Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(1):14-19
Considering the increased frequency of maternal deaths reported from 2001 to 2005 for Indigenous andmestizo women from the Ecuadorian rural area ofOtavalo,where the Kichwa people has lived for centuries, the objective of the present article is to describehow the efforts of the local health community and hospital workers together with a propitious political environment facilitated the implementation of intercultural childbirth,which is a strategy that respects the Andean childbirth worldview.
We evaluated a 3-year follow-up (2014-16) of the maternal mortality and the childbirth features (4,213 deliveries).
Although the Western-style (lying down position) childbirth was adopted by 80.6% of the pregnant women, 19.4% of bothmestizo and Indigenous women adopted the intercultural delivery (squatting and kneeling positions). Both intercultural (42.2%) and Western-style (57.8%) childbirths were similarly adopted by Kichwa women, whereas Western-style childbirth predominated among mestizo women (94.0%). After the implementation of the intercultural strategy in 2008, a dramatic decrease of maternal deaths has been observed until now in both rural and urban Otavalo regions.
This scenario reveals that the intermingling of cultures and respect for childbirth traditions have decreased maternal mortality in this World Health Organization- awarded program.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(3):140-145
To describe the referral for colposcopy in a Hospital in Brazil and the relative frequency of patients who benefited from it, considering the correct indications for the examination and its final diagnoses.
A retrospective study was performed in the colposcopy service database of the Hospital Universitário de Taubaté, Taubaté, state of São Paulo, Brazil. The frequency validated in the analysis of the medical records of women referred for clinical indication or cytological alteration, attended from March 2015 to March 2017. The population selected and analyzed included 256 results that were correlated to the cytological, clinical data and the result of the colposcopy.
Of the women referred, 45% presented out of the age of screening according to the guidelines of cervical cancer screening, 8.6% being adolescents and young adults < 25 years old, and 36.4% of the patients being ≥ 65 years old. A total of 50% of the patients had no indication of colposcopy, that is, normal cytologies, benign changes, ectopia, cervicitis, atypical squamous cells of indeterminate significance (ASC-US) and low-grade intraepithelial lesion (LSIL) without persistence and normal clinical appearance. A total of 39.84% who underwent colposcopy had high-grade lesion or cancer results, thus benefiting from the adequate referral.
Most (60.16%) of the patients referred to the colposcopy service did not benefit from the referral for results without changes, such as negative colposcopies, histologies with no cervical intraepithelial neoplasm (CIN) or only CIN 1, or were out of the age for screening. These findings therefore demonstrate a significant number of unnecessary and inadequate referrals.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(3):140-146
The aim of this study was to study the effects of Tribulus terrestris on sexual function in menopausal women.
This was a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial that included 60 postmenopausal women with sexual dysfunction. The women were divided into two groups, placebo group and Tribulus group, and evaluated by using the Sexual Quotient-female version (SQ-F) and Female Intervention Efficacy Index (FIEI) questionnaires.
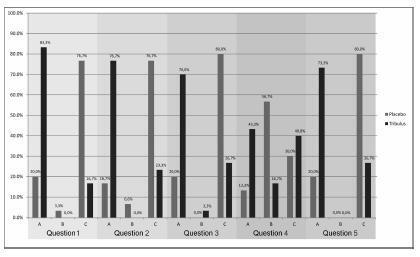
There was no significant difference between the groups in age, age at menopause, civil status, race, and religion. In the evaluation with the SQ-F questionnaire, there were significant differences between the placebo (7.6±3.2) and Tribulus (10.2±3.2) groups in the domains of desire and sexual interest (p d" 0.001), foreplay (3.3±1.5 versus 4.2±1.0) (p d" 0.01), arousal and harmonious interaction with the partner (5.7±2.1 versus 7.2±2.6) (p d" 0.01), and comfort in sexual intercourse (6.5±2.4 versus 8.0±1.9) (p d" 0.01). There was no significant difference between the placebo and Tribulus groups in the domains of orgasm and sexual satisfaction (p = 0.28). In the FIEI questionnaire, there was a significant improvement (p < 0.001) in the domains of vaginal lubrication during coitus and/or foreplay (20 versus 83.3%), sensation in the genitalia during sexual intercourse or other stimuli (16.7 versus 76.7%), sensation in the genital region (20 versus 70%), sexual intercourse and/or other sexual stimulations (13.3 versus 43.3%), and the ability to reach orgasm (20% versus 73.3%). There was no significant difference in adverse effects between the two groups.
After 90 days of treatment, at the doses used, we found Tribulus terrestris to be effective in treating sexual problems among menopausal women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(3):140-147
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320150005203
The congenital diaphragmatic hernia is a defect in the formation of the diaphragm, which affects between 1:2,000 and 1:4,000 live births and represents 8% of major congenital anomalies. Medical advances in the last 30 years involving prenatal diagnosis, fetal intervention, neonatal surgical and clinical management have changed the survival of these patients. The historical evolution of these advances helps us to understand the effort in pursuit of better results of this defect, which is often lethal. Perspectives on the use of bioengineering and therapy involving stem cells may bring new hope for fetuses with congenital diaphragmatic hernia.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(3):141-146
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000300004
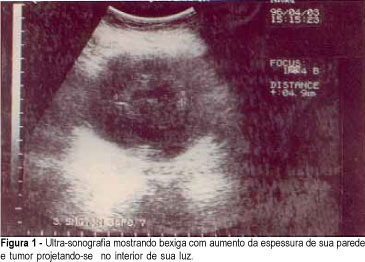
Purpose: urinary tract involvement by endometriosis is uncommon and the bladder is the most common site. We observed that clinical misdiagnosis of bladder cancer frequently is made. Because the disease is generally described in case reports there is not a consensual management. We present and discuss our experience of diagnostic and therapeutic issues. Methods: retrospective analysis of urinary endometriosis slides of the Department of Pathology files was made. Medical charts and follow-up were reviewed in detail and interviews were performed during or after treatment. Results: we describe four cases with cyclic disuria, abdominal mass, pelvic pain and imaging diagnosis of bladder tumor. Pathological specimens were obtained by endoscopic resection (3 cases) and laparoscopic biopsy (1 case). Therapeutic options were exclusive medical treatment or surgical removal with transurethral resection or partial cystectomy supplemented with adjuvant medication. Conclusions: we review the clinical and therapeutic aspects of urinary tract endometriosis stressing that this is an important differential diagnosis of bladder cancer in reproductive women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(3):141-146
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000300004
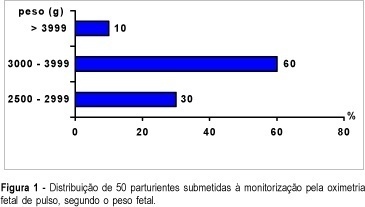
Purpose: to study fetal oxygen saturation (SpO2) levels during labor by continuous pulse oximetry tecnique, and its relation to umbilical artery (UA) pH. Patients and Methods: fetal SpO2 levels were measured during labor by the pulse oximetry technique in 50 subjects. Average values of SpO2 were compared between the first and second stage of labor, with the first stage further subdivided into phases, according to cervical dilatation of (<=4 cm, 5-7 cm and 8-9 cm). SpO2 values were studied in relation to umbilical artery pH at birth ( > or = 7.20 and <7.20). SpO2 > or = 30.0% was considered normal. Results: fetal SpO2 averages during the first stage were 53.0 ± 7.3% and 44.2 ± 6.8% (UA pH > or = 7.20 and <7.20, respectively; p<0.01). When the first stage was subdivided, the fetal SpO2 averages (UA pH > or = 7.20) were 55.1 ± 5.1% (<=4 cm), 52.3 ± 4.6% (5-7 cm) and 51.5 ± 7.2% (8-9 cm); for UA pH <7.20, the fetal SpO2 averages were 46.3 ± 5.1% (<=4 cm), 43.6 ± 6.7% (5-7 cm) and 42.8 ± 5.8% (8-9 cm). Considering the UA pH, these differences were statistically significant (p<0.01). Conclusion: a significant decrease of oxygen saturation values was observed during labor when fetal pulse oximetry was used.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(3):141-141
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000300009
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(3):141-146
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000300005
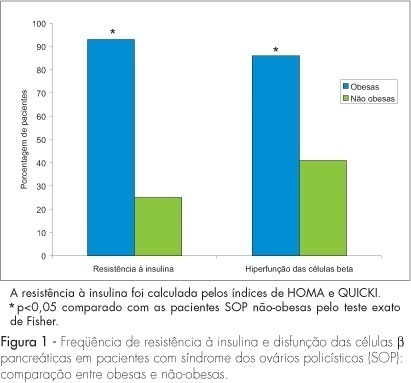
PURPOSE: to evaluate the effect of obesity on beta-cell function in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). METHODS: this cross-section study evaluated 82 patients with PCOS selected consecutively, at the moment of the diagnosis. We compared 31 PCOS obese women (BMI >30 kg/m²) to 51 age-matched PCOS nonobese patients (BMI <30 kg/m²). Using fasting glucose and insulin levels, homeostatic model assessment values for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR and QUICKI) and percent beta-cell function (HOMA-%beta-cell) were calculated. As secondary variables, the age at PCOS diagnosis, age of menarche, hormonal levels (testosterone, prolactin, FSH and LH), total cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL cholesterol and LDL cholesterol were also analyzed. RESULTS: menarche was significantly earlier in obese PCOS patients (11.7±1.8 years) than in nonobese patients (12.67±1.86 years) (p<0.05). Obese patients presented lower LH levels (7.9±5 mIU/mL) than did nonobese patients (10.6±6 mIU/mL) (p<0.05). Both groups presented mean HDL cholesterol levels below 50 mg/dL. Obese patients presented significantly higher baseline insulin levels (32.5±25.2 mIU/mL) and fasting blood glucose levels (115.9±40.7 mg/dL) than did nonobese patients (8.8±6.6 mIU/mL and 90.2±8.9 mg/dL, respectively) (p<0.01). Of the obese PCOS patients, 93% presented insulin resistance versus 25% of nonobese PCOS patients (p<0.01). Eighty-six perecent of the obese women had hyperfunction of beta-cell versus 41% of nonobese with PCOS (p<0.0001). CONCLUSIONS: obese PCOS patients presented higher prevalence of insulin resistance and hyperfunction of beta-cell than did nonobese PCOS patients.