Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(3):133-137
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000300003
Purpose: to evaluate how knowledgeable medical students at the Universidade Federal de Goiás were concerning the basic diagnostic principles breast cancer. The study also aimed at promoting a debate among the students and at assessing the understanding of the students in the fifth year of medical school, who had already attended the Gynecology course. Methods: Through questionnaires given to 348 individuals, from the first to the fifth year, out of a total population of 550 students, the authors searched for information with regard to basic knowledge on the diagnosis of breast cancer. Of the 348 questionnaires, 55 (16%) were given to fifth-year students, who had already attended the Gynecology course. Furthermore, 43% of the students were women, 62% had medical doctors in their immediate family, and 17% had a family history of breast cancer. Results: in regard to the knowledge of diagnostic methods, 84% of the students were aware of the most frequent sign of breast cancer, 34% knew which was the best screening method, 49% knew when to refer asymptomatic women to mammography, 37% knew the recommended interval between mammography for women above the age of 50, and 24% knew when to associate ultrasound to mammography for the detection of breast cancer. The fifth-year students provided correct answers at a significantly higher rate, when compared to the others. Concerning gender, the only difference regarded the fact that women showed a better knowledge as to the best time for self-examination and when to recommend ultrasound associated with mammography. The presence of medical doctors in the family and a history of family members with breast cancer did not have any influence on the answers. Conclusion: The lack of information in regard to the diagnosis of breast cancer is very high, even among medical students. Nevertheless, the rate of information increases significantly after students are taught Gynecology, which is only offered during the fifth year of the medical school.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):133-141
To investigate the prevalence of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) in university students, the factors associated with PMS, the most prevalent symptoms, and the interference of symptoms in academic, family, social, and work activities.
This cross-sectional study included 1,115 university students aged ≥ 18 years from the University of Rio Verde, Goiás. Premenstrual syndrome and PMDD were identified using the Premenstrual Symptoms Screening Tool. Associations with sociodemographic, behavioral, reproductive, nutritional, and health factors were investigated using the Poisson regression.
The prevalence of PMS was 46.9% (95% confidence interval [CI] 44.0-49.8), and of PMDD, 11.1% (95% CI 9.3-13.0). The most prevalent symptoms were physical, such as breast tenderness, bloating, e weight gain (73%); followed by psychological ones such as overeating/food cravings, tearful/more sensitive to rejection (> 60%). More than 30% of the patients reported that the symptoms interfered in a moderate-tosevere way in their social and academic activities. After adjusted analysis, PMS was more prevalent in those who were attending the 1st/2nd semester of college (prevalence ratio [PR] 1.44; 95% CI 1.14-1.80), those who consumed alcohol in the last 30 days (PR 1.23; 95% CI 1.04-1.47), and those who had depression (PR 1.49; 95% CI 1.30-1.71).
Almost half of the university students had PMS and ~ 11%, PMDD. Physical symptoms were themost common and interfered in amoderate-to-severe way in various aspects of life. Attending the first semesters, consuming alcohol, and having depression were risk factors for PMS. The identification of risk factors for PMS is essential to prevent symptoms and reduce the impact of the syndrome.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(3):133-139
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005132
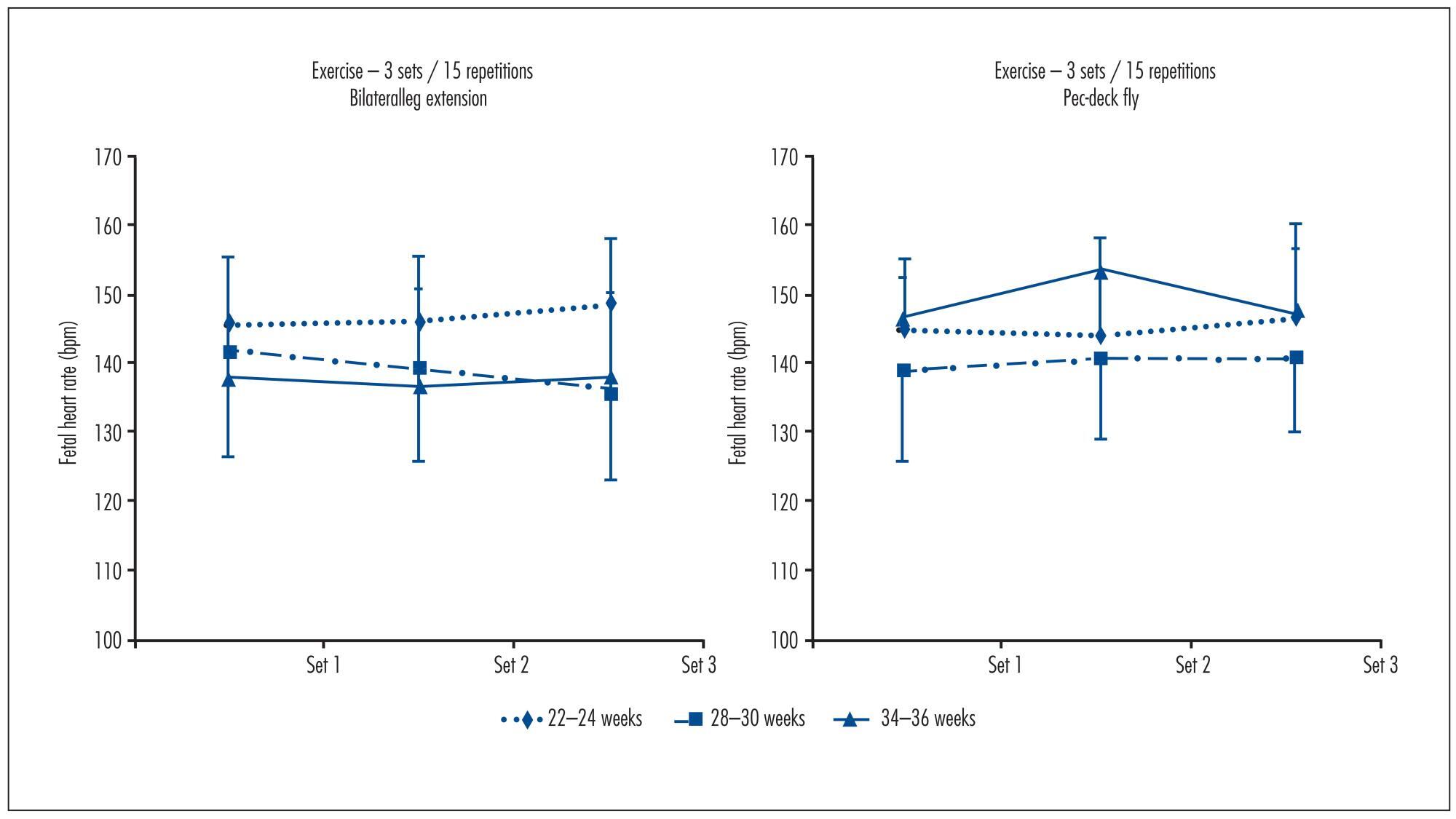
To determine fetal heart rate (FHR) responses to maternal resistance exercise for the upper and lower body at two different volumes, and after 25 minutes post-exercise.
Ten pregnant women (22-24 weeks gestation, 25.2±4.4 years of age, 69.8±9.5 kg, 161.6±5.2 cm tall) performed, at 22-24, 28-32 and 34-36 weeks, the following experimental sessions: Session 1 was a familiarization with the equipment and the determination of one estimated maximum repetition. For sessions 2, 3, 4 and 5,FHR was determined during the execution of resistance exercise on bilateral leg extension and pec-deck fly machines, with 1 and 3 sets of 15 repetitions; 50% of the weight load and an estimated repetition maximum. FHR was assessed with a portable digital cardiotocograph. Results were analyzed using Student's t test, ANOVA with repeated measures and Bonferroni (α=0.05; SPSS 17.0).
FHR showed no significant differences between the exercises at 22-24 weeks (bilateral leg extension=143.8±9.4 bpm, pec-deck fly=140.2±10.2 bpm, p=0.34), 28-30 weeks (bilateral leg extension=138.4±12.2 bpm, pec-deck fly=137.6±14.0 bpm, p=0.75) and 34-36 weeks (bilateral leg extension=135.7±5.8 bpm, pec-deck fly=139.7±13.3 bpm, p=0.38), between the volumes(bilateral leg extension at 22-24 weeks: p=0.36, at 28-30 weeks: p=0.19 and at 34-36 weeks: p=0.87; pec-deck fly at 22-24 weeks: p=0.43, at 28-30 weeks: p=0.61 and at 34-36 weeks: p=0.49) and after 25 minutes post-exercise.
Results of this pilot study would suggest that maternal resistance exercise is safe for the fetus.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(3):133-138
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000300006
PURPOSE: to assess the influence of physiotherapy performed during radiotherapy (RT) on the quality of life (QL) of women under treatment for breast cancer. METHODS: this was a randomized clinical trial conducted on 55 women under RT treatment, 28 of whom were assigned to a group submitted to physiotherapy (PG) and 27 to the control group receiving no PG (CG). The physiotherapy technique used for PG was kinesiotherapy for the upper limbs using 19 exercises actively performed, with a series of ten rhythmic repetitions or stretching movements involving flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, internal and external shoulder rotation, separate or combined. QL was evaluated using the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Breast (FACT-B), at the beginning and at the end of RT and six months after the end of RT. The physiotherapy sessions were started concomitantly with RT, 90 days after surgery, on average. RESULTS: there was no difference between subgroups regarding the following subscales: physical well-being (p=0.8), social/family well-being (p=0.3), functional well-being (p=0.2) and breast subscale (p=0.2) at the three time points assessed. A comparison of the emotional subscale applied at the three evaluations demonstrated a better behavior of PG as compared to CG (p=0.01), with both groups presenting improvement on the breast subscale between the beginning and the end of RT (PG p=0.0004 and CG p=0.003). There was improvement in FACT-B scores at the end of RT in both groups (PG p=0.0006 and CG p=0.003). However, at the sixth month after RT, this improvement was maintained only in PG (p=0,005). QL assessed along time by the FACT B (p=0.004) and the Trial Outcome Index (TOI) (sums of the physical and functional well-being subscales and of the breast subscale) was better for PG (p=0.006). There was no evidence of negative effects associated with the exercises. CONCLUSIONS: the execution of exercises for the upper limbs was beneficial for QL during and six months after RT.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(2):133-134
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(2):133-134
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(3):134-140
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000300004
PURPOSE: to compare women's quality of life (QoL) before and after physical therapy treatment for stress urinary incontinence (SUI). METHODS: an uncontrolled clinical trial of 26 women, who had mainly complaints of SUI. Post-menopausal women with overactive bladder, cystocele >grade II and previous surgical/conservative treatments were excluded from the study. The physiotherapy treatment relied on 12 individual pelvic floor exercises assisted by electromyographyc-biofeedback sessions. A total of 200 contractions were carried out, divided in phasic (quick) and tonic (slow). The tool used to evaluate QoL was the King's Health Questionnaire (KHQ), before and after the treatment. RESULTS: there was a decrease in the urinary symptoms, particularly in urinary frequency, nocturia, urgency and urinary incontinence. Regarding the QoL, there was a significant improvement in the following domain scores: general health perception (49.0±24.0 versus 26.9±15.7; p=0.0015), incontinence impact (78.2±28.2 versus 32.1±30.5; p=0.001), activity limitation (75.0±28.2 versus 13.5±22.6; p<0.001), physical limitation (72.4±29.4 versus 15.4±24.5; p<0.001), social limitations (38.3±28.6 versus 6.4±14.5; p<0.001), emotions (59.0±33.8 versus 14.1±24.7; p=0.0001, sleep/energy (34.0±23.8 versus 6.4±16.4; p=0.001) and severity measures (66.9±19.6 versus 22.3±24.2; p<0.001), except for personal relationships (60.5±33.9 versus 41.7±16.7; p=0.0679). CONCLUSIONS: there was an improvement in several aspects of women's QoL treated by physiotherapy, when evaluated with a specific tool, the KHQ.