Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(5):199-202

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(3):199-202
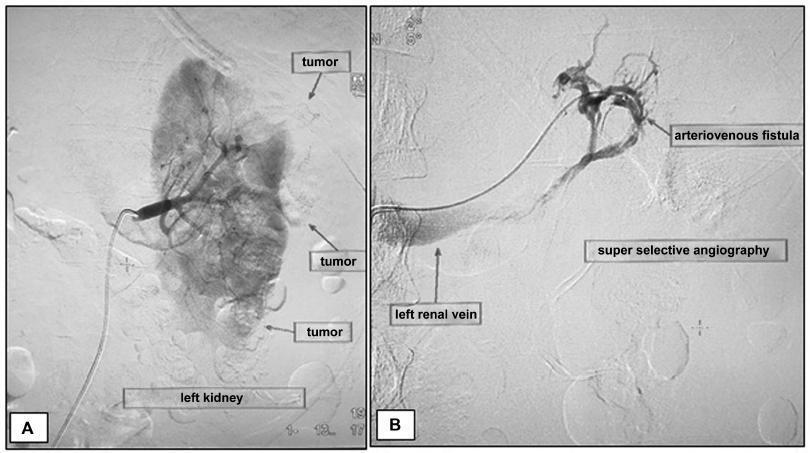
Angiomyolipomas (AMLs) are rare benign tumors derived from mesenchymal tissue and composed of varying degrees of adipose tissue, muscle and blood vessels. Renal AMLs (RAMLs) are the result of a sporadic event, and, in most of cases, the diagnosis is usually incidental, but hemorrhage and shock may be present. During pregnancy, the size of AMLs may increase and they may rupture, probably due to the high expression of hormone receptors, and the increase in maternal circulation and abdominal pressure. The authors present a case of a woman with ruptured RAML submitted to urgent endovascular treatment four days after giving birth by cesarean section.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(5):199-201
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(1):20-25
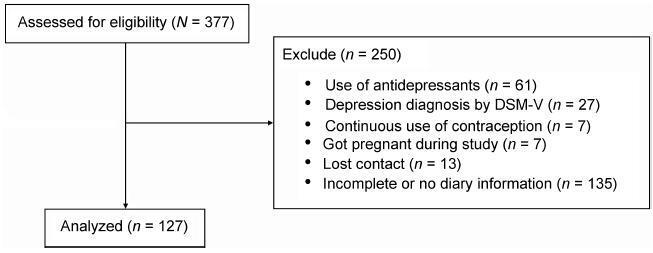
To validate the premenstrual symptoms screening tool (PSST) in relation to the daily record of severity of problems (DRSP) for premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) diagnoses.
A cross-sectional study with 127 women (20 45 years) with PMS complaints. The women were evaluated in terms of weight, height and body mass index (BMI). After using the primary care evaluation of mental disorders (PRIME-MD) questionnaire to exclude the diagnosis of depression, the PSST was completed and the women were instructed to fill out the DRSP for two consecutive menstrual cycles. The agreement between the two questionnaires was assessed by the Kappa (k) and the prevalence-adjusted, bias-adjusted kappa (PABAK) values.
Two-hundred and eighty-two women met the eligibility criteria and answered the PSST. The DRSP was completed for two cycles by 127 women. The percentages of women with PMS and PMDD diagnoses by the DRSP were 74.8% and 3.9% respectively; by PSST, the percentages were41.7% and 34.6% respectively. The number of patients considered "normal" (with symptoms below the threshold for the diagnosis of PMS) was similar in both questionnaires. There was no agreement (Kappa = 0.12) in the results of PMS/ PMDD diagnosis (the PABAK coefficient confirmed this result = 0.39). The PSST had a high sensitivity (79%) and a low specificity (33.3%) for PMS/PMDD diagnosis.
The PSST should be considered a diagnostic screening tool. Positive PMS/PMDD cases by PSST should be further evaluated by DRSP to confirm the diagnosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(1):20-27
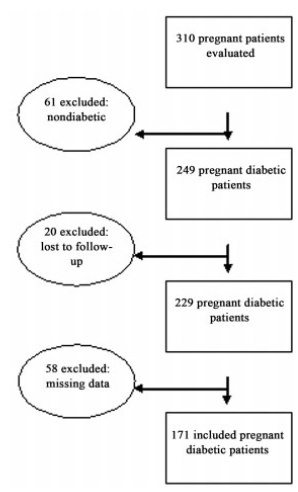
To analyze the agreement, in relation to the 90th percentile, of ultrasound measurements of abdominal circumference (AC) and estimated fetal weight (EFW), between the World Health Organization (WHO) and the International Fetal and Newborn Growth Consortium for the 21st Century (intergrowth-21st) tables, as well as regarding birth weight in fetuses/newborns of diabetic mothers.
Retrospective study with data from medical records of 171 diabetic pregnant women, single pregnancies, followed between January 2017 and June 2018. Abdominal circumference and EFW data at admission (from 22 weeks) and predelivery (up to 3 weeks) were analyzed. These measures were classified in relation to the 90th percentile. The Kappa coefficient was used to analyze the agreement of these ultrasound variables between the WHO and intergrowth-21st tables, as well as, by reference table, these measurements and birth weight.
The WHO study reported 21.6% large-for-gestational-age (LGA) newborns while the intergrowth-21st reported 32.2%. Both tables had strong concordances in the assessment of initial AC, final AC, and initial EFW (Kappa = 0.66, 0.72 and 0.63, respectively) and almost perfect concordance in relation to final EFW (Kappa = 0.91). Regarding birth weight, the best concordances were found for initial AC (WHO: Kappa = 0.35; intergrowth-21st: Kappa= 0.42) and with the final EFW (WHO: Kappa = 0.33; intergrowth- 21st: Kappa = 0.35).
The initial AC and final EFW were the parameters of best agreement regarding birth weight classification. The WHO and intergrowth-21st tables showed high agreement in the classification of ultrasound measurements in relation to the 90th
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(1):20-26
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000100003
PURPOSE: to evaluate associations between parental exposure to pesticides and births with congenital defects in São Francisco Valley, as well as the demographic profile and the defects found. METHODS: in this case-control study, each case (newborns with congenital defects) had two controls (healthy newborns). The subjects were born in the city of Petrolina, in São Francisco Valley, in 2009. The sample consisted of 42 cases and 84 controls. Data were gathered by a structured questionnaire adapted from Latin-American Collaborative Study of Congenital Malformations (ECLAMC), with the addition of questions related to exposure to pesticides, analysis of the medical records and contact with the hospital's pediatrician. The χ2 test was performed with a significance level of 5% to identify the variables with the greatest differences between case and control groups. Odds Ratio (OR) for the sample was calculated, as well as the OR obtained by logistic regression analysis, and finally, multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed. RESULTS: there was a greater exposure to pesticides during pregnancy in infants with congenital defects compared to healthy subjects. Increased risk was observed when at least one parent was exposed to pesticides (adjusted OR = 1.3; 95%CI = 0.4 - 3.9). The sociodemographic variables associated with congenital defects were: low school level, low weight, prematurity, young parents, chronic diseases, and physical factors. Multiple malformations and defects of the musculoskeletal and nervous systems were more frequently found. CONCLUSIONS: the present study suggests an association between exposure to pesticides and the occurrence of congenital defects, although the data were not significant.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(1):20-26
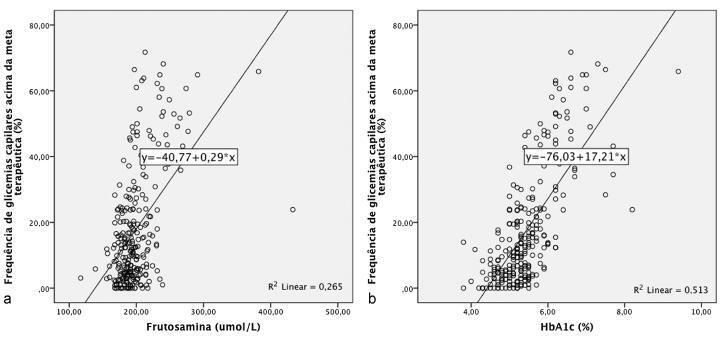
To evaluate the correlation of the levels of fructosamine and of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) with the frequency of blood glucose self-monitoring values out of the treatment target range in pregnant women with diabetes mellitus.
We performed an observational, retrospective, cross-sectional study, including all pregnant women with diabetes who attended prenatal care visits at a tertiary teaching hospital during the year of 2014 and who presented at least 20 days of blood glucose self-monitoring prior to assessment of serum levels of fructosamine and HbA1c. Capillary blood glucose values out of the treatment target range were considered "hypoglycemia" when lower than 70 mg/dL and "hyperglycemia" when above the glycemic therapeutic target. We evaluated the correlation of the levels of fructosamine and of HbA1c with the frequencies of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia recorded in the glucometer device by performing Tau-b of Kendall correlation tests. Next, linear regression tests were performed between the levels of HbA1c and of fructosamine and the frequencies of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia.
We included 158 pregnant women, from whom 266 blood samples were obtained for assessing fructosamine and HbA1c levels. Measurements of fructosamine and of HbA1c presented, respectively, Kendall's τ coefficient of 0.29 (p < 0.001) and 0.50 (p < 0.001) regarding the frequency of hyperglycemia, and of 0.09 (p = 0.046) and 0.25 (p < 0.001) regarding the frequency of hypoglycemia. In the linear regression model, levels of fructosamine and of HbA1c respectively presented determination coefficients R2 = 0.265 (p < 0.001) and R2 = 0.513 (p < 0.001) for the prediction of hyperglycemia, and R2 = 0.033 (p = 0.003) and R2 = 0.059 (p < 0.001) for the prediction of hypoglycemia.
Levels of fructosamine and of HbA1c presented a weak to moderate correlation with the frequencies of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia at blood glucose self-monitoring and were not able to accurately translate the deviations from the glycemic goals in pregnant women with diabetes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):200-206
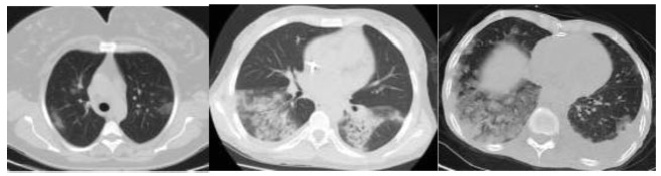
Covid-19 became a pandemic, and researchers have not been able to establish a treatment algorithm. The pregnant population is also another concern for health care professionals. There are physiological changes related to pregnancy that result in different laboratory levels, radiological findings and disease progression. The goal of the present article is to determine whether the laboratory results and radiological findings were different in non-pregnant women (NPWs) of reproductive age and pregnant women (PWs) diagnosed with the Covid-19 infection.
Out of 34 patients, 15 (44.11%) PWs and 19 (55.8%) NPWs were included in the study. Age, comorbidities, complaints, vitals, respiratory rates, computed tomography (CT) findings and stages, as well as laboratory parameters, were recorded from the hospital database.
Themean age of the PWs was of 27.6 ± 0.99 years, and that of the NPWs was of 37.63 ± 2.00; when agewas compared between the groups, a statistically significant difference (p=0.001) was found. The mean systolic blood pressure of the PWs was of 116.53 ± 11.35, and that of the NPWs was of 125.53 ± 13.00, and their difference was statistically significant (p=0.05). The difference in the minimum respiratory rates of the patients was also statistically significant (p=0.05). The platelet levels observed among the PWs with Covid-19 were lower than those of the NPWs (185.40 ± 39.09 x 109/mcL and 232.00 ± 71.04 x 109/mcL respectively; p=0.05). The mean D-dimer value of the PWs was lower in comparison to that of the NPWs (p<0.05).
The laboratory findings and imaging studiesmay differ between pregnant and non-pregnant populations. It is important to properly interpret these studies. Future studies with a higher number of patients are required to confirm these preliminary data.