Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(3):165-168
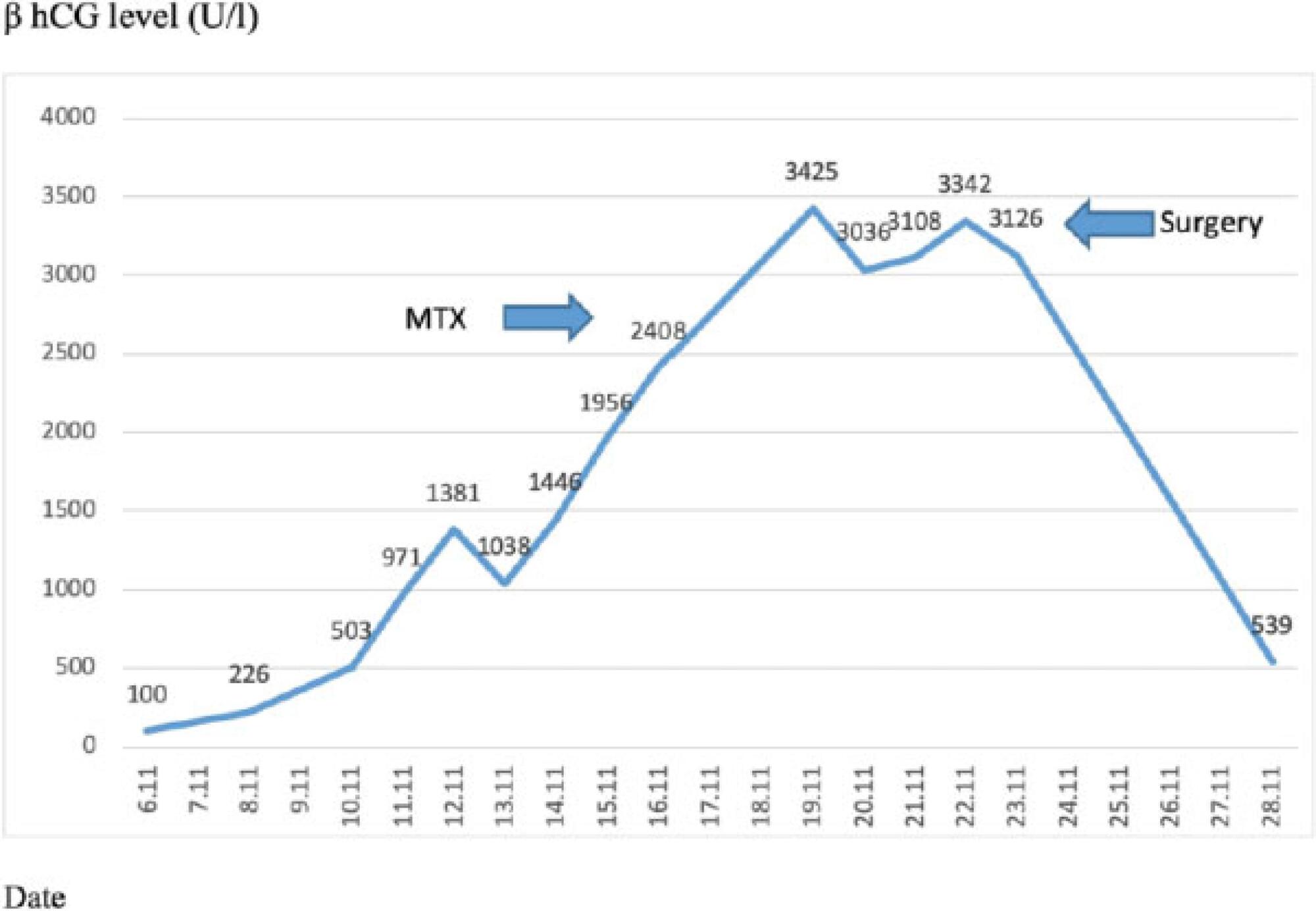
Bilateral tubal ectopic pregnancy is a very rare form of ectopic pregnancy. The incidence is higher in women undergoing assisted reproductive techniques or ovulation induction. We report the case of bilateral tubal ectopic pregnancy. The patient was 30 years old and had a 3-year history of infertility; she was referred to the in-vitro fertilization (IVF) program because of tubal factor infertility. A pregnancy resulted from the transfer of two embryos during an artificial cycle. Despite the increase in β-hCG values during the follow-up, 22 days after the embryo transfer, the β-hCG levels were 2,408 U/L and the serum progesterone (P4) level was 10.53 ng/ml. After application with methotrexate, β-hCG levels did not decrease effectively. Moreover, the sonographic screening revealed a suspicious bilateral tubal focus for ectopic pregnancy. A mini-laparotomy was performed and a bilateral tubal pregnancy was found. In the case of unilateral tubal pregnancy after the transfer of two embryos, the situation of the other tube should be systematically checked and β-hCG levels should be monitored.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(3):167-169
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000300008
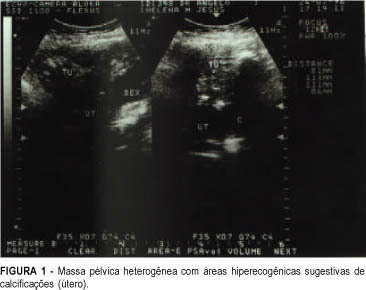
Uterine torsion is an unusual pathology of difficult diagnosis and it is generally associated with an enlargement of uterine volume combined with other alterations of the pelvic organs. This report presents a case of a malnourished elderly woman with acute abdomen and intraoperative diagnosis of myoma and uterine torsion of 360 degrees to the right. The uterus showed signs of severe ischemia.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(3):167-173
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000300008
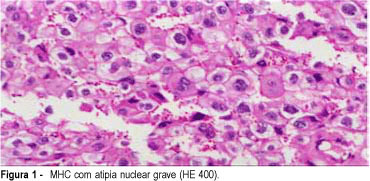
Purpose: to determine the most efficient clinical and histopathological predictors of complete hydatidiform mole (CHM) after gestational trophoblastic tumors (GTT). Methods: a prospective clinical and histopathological study was performed on all patients with CHM treated at the University Hospital of Botucatu between 1990 and 1998. Preevacuation clinical evaluation allowed the classification of molar pregnancy into high risk and low risk CHM. The author analyzed the clinical predictors of GTT established by Goldstein et al.¹ and by other authors2--10. The histopathological evaluation included the confirmation of CHM diagnosis based on the criteria by Szulman and Surti11 and the understanding of risk factors for GTT by Ayhan et al.8. The clinical and histopathological predictors were correlated with the postmolar GTT. Results: ovarian cysts larger than 6 cm and uterus size larger than 16 cm were the most efficient clinical predictors of GTT in 65 patients with CHM. Trophoblastic proliferation, nuclear atypia, necrosis/hemorrhage, trophoblastic maturation, and the ratio cytotrophoblast to syncytiotrophoblast were not significant predictors of GTT. The correlation between the clinical and histopathological predictors for the development of GTT was not possible, as no histopathological parameter was significant. Conclusion: additional investigations could evaluate other predictors for persistent disease, and its usefulness in a clinical context. The sequential determination of plasmatic beta-hCG remains the only safe predictor for persistent disease.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(3):167-173
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000300004
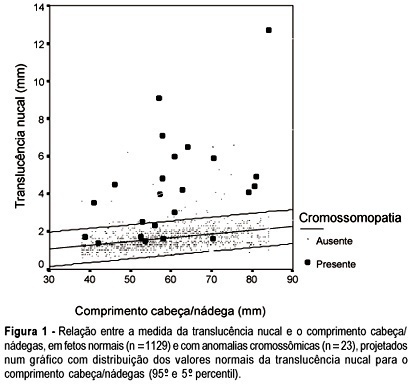
Purpose: to study the value of nuchal translucency (NT) measurement in the screening for chromosomal abnormalities at 10-14 weeks of gestation. Methods: a total of 1152 fetuses were studied consecutively. In 124 cases a cytogenetic study was performed on material obtained from a biopsy of the chorionic villus, and in 1028 cases the result was based on the postnatal phenotype. In addition to the routine ultrasonographic examination, all fetuses were submitted to measurement of the NT thickness. For statistical analysis Student's t test and ANOVA were used. Sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values, false-positive rate and likelihood ratio were calculated. Results: twenty-three cases of chromosomal abnormalities occurred. Of these abnormal cases, NT measurement was above the 95th percentile in 16 (sensitivity of 69.5%). In the group of normal fetuses (1129 cases), NT measurement was above the 95th percentile in 41 (specificity of 96.3%, positive and negative predictive values of 28.0% and 99.3%, respectively, false-positive rate of 3.7% and likelihood ratio of 19.1). Conclusion: our results suggest that the presence of chromosomal abnormalities may be strongly suspected when there is an increased NT thickness. One can infer that the quantitative NT analysis is sufficient to classify the risk of chromosomal anomalies in the first trimester of the pregnancy. Although the ultrasound operator's training and skill is still necessary, it is a method of clinical applicability.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(4):168-173
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000400002
PURPOSE: to evaluate ophthalmic and retinal central artery Doppler indices during the second and third trimesters of normal pregnancy and to compare the right with left eye Doppler indices of normotensive women. METHODS: a cross-sectional study which evaluated central retinal and ophthalmic artery Doppler velocimetry values of 51 normal pregnant women, in the 20th to 38th week of gestation. The following values were analyzed: pulsatility and resistance indexes (PI, RI), peak systolic and end-diastolic flow velocity (PSV, EDFV) and peak velocity ratio (PVR). The Doppler indices in the right and left eyes were studied by the median. The paired Student's t test was used to confront the right and left eye values and the Pearson linear correlation analysis was performed to study the value changes throughout the gestation, with the level of significance set at 5%. RESULTS: Doppler velocimetry indices of ophthalmic and central retinal arteries (median values) were, respectively: PI=1.83; RI=0.78; PSV=34.20; EDFV=6.80; PVR=0.48 and PI=1.34; RI=0.70; PSV=7.40; EDFV=2.10. There was no significant difference between the right and left side Doppler values. Linear correlation analysis showed no association between the arterial values and pregnancy age. CONCLUSION: the unilateral analysis of ophthalmic and central retinal artery Doppler velocimetry values can be used in systemic maternal disease. There is no significant change in ophthalmic and central retinal artery Doppler velocimetry values throughout normal pregnancy.
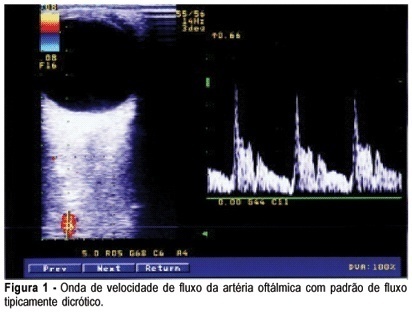
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(3):169-176
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000300005
PURPOSE: to compare intra- and postoperative results of vaginal hysterectomy with those of abdominal hysterectomy in women without genital prolapse or adnexal pathology. METHODS: a randomized, open clinical trial was conducted, involving 35 patients without genital prolapse scheduled for total hysterectomy due to benign disease, at IMIP, Recife, Brazil. These patients were randomly assigned to vaginal hysterectomy (19 patients) or abdominal hysterectomy (16 patients). Main outcome measures included estimated blood loss, rate of blood transfusion, duration of surgery, postoperative pain (intensity and analgesic requirement), time in hospital, postoperative complications, recovery time and patient satisfaction. Statistical analysis was performed using chi2, exact Fisher and Mann-Whitney tests at a 5% level of significance. RESULTS: estimated blood losses were significantly lower in vaginal hysterectomy (median of 520 mL) than in abdominal hysterectomy (median 902 mL). There was no blood transfusion among patients of the vaginal hysterectomy group, in contrast to 19% of the abdominal hysterectomy group. Duration of surgery was similar (median of 120 min in both groups). Postoperative pain, as measured by visual analog scale and analgesic requirement, was lower for vaginal hysterectomy than for abdominal hysterectomy. There was no statistically significant difference regarding frequency of postoperative complications. There was one case of infection in each group and one case of thrombosis in the vaginal hysterectomy group. Postoperative hospital stay was shorter in the vaginal group. Recovery time was significantly shorter in the vaginal group (median of 35 days) versus the abdominal group (median 40 days). Overall patient satisfaction with the operation was similar in the two groups. CONCLUSIONS: patients without genital prolapse submitted to vaginal hysterectomy for treatment of benign diseases had some advantages in relation to those submitted to abdominal hysterectomy: lower intraoperative blood loss, lower postoperative pain and faster recovery time. Vaginal hysterectomy may replace abdominal hysterectomy in most patients who require hysterectomy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(4):169-175
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000400004
PURPOSE: to determine the factors associated with cesarean section in pregnancies with fetal death at a maternity hospital in Recife, Pernambuco, Brazil. METHODS: a cross-sectional study was performed, which analyzed data from the information system about mortality and medical records, from January 2005 to December 2008, of Hospital Barão de Lucena (HBL). We analyzed women with fetal death diagnosis, with gestational age of 20 weeks or more, in terms of sociodemographic characteristics, causes and types of fetal death, obstetrical precedents and birth characteristics. The associations between the variables were analyzed by the χ2 test of association and Fisher exact test, with the level of significance set at 5%. We calculated the prevalence ratio as the measure of risk and the confidence interval (CI) at 95%. Logistic regression analysis was also performed and the Odds Ratio (OR) was calculated. RESULTS: among the 258 pregnant women with fetal death, 27.5% (n=71) underwent cesarean section. After multivariate analysis, the factors that remained significantly associated with cesarean section were maternal age below 20 years (OR=0.23; 95%CI=0.06-0.85), history of one or more cesarean sections (OR=7.02; 95%CI=2.29-21.55), multiple gestation (OR=9.06; 95%CI=2.01-40.71), use of misoprostol for birth induction (OR=0.07; 95%CI=0.01-0.32), fetal death occurring during birth (OR=4.01; 95%CI=1.13-14.24), low birth weight (OR=0.33; 95%CI=0.11-0.94), presence of hypertensive disorders (OR=3.7; 95%CI=1.46-9.39) and abruptio placentae (OR=13.9; 95%CI=4.67-41.69). CONCLUSION: in HBL, the risk factors for cesarean section in pregnancies with fetal death were previous cesarean section, multiple gestation, intrapartum deaths, hypertensive disorders and abruptio placentae. The protective factors were teenage pregnancy, use of misoprostol and low birth weight.