positive cases by one or the other method or concomitanty by both, the sensitivity reached 86% and specificity was 60%. Conclusion: the echographic method was not better than the clinical for the diagnosis of adenomyosis.