Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(4):211-219
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000400008
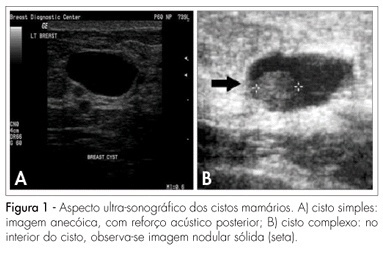
The benign mammary tumors are responsible for up to 80% of the clinical masses. Its differential diagnosis is wide, involving mammary cysts, fibroadenomas, phyllodes tumors, papillomas, hamartomas, and adenomas, among others. The fibroadenoma is the most common mammary neoplasia in patients under 35 years old, while the cysts are more frequent in the perimenopause. The differential diagnosis among solid or cystic nodules can be made through the fine-needle aspiration or by ultrasound, being therapeutic for the last ones. In this article, the differential diagnostic aspects will be revised between these tumors, as well as the new therapeutic approaches.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(3):211-213
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(5):211-215
DOI 10.1590/S0100-7203201400050005
To evaluate the correlation between the use of antenatal corticosteroid therapy (AC), the frequency of resuscitation in delivery room and mortality of newborn infants under 1,500 g and gestational age less than or equal to 34 weeks.
A cohort study was conducted on all newborn infants under 1,500 g and with a gestational age less than or equal to 34 weeks admitted at the neonatal ICU between January 2006 and December 2011. Newborns who had congenital anomalies, genetic syndromes, congenital infections and those who were transferred to or came from other institutions were excluded. The studied infants were divided into 2 groups: those who received (n=182) and those who did not receive (n=38) AC. The main outcomes studied were the necessity of neonatal resuscitation, the presence of the main neonatal diseases and mortality during hospitalization. The means of the variables were compared using Student's t-test or non-parametric test and frequencies were compared by χ2test with Fisher's correction. The variables that presented difference between groups were assessed by logistic regression. The Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) 16.0 was used and the significance level was set at 0.05.
In this study, 220 patients were evaluated. The groups were similar concerning birth weight, gestational age and the presence of the main neonatal morbidity during hospitalization. The infants who received antenatal corticosteroids showed lower mortality (OR=3.0; 95%CI 1.4-6.5) and required less resuscitation (OR=2.4; 95%CI 1.1-5.0). Besides, they required less advanced resuscitation procedures, such as tracheal cannula (OR=3.7; 95%CI 1.7-7.6), cardiac massage (OR=5.7; 95%CI 2.0-16.5) and medications (OR=8.9; 95%CI 2.0-39.4).
The use of antenatal corticosteroids reduced the need for resuscitation in delivery room, especially advanced procedures, and reduced the mortality in the studied groups.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(4):211-217
To reveal the changes in the quality of life reported by women with Human papillomavirus (HPV)-induced lesions.
This is a cross-sectional, descriptive-exploratory study of a qualitative approach performed from June to August 2016. Semi-structured face-to-face interviews based on five questions on the concept of quality of life were used. The data were submitted to thematic analysis. All ethical aspects have been contemplated.
A total of 20 women aged between 25 and 59 years old were interviewed. From the analysis of the data, the following thematic units emerged: physical and emotional changes, especially complaints of pruritus, discharge and pain, worry, fear, shame and sadness; changes in sexual and affective relationships with decreased libido, dyspareunia and interruption of sexual activity; changes in social relationships resulting in absenteeism at work.
Human papillomavirus infection impairs the quality of life of women as it significantly affects sexual, affective, physical, emotional, and everyday habits. Therefore, HPV infection can lead to exponential changes in the quality of life of women, which can be mitigated by the availability of sources of support such as family, friends and the multi-professional team, helping to improve knowledge and cope with HPV.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(10):212-216
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002001000006
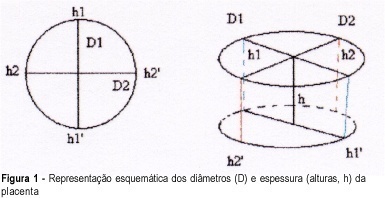
PURPOSE: to compare two methodologies for the calculation of placental volume in normal term pregnancies: one according to the Archimedes principle and the other to the cylinder volume, to estimate the absolute placental densities. Also, to define the methodology which relates to the weight and to the newborn classification. METHOD: fifty placentas from normal term pregnancies were tested by the two methodologies to estimate the placental volume and absolute density: a) Archimedes principle, and b) the cylinder volume with two possible different heights. The absolute placental densities were calculated, respectively, by the quotient between the placenta weight, properly standardized, and the different estimated volumes. RESULTS: most of the pregnant women had more than one gestation, average age of 25.4 years, mean placental volume between 547.8 and 610 cm³ and mean density between 0.94 and 1.14 g/cm³, depending on the used methodology. CONCLUSIONS: the Archimedes principle was the most appropriate methodology to estimate the term placental volume, best correlating with the newborn weight, the placental index and the classification of newborn weight in relation to gestational age.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(4):213-219
To describe the immunological and hematological reference intervals of low-risk pregnant women.
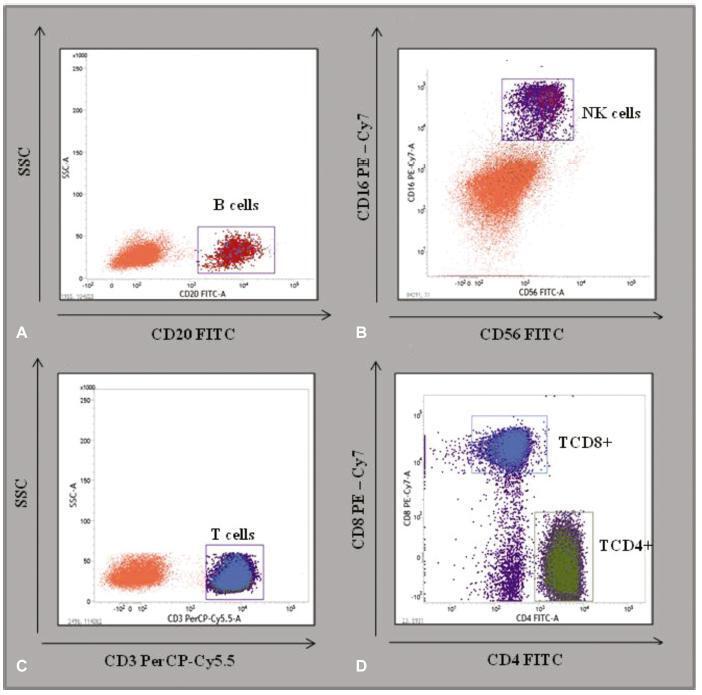
A cross-sectional retrospective database analysis of a basic and translational study analyzing the hematological evaluation blood counts and immunophenotyping of TCD3 + , TCD4 + , TCD8 + , B, and natural killer (NK) cells of the peripheral blood in 79 low-risk pregnant women and of 30 control women from the state of Pernambuco, Brazil, was performed.
No significant differences were detected between the hematological profiles of the 2nd and 3rd trimesters. Nevertheless, the median level of B cells decreased significantly in the 2nd (174 x 103 μL; p < 0.002) and 3rd trimesters (160 x 103 μL; p < 0.001), compared with the control group (296 x 103 μL). Similarly, the median level of NK cells was lower in the 2nd (134 x 103 μL; p < 0.0004) and 3rd trimesters (100 x 103 μL, p < 0.0004), compared with the control group (183 x 103 μL). In contrast, relative TCD4+ and TCD8+ levels increased in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters compared with the controls (TCD4 + : 2nd trimester = 59%; p < 0.001; 3rd trimester = 57%; p < 0.01; control = 50%; and TCD8 + : 2nd trimester = 31%; p < 0.001; 3rd trimester = 36%; p < 0.01; control = 24%).
Low-risk pregnant women have ~ 40% less B and NK cells in the peripheral blood, compared with non-pregnant women. These parameters may improve health assistance for mothers and contribute to define reference values for normal pregnancies.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(5):213-215
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(3):213-219
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000300007
OBJECTIVE: to evaluate the effectiveness of the hygroscopic dilator in the colposcopic examination of the endocervical canal in patients with high-grade lesion in the cytopathology and unsatisfactory colposcopy. METHODS: prospective study, including 62 patients with unsatisfactory colposcopic examination and cytology compatible with high-grade intraepithelial lesion. The patients were submitted to dilation of the endocervical canal by means of a hygroscopic dilator. After dilation, the new colposcopic findings were recorded, and then conization was made through loop electrosurgical excision procedure. The incidence of neoplasic involvement of surgical margins was compared between patients with examinations modified toward satisfactory results and those that remained with unsatisfactory colposcopy. In order to compare the incidence of involved margins and the incidence of residual disease, two retrospective control-groups were used: the GinSat group (n = 35): patients with unsatisfactory colposcopy; GSat group (n = 38): patients with satisfactory colposcopy and endocervical atypy. RESULTS: 80.6% of the cases presented satisfactory colposcopic vision after dilation. 80.4% of those presented disease-free resection margins. The incidence of disease-free resection margins in patients with persistent unsatisfactory colposcopy after dilation was 36.3%. Affected surgical margins occurred in 28% of the group that had undergone dilation, 28.5% of the cases in GinSat group, and 31.5% in the Gsat group. Follow-up showed the incidence of residual disease in 7.5% of the patients under dilation, 28.5% in the GinSat group and 28.9% in the GSat group. CONCLUSION: the use of hygroscopic dilation improved visualization of lesions of difficult access to the colposcopic examination, thus permitting reduction in the percentage of residual neoplasic disease in patients with unsatisfactory colposcopy treated with loop electrosurgical excision procedure.